|
Signal Automaton
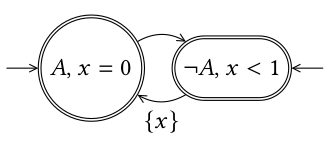
In automata theory, a field of computer science, a signal automaton is a finite automaton extended with a finite set of real-valued clocks. During a run of a signal automaton, clock values increase all with the same speed. Along the transitions of the automaton, clock values can be compared to integers. These comparisons form guards that may enable or disable transitions and by doing so constrain the possible behaviors of the automaton. Further, clocks can be reset. Example Before formally defining what a signal automaton is, an example will be given. Let one consider the language \mathcal L of signals, over a binary alphabet \, which contains signals \gamma such that: * A appears in singular intervals. That is, the set of times \ is discrete, and * A appears at least once during each interval of length one. This language can be accepted by the automaton pictured nearby. As for finite automaton, incoming arrows represents initial locations and double circle represents accepting l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Automata Theory
Automata theory is the study of abstract machines and automata, as well as the computational problems that can be solved using them. It is a theory in theoretical computer science with close connections to cognitive science and mathematical logic. The word ''automata'' comes from the Greek word αὐτόματος, which means "self-acting, self-willed, self-moving". An automaton (automata in plural) is an abstract self-propelled computing device which follows a predetermined sequence of operations automatically. An automaton with a finite number of states is called a finite automaton (FA) or finite-state machine (FSM). The figure on the right illustrates a finite-state machine, which is a well-known type of automaton. This automaton consists of states (represented in the figure by circles) and transitions (represented by arrows). As the automaton sees a symbol of input, it makes a transition (or jump) to another state, according to its transition function, which takes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Finite Automaton
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of ''states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types— deterministic finite-state machines and non-deterministic finite-state machines. For any non-deterministic finite-state machine, an equivalent deterministic one can be constructed. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions depending on a sequence of events with which they are presented. Simple examples are: vending machines, which dispens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Signal Automaton Ensuring A Holds Discretly And At Least Once By Time Unit
A signal is both the process and the result of Signal transmission, transmission of data over some transmission media, media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology. In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' includes audio signal, audio, video, speech, image, sonar, and radar as examples of signals. A signal may also be defined as observable change in a quantity over space or time (a time series), even if it does not carry information. In nature, signals can be actions done by an organism to alert other organisms, ranging from the release of plant chemicals to warn nearby plants of a predator, to sounds or motions made by animals to alert other animals of food. Signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |