|
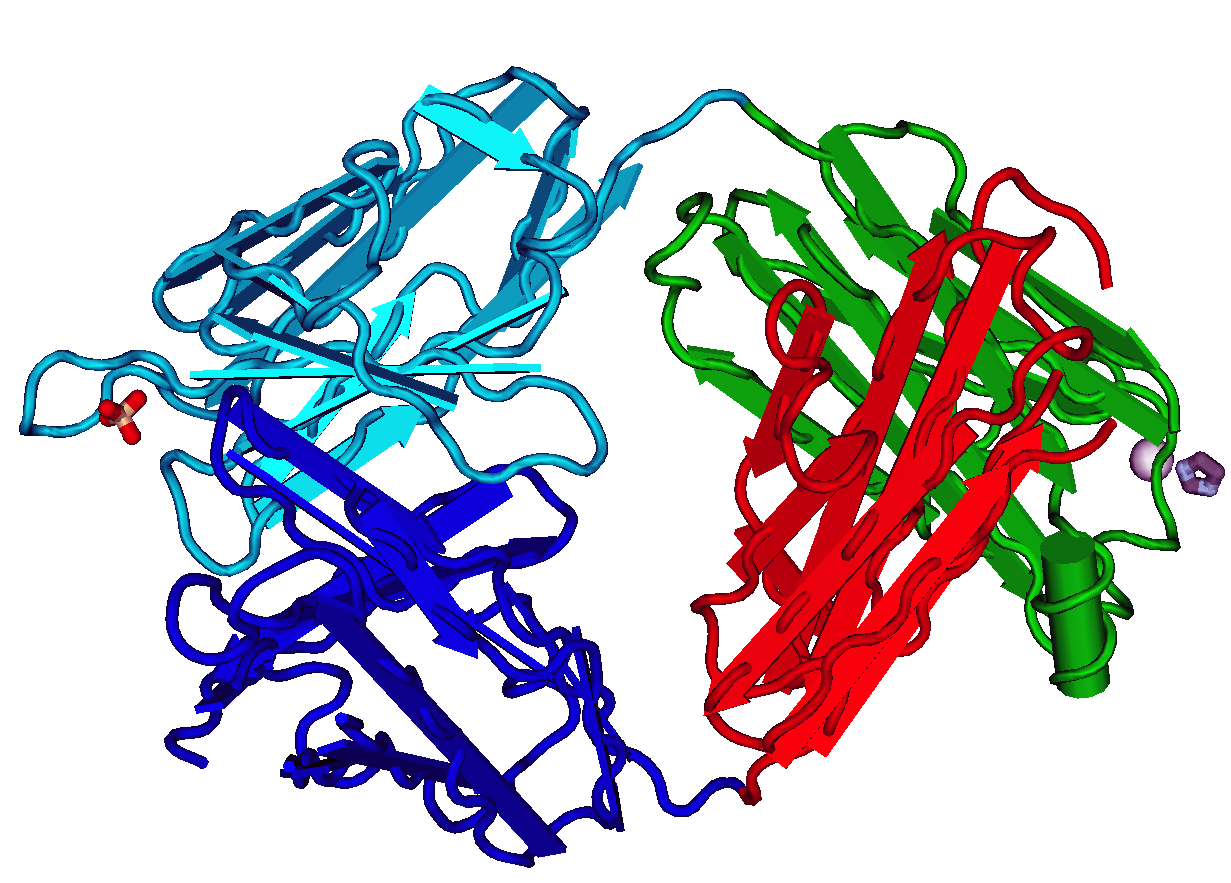
ScFv
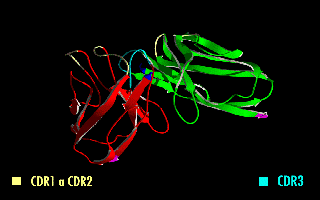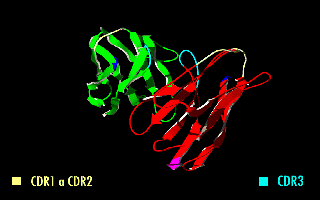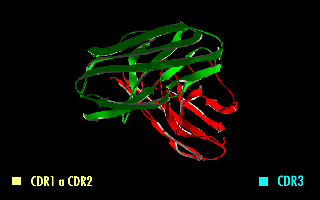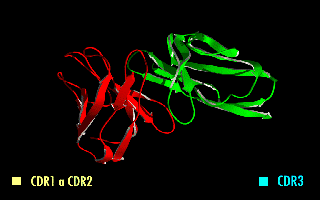
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a Antibody fragment, fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the Immunoglobulin heavy chain, heavy (VH) and Immunoglobulin light chain, light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of ten to about 25 amino acids. The linker is usually rich in glycine for flexibility, as well as serine or threonine for solubility, and can either connect the N-terminus of the VH with the C-terminus of the VL, or ''vice versa''. This protein retains the specificity of the original immunoglobulin, despite removal of the constant regions and the introduction of the linker. The image to the right shows how this modification usually leaves the specificity unaltered. These molecules were created to facilitate phage display, where it is highly convenient to express the Fragment antigen-binding, antigen-binding domain as a single peptide. As an alternative, scFv can be created d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Chain Variable Fragment
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of ten to about 25 amino acids. The linker is usually rich in glycine for flexibility, as well as serine or threonine for solubility, and can either connect the N-terminus of the VH with the C-terminus of the VL, or ''vice versa''. This protein retains the specificity of the original immunoglobulin, despite removal of the constant regions and the introduction of the linker. The image to the right shows how this modification usually leaves the specificity unaltered. These molecules were created to facilitate phage display, where it is highly convenient to express the antigen-binding domain as a single peptide. As an alternative, scFv can be created directly from subcloned heavy and light chains derived from a hybridoma. ScFvs have many uses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial T Cell Receptors
In biology, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs)—also known as chimeric immunoreceptors, chimeric T cell receptors or artificial T cell receptors—are receptor proteins that have been engineered to give T cells the new ability to target a specific antigen. The receptors are chimeric in that they combine both antigen-binding and T cell activating functions into a single receptor. CAR T cell therapy uses T cells engineered with CARs to treat cancer. T cells are modified to recognize cancer cells and destroy them. The standard approach is to harvest T cells from patients, genetically alter them, then infuse the resulting CAR T cells into patients to attack their tumors. CAR T cells can be derived either autologously from T cells in a patient's own blood or allogeneically from those of a donor. Once isolated, these T cells are genetically engineered to express a specific CAR, using a vector derived from an engineered lentivirus such as HIV (see Lentiviral vector in gene therapy). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phage Display
Phage display is a laboratory technique for the study of protein–protein, protein–peptide, and protein–DNA interactions that uses bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) to connect proteins with the genetic information that encodes them. In this technique, a gene encoding a protein of interest is inserted into a phage coat protein gene, causing the phage to "display" the protein on its outside while containing the gene for the protein on its inside, resulting in a connection between genotype and phenotype. The proteins that the phages are displaying can then be screened against other proteins, peptides or DNA sequences, in order to detect interaction between the displayed protein and those of other molecules. In this way, large libraries of proteins can be screened and amplified in a process called ''in vitro'' selection, which is analogous to natural selection. The most common bacteriophages used in phage display are M13 and fd filamentous phage, though T4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bi-specific T-cell Engager
Bi-specific T-cell engager (BiTE) is a class of artificial bispecific monoclonal antibody, bispecific monoclonal antibodies that are investigated for use as anti-cancer drugs. They direct a host's immune system, more specifically the T cells' cytotoxic activity, against cancer cells. ''BiTE'' is a registered trademark of Micromet AG (fully owned subsidiary of Amgen Inc). BiTE molecules are fusion proteins consisting of two single-chain variable fragments (scFvs) of different antibodies, or amino acid sequences from four different genes, on a single peptide chain of about 55 kilodaltons. One of the scFvs binds to T cells via the CD3 (immunology), CD3 receptor, and the other to a tumor cell via a tumor specific molecule. Mechanism of action Like other bispecific antibodies, and unlike ordinary monoclonal antibodies, BiTEs form a link between T cells and tumor cells. This causes T cells to exert cytotoxic activity on tumor cells by producing proteins like perforin and granzymes, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bispecific Antibodies
A bispecific monoclonal antibody (BsMAb, BsAb) is an artificial protein that can simultaneously bind to two different types of antigen or two different epitopes on the same antigen. Naturally occurring antibodies typically only target one antigen. BsAbs can be manufactured in several structural formats. BsAbs can be designed to recruit and activate immune cells, to interfere with receptor signaling and inactivate signaling ligands, and to force association of protein complexes. BsAbs have been explored for cancer immunotherapy, drug delivery, and Alzheimer's disease. Development history The original concept of BsAbs was proposed by Nisonoff and his collaborators in the 1960s, including the first idea of antibody architecture and other findings. In 1975, the problem of producing pure antibodies was solved by the creation of hybridoma technology, and the new era of monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) came. In 1983, Milstein and Cuello created hybrid-hybridoma ( quadroma) technology. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulins
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Each individual antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens, and antigens of virtually any size and chemical composition can be recognized. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each of the branching chains comprising the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" the antigen (or a microbe or an infected cell bearing such an antigen) for attack by cells of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a Lineage (evolution), cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies are identical and can thus have Valence (chemistry), monovalent affinity, binding only to a particular epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies are mixtures of antibodies derived from multiple plasma cell lineages which each bind to their particular target epitope. Artificial antibodies known as bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered which include two different antigen binding sites (Fragment antigen-binding region, FABs) on the same antibody. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to almost any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragment Antigen-binding
The fragment antigen-binding region (Fab region) is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain. The variable domain contains the paratope (the antigen-binding site), comprising a set of complementarity-determining regions, at the amino terminal end of the monomer. Each arm of the Y thus binds an epitope on the antigen. Preparation In an experimental setting, Fc and Fab fragments can be generated in the laboratory. The enzyme papain can be used to cleave an immunoglobulin monomer into two Fab fragments and an Fc fragment. Conversely, the enzyme pepsin cleaves below the hinge region, so the result instead is a F(ab')2 fragment and a pFc' fragment. Recently another enzyme for generation of F(ab')2 has been commercially available. The enzyme IdeS (Immunoglobulin degrading enzyme from ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', trade name FabRICATOR) cleaves IgG in a sequence specific manner a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pexelizumab
Pexelizumab is a drug designed to reduce side effects of coronary artery bypass grafting and angioplasty, among other types of cardiac surgery. It is a single chain variable fragment of a monoclonal antibody targeted against component 5 of the complement system The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the humoral, innate immune system and enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inf .... Current status Alexion, the developer of pexelizumab, stopped development when the phase 3 trial indicated the heart-attack drug is no better than placebo. References Monoclonal antibodies Abandoned drugs {{antineoplastic-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein L
Protein L was first isolated from the surface of bacterial species '' Peptostreptococcus magnus'' and was found to bind immunoglobulins through L chain interaction, from which the name was suggested. It consists of 719 amino acid residues. The molecular weight of protein L purified from the cell walls of '' Peptostreptoccus magnus'' was first estimated as 95kD by SDS-PAGE in the presence of reducing agent 2-mercaptoethanol, while the molecular weight was determined to 76kD by gel chromatography in the presence of 6 M guanidine HCl. Protein L does not contain any interchain disulfide loops, nor does it consist of disulfide-linked subunits. It is an acidic molecule with a pI of 4.0. Unlike protein A and protein G, which bind to the Fc region of immunoglobulins (antibodies), protein L binds antibodies through light chain interactions. Since no part of the heavy chain is involved in the binding interaction, Protein L binds a wider range of antibody classes than protein A or G. Prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein G
Protein G is an immunoglobulin-binding protein expressed in group C and G streptococcal bacteria much like protein A but with differing binding specificities. It is a ~60-kDA (65 kDA for strain G148 and 58 kDa for strain C40) cell surface protein that has found application in purifying antibodies through its binding to the Fab and Fc region. The native molecule also binds albumin, but because serum albumin is a major contaminant of antibody sources, the albumin binding site has been removed from recombinant forms of protein G. This recombinant protein G, either labeled with a fluorophore or a single-stranded DNA strand, was used as a replacement for secondary antibodies in immunofluorescence and super-resolution imaging. Other antibody binding proteins In addition to protein G, other immunoglobulin-binding bacterial proteins such as protein A, protein A/G and protein L are all commonly used to purify, immobilize or detect immunoglobulins. Each of these immunoglobulin-bindin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fc Region
The fragment crystallizable region (Fc region) is the tail region of an antibody that interacts with cell surface receptors called Fc receptors and some proteins of the complement system. This region allows antibodies to activate the immune system, for example, through binding to Fc receptors. In IgG, IgA and IgD antibody isotypes, the Fc region is composed of two identical protein fragments, derived from the second and third constant domains of the antibody's two heavy chains; IgM and IgE Fc regions contain three heavy chain constant domains (CH domains 2–4) in each polypeptide chain. The Fc regions of IgGs bear a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. Glycosylation of the Fc fragment is essential for Fc receptor-mediated activity. The N-glycans attached to this site are predominantly core- fucosylated diantennary structures of the complex type. In addition, small amounts of these N-glycans also bear bisecting GlcNAc and α-2,6 linked sialic acid residues. The other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |