|
Silicification
In geology, silicification is a process in which silica-rich fluids seep into the voids of Earth materials, e.g., rocks, wood, bones, shells, and replace the original materials with silica (SiO2). Silica is a naturally existing and abundant compound found in organic and inorganic materials, including Earth's crust and mantle. There are a variety of silicification mechanisms. In silicification of wood, silica permeates into and occupies cracks and voids in wood such as vessels and cell walls. The original organic matter is retained throughout the process and will gradually decay through time. In the silicification of carbonates, silica replaces carbonates by the same volume. Replacement is accomplished through the dissolution of original rock minerals and the precipitation of silica. This leads to a removal of original materials out of the system. Depending on the structures and composition of the original rock, silica might replace only specific mineral components of the rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, opal, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics, and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored. Silicon dioxide is a common fundamental constituent of glass. Structure In the majority of silicon dioxides, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
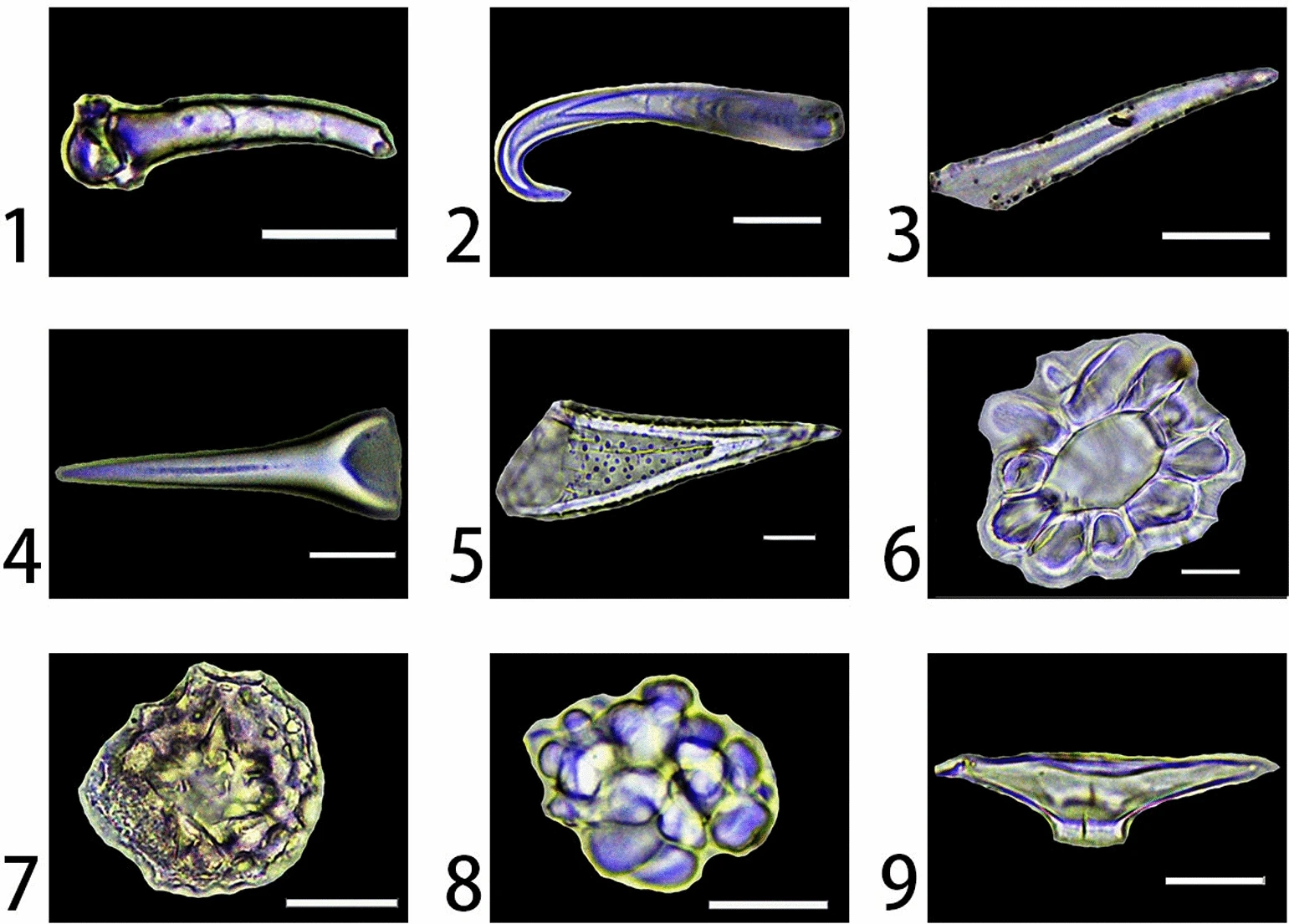
Sponge Spicule
Spicules are structural elements found in most sponges. The meshing of many spicules serves as the sponge's skeleton and thus it provides structural support and potentially defense against predators. Sponge spicules are made of calcium carbonate or silica. Large spicules visible to the naked eye are referred to as megascleres or macroscleres, while smaller, microscopic ones are termed microscleres. The composition, size, and shape of spicules are major characters in sponge systematics and taxonomy. Overview Sponges are a species-rich clade of the earliest-diverging (most basal) animals. They are distributed globally, with diverse ecologies and functions, and a record spanning at least the entire Phanerozoic. Most sponges produce skeletons formed by spicules, structural elements that develop in a wide variety of sizes and three dimensional shapes. Among the four sub-clades of Porifera, three ( Demospongiae, Hexactinellida, and Homoscleromorpha) produce skeletons of am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yanjiahe Formation
The Yanjiahe Formation is an Ediacaran to Cambrian fossiliferous geologic formation found in South China.Dong et al., 2009Yanjiahe Formation at Fossilworks
Fossilworks was a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world.
History
Fossilworks was cr ... .org
Fossil content Among others, the following fossils were found in the formation: * '' Aldane ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedimentation is any process that causes these particles to settle in place. Geological detritus originates from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or Mass wasting, mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus is formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur when dissolved minerals precipitate from aqueous solution, water solution. The sedimentary rock cover of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
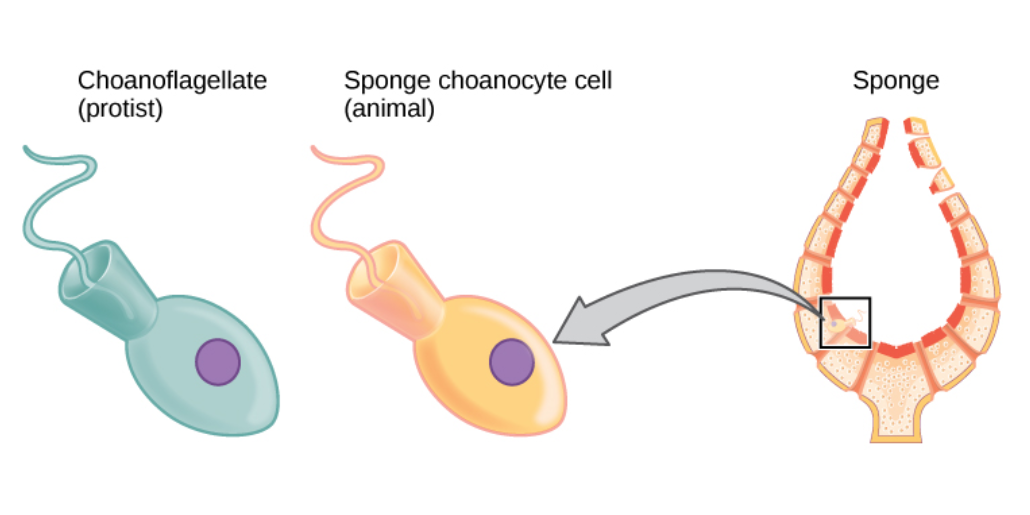
Sponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes, usually via flagella movements of the so-called " collar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about eight phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships among phyla within larger clades like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes, usually via flagella movements of the so-called " collar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Equisetaceae
Equisetaceae, also known as the horsetail family, is a family of ferns and the only surviving family of the order Equisetales, with one surviving genus, ''Equisetum'', comprising about twenty species. Evolution and systematics Equisetaceae is the only surviving family of the Equisetales, a group with many fossils of large tree-like plants that possessed ribbed stems similar to modern horsetails. '' Pseudobornia'' is the oldest known relative of ''Equisetum''; it grew in the late Devonian, about 375 million years ago and is assigned to its own order. All living horsetails are placed in the genus ''Equisetum''. But there are some fossil species that are not assignable to the modern genus. '' Equisetites'' is a " wastebin taxon" uniting all sorts of large horsetails from the Mesozoic; it is almost certainly paraphyletic and would probably warrant being subsumed in ''Equisetum''. But while some of the species placed there are likely to be ancestral to the modern horsetails, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phytolith
Phytoliths (from Greek language, Greek, "plant stone") are rigid, microscopic mineral deposits found in some plant tissues, often persisting after the decay of the plant. Although some use "phytolith" to refer to all mineral secretions by plants, it more commonly refers to Silicon dioxide, siliceous plant remains. Phytoliths come in varying shapes and sizes. The plants which exhibit them take up dissolved silica from the groundwater, whereupon it is deposited within different intracellular and extracellular structures of the plant.Piperno, Dolores R. (2006). Phytoliths: A Comprehensive Guide for Archaeologists and Paleoecologists. AltaMira Press . The silica is absorbed in the form of orthosilicic acid, monosilicic acid (Si(OH)4), and is carried by the plant's Circulatory system, vascular system to the cell walls, cell lumen, and intercellular spaces. Depending on the plant Taxon, taxa and soil condition, absorbed silica can range from 0.1% to 10% of the plant's total dry weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Silicate Mineral
Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class of minerals and make up approximately 90 percent of Earth's crust. In mineralogy, the crystalline forms of silica (silicon dioxide, ) are usually considered to be Silicate mineral#Tectosilicates, tectosilicates, and they are classified as such in the Dana system (75.1). However, the Nickel-Strunz system classifies them as oxide minerals (4.DA). Silica is found in nature as the mineral quartz, and its polymorphism (materials science), polymorphs. On Earth, a wide variety of silicate minerals occur in an even wider range of combinations as a result of the processes that have been forming and re-working the crust for billions of years. These processes include partial melting, crystallization, fractionation, metamorphism, weathering, and diagenesis. Living organisms also contribute to this carbonate–silicate cycle, geologic cycle. For example, a type of plankton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Biogenic Silica
Biogenic silica (bSi), also referred to as opal, biogenic opal, or amorphous opaline silica, forms one of the most widespread biogenic minerals. For example, microscopic particles of silica called phytoliths can be found in grasses and other plants. Silica is an amorphous metalloid oxide formed by complex inorganic polymerization processes. This is opposed to the other major biogenic minerals, comprising carbonate and phosphate, which occur in nature as crystalline iono-covalent solids (e.g. salts) whose precipitation is dictated by solubility equilibria.Coradin, T., Lopez, P.J. (2003). "Biogenic Silica Patterning: Simple Chemistry or Subtle Biology?" ChemBioChem 3: 1-9. Chemically, bSi is hydrated silica (SiO2·''n''H2O), which is essential to many plants and animals. Diatoms in both fresh and salt water extract dissolved silica from the water to use as a component of their cell walls. Likewise, some holoplanktonic protozoa ( Radiolaria), some sponges, and some plants (leaf p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Different Sources Of Silica
Different may refer to: Music * "Different", a song by Cass Elliot from the soundtrack of the 1970 film '' Pufnstuf'' * '' Different'', a 1989 album by Thomas Anders * '' Different'', a 2002 album by Kate Ryan * "Different", a song by Egypt Central from their eponymous 2005 album * "Different", a song by Acceptance from the 2005 album '' Phantoms'' * "Different", a 2006 song by Jamie Shaw * "Different", a song by Dreamscape from the 2007 album '' 5th Season'' * "Different", a song by Pendulum from the 2008 album ''In Silico'' * "Different", a song by Ximena Sariñana from the 2011 album Ximena Sariñana * " Different", a 2012 song by Robbie Williams * "Different", a song by No Malice from the 2013 album ''Hear Ye Him'' * "Different", a song by Winner from the 2014 album ''2014 S/S'' * "Different", a 2017 song by Micah Tyler * "Different", a song by Future and Juice Wrld from the 2018 mixtape ''Wrld on Drugs'' * "Different", a song by Burna Boy from the 2019 album ''African Giant'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |