|
Scene Graph
A scene graph is a general data structure commonly used by vector-based graphics editing applications and modern computer games, which arranges the logical and often spatial representation of a graphical scene. It is a collection of nodes in a graph or tree structure. A tree node may have many children but only a single parent, with the effect of a parent applied to all its child nodes; an operation performed on a group automatically propagates its effect to all of its members. In many programs, associating a geometrical transformation matrix (see also transformation and matrix) at each group level and concatenating such matrices together is an efficient and natural way to process such operations. A common feature, for instance, is the ability to group related shapes and objects into a compound object that can then be manipulated as easily as a single object. Scene graphs in graphics editing tools In vector-based graphics editing, each leaf node in a scene graph represents some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
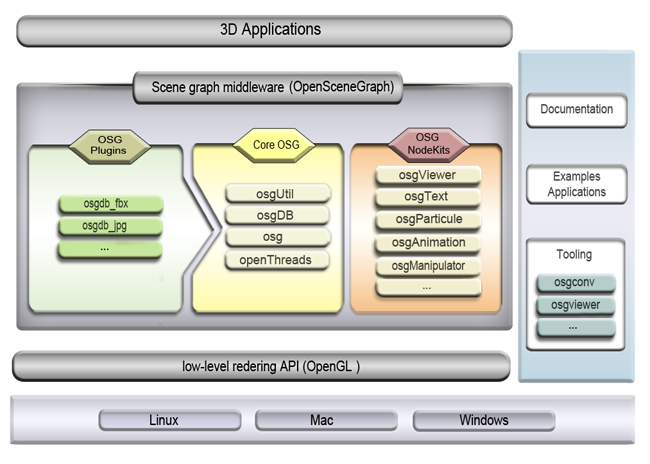
Architecture Of OpenSceneGraph
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings or other structures. The term comes ; ; . Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural symbols and as works of art. Historical civilizations are often identified with their surviving architectural achievements. The practice, which began in the prehistoric era, has been used as a way of expressing culture by civilizations on all seven continents. For this reason, architecture is considered to be a form of art. Texts on architecture have been written since ancient times. The earliest surviving text on architectural theories is the 1st century AD treatise by the Roman architect Vitruvius, according to whom a good building embodies , and (durability, utility, and beauty). Centuries later, Leon Bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linked List
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a collection of nodes which together represent a sequence. In its most basic form, each node contains data, and a reference (in other words, a ''link'') to the next node in the sequence. This structure allows for efficient insertion or removal of elements from any position in the sequence during iteration. More complex variants add additional links, allowing more efficient insertion or removal of nodes at arbitrary positions. A drawback of linked lists is that data access time is linear in respect to the number of nodes in the list. Because nodes are serially linked, accessing any node requires that the prior node be accessed beforehand (which introduces difficulties in pipelining). Faster access, such as random access, is not feasible. Arrays have better cache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painter's Algorithm
The painter's algorithm (also depth-sort algorithm and priority fill) is an algorithm for Hidden-surface determination#Visible surface determination, visible surface determination in 3D computer graphics that works on a polygon, polygon-by-polygon basis rather than a pixel, pixel-by-pixel, row by row, or area by area basis of other hidden surface removal, Hidden-Surface Removal algorithms. The painter's algorithm creates images by sorting the polygons within the image by their depth and placing each polygon in order from the farthest to the closest object. The painter's algorithm was initially proposed as a basic method to address the Hidden-surface determination problem by Martin Newell (computer scientist), Martin Newell, Dick Newell, Richard Newell, and Tom Sancha in 1972, while all three were working at CADCentre. The name "painter's algorithm" refers to the technique employed by many painters where they begin by painting distant parts of a scene before parts that are nearer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Traversal
In computer science, tree traversal (also known as tree search and walking the tree) is a form of graph traversal and refers to the process of visiting (e.g. retrieving, updating, or deleting) each node in a Tree (data structure), tree data structure, exactly once. Such traversals are classified by the order in which the nodes are visited. The following algorithms are described for a binary tree, but they may be generalized to other trees as well. Types Unlike linked lists, one-dimensional arrays and other List of data structures#Linear data structures, linear data structures, which are canonically traversed in linear order, trees may be traversed in multiple ways. They may be traversed in Depth-first search, depth-first or Breadth-first search, breadth-first order. There are three common ways to traverse them in depth-first order: in-order, pre-order and post-order. Beyond these basic traversals, various more complex or hybrid schemes are possible, such as depth-limited searche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function Object
In computer programming, a function object is a construct allowing an object (computer science), object to be invoked or called as if it were an ordinary subroutine, function, usually with the same syntax (a function parameter that can also be a function). In some languages, particularly C++, function objects are often called functors (not related to Functor (functional programming), the functional programming concept). Description A typical use of a function object is in writing callback (computer science), callback functions. A callback in procedural programming, procedural languages, such as C (programming language), C, may be performed by using function pointers. However it can be difficult or awkward to pass a state into or out of the callback function. This restriction also inhibits more dynamic behavior of the function. A function object solves those problems since the function is really a facade pattern, façade for a full object, carrying its own state. Many modern (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callback (computer Programming)
In computer programming, a callback is a function that is stored as data (a reference) and designed to be called by another function often ''back'' to the original abstraction layer. A function that accepts a callback parameter may be designed to call back before returning to its caller which is known as '' synchronous'' or ''blocking''. The function that accepts a callback may be designed to store the callback so that it can be called back after returning which is known as ''asynchronous'', '' non-blocking'' or ''deferred''. Programming languages support callbacks in different ways such as function pointers, lambda expressions and blocks. A callback can be likened to leaving instructions with a tailor for what to do when a suit is ready, such as calling a specific phone number or delivering it to a given address. These instructions represent a callback: a function provided in advance to be executed later, often by a different part of the system and not necessarily by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Run-Time Type Information
In computer programming, run-time type information or run-time type identification (RTTI) is a feature of some programming languages (such as C++, Object Pascal, and Ada) that exposes information about an object's data type at runtime. Run-time type information may be available for all types or only to types that explicitly have it (as is the case with Ada). Run-time type information is a specialization of a more general concept called type introspection. In the original C++ design, Bjarne Stroustrup did not include run-time type information, because he thought this mechanism was often misused. Overview In C++, RTTI can be used to do safe typecasts using the dynamic_cast operator, and to manipulate type information at runtime using the typeid operator and std::type_info class. In Object Pascal, RTTI can be used to perform safe type casts with the as operator, test the class to which an object belongs with the is operator, and manipulate type information at run time with classe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visitor Pattern
A visitor pattern is a software design pattern that separates the algorithm from the object structure. Because of this separation, new operations can be added to existing object structures without modifying the structures. It is one way to follow the open/closed principle in object-oriented programming and software engineering. In essence, the visitor allows adding new virtual functions to a family of classes, without modifying the classes. Instead, a visitor class is created that implements all of the appropriate specializations of the virtual function. The visitor takes the instance reference as input, and implements the goal through double dispatch. Programming languages with sum types and pattern matching obviate many of the benefits of the visitor pattern, as the visitor class is able to both easily branch on the type of the object and generate a compiler error if a new object type is defined which the visitor does not yet handle. Overview The Visitor design pattern i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Functions
In object-oriented programming such as is often used in C++ and Object Pascal, a virtual function or virtual method is an inheritable and overridable function or method that is dispatched dynamically. Virtual functions are an important part of (runtime) polymorphism in object-oriented programming (OOP). They allow for the execution of target functions that were not precisely identified at compile time. Most programming languages, such as JavaScript, PHP and Python, treat all methods as virtual by default and do not provide a modifier to change this behavior. However, some languages provide modifiers to prevent methods from being overridden by derived classes (such as the ''final'' and ''private'' keywords in Java and PHP). Purpose The concept of the virtual function solves the following problem: In object-oriented programming, when a derived class inherits from a base class, an object of the derived class may be referred to via a pointer or reference of the base clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendering API
This is a glossary of terms relating to computer graphics. For more general computer hardware terms, see glossary of computer hardware terms. 0–9 A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P Q R S T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenGL
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a Language-independent specification, cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D computer graphics, 2D and 3D computer graphics, 3D vector graphics. The API is typically used to interact with a graphics processing unit (GPU), to achieve Hardware acceleration, hardware-accelerated Rendering (computer graphics), rendering. Silicon Graphics, Inc. (SGI) began developing OpenGL in 1991 and released it on June 30, 1992. It is used for a variety of applications, including computer-aided design (CAD), video games, scientific visualization, virtual reality, and Flight simulator, flight simulation. Since 2006, OpenGL has been managed by the Non-profit organization, non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group. Design The OpenGL specification describes an abstract application programming interface, application programming interface (API) for drawing 2D and 3D graphics. It is designed to be implemented mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DirectX
Microsoft DirectX is a collection of application programming interfaces (APIs) for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms. Originally, the names of these APIs all began with "Direct", such as Direct3D, DirectDraw, DirectMusic, DirectPlay, DirectSound, and so forth. The name ''DirectX'' was coined as a shorthand term for all of these APIs (the ''X'' standing in for the particular API names) and soon became the name of the collection. When Microsoft later set out to develop a Video game console, gaming console, the ''X'' was used as the basis of the name Xbox (console), Xbox to indicate that the console was based on DirectX technology. The ''X'' initial has been carried forward in the naming of APIs designed for the Xbox such as DirectInput, XInput and the Cross-platform Audio Creation Tool (XACT), while the DirectX pattern has been continued for Windows APIs such as Direct2D and DirectWrite. Direct3D (the 3D graphics A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |