single chain variable fragment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
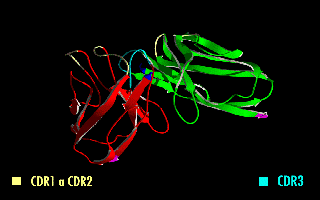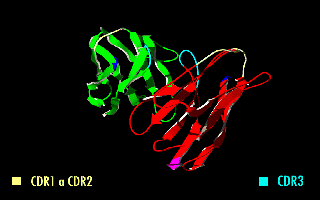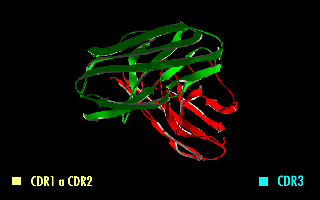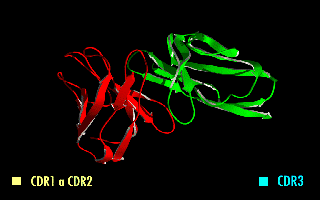
 A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker
 ''Divalent'' (or ''bivalent'') single-chain variable fragments (di-scFvs, bi-scFvs) can be engineered by linking two scFvs. This can be done by producing a single peptide chain with two VH and two VL regions, yielding ''tandem scFvs''. Another possibility is the creation of scFvs with linker peptides that are too short for the two variable regions to fold together (about five amino acids), forcing scFvs to dimerize. This type is known as ''diabodies''. Diabodies have been shown to have
''Divalent'' (or ''bivalent'') single-chain variable fragments (di-scFvs, bi-scFvs) can be engineered by linking two scFvs. This can be done by producing a single peptide chain with two VH and two VL regions, yielding ''tandem scFvs''. Another possibility is the creation of scFvs with linker peptides that are too short for the two variable regions to fold together (about five amino acids), forcing scFvs to dimerize. This type is known as ''diabodies''. Diabodies have been shown to have

peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
of ten to about 25 amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s. The linker is usually rich in glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
for flexibility, as well as serine
Serine
(symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − ...
or threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form when dissolved in water), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− ...
for solubility, and can either connect the N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amin ...
of the VH with the C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comp ...
of the VL, or ''vice versa''.
This protein retains the specificity of the original immunoglobulin, despite removal of the constant regions and the introduction of the linker. The image to the right shows how this modification usually leaves the specificity unaltered.
These molecules were created to facilitate phage display
Phage display is a laboratory technique for the study of protein–protein, protein–peptide, and protein–DNA interactions that uses bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) to connect proteins with the genetic information that encodes ...
, where it is highly convenient to express the antigen-binding domain as a single peptide. As an alternative, scFv can be created directly from subcloned heavy and light chains derived from a hybridoma. ScFvs have many uses, e.g., flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of Antibody, antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Alber ...
, and as antigen-binding domains of artificial T cell receptors (chimeric antigen receptor).
Unlike monoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a Lineage (evolution), cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Mon ...
, which are often produced in mammalian cell cultures, scFvs are more often produced in bacteria cell cultures such as '' E. coli''.
Purification
Single-chain variable fragments lack the constant Fc region found in complete antibody molecules, and, thus, the common binding sites (e.g., protein G) cannot be used to purify antibodies. These fragments can often be purified or immobilized using protein L, since protein L interacts with the variable region of kappa light chains. More commonly, scientists incorporate a six histidine tag on the c-terminus of the scFv molecule and purify them using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC). Some scFv can also be captured by protein A if they contain a human VH3 domain.Bivalent and trivalent scFvs
dissociation constant
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant (''K''D) is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate (dissociate) reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex ...
s up to 40-fold lower than corresponding scFvs, meaning that they have a much higher affinity
Affinity may refer to:
Commerce, finance and law
* Affinity (law), kinship by marriage
* Affinity analysis, a market research and business management technique
* Affinity Credit Union, a Saskatchewan-based credit union
* Affinity Equity Pa ...
to their target. Consequently, diabody drugs could be dosed much lower than other therapeutic antibodies and are capable of highly specific targeting of tumors in vivo. Still shorter linkers (one or two amino acids) lead to the formation of trimers, so-called ''triabodies'' or ''tribodies''. ''Tetrabodies'' have also been produced. They exhibit an even higher affinity to their targets than diabodies.
All of these formats can be composed from variable fragments with specificity for two different antigens, in which case they are types of bispecific antibodies. The furthest developed of these are bispecific tandem di-scFvs, known as bi-specific T-cell engagers (BiTE antibody constructs).
Examples
* Pexelizumab, a scFv binding to component 5 of thecomplement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the humoral, innate immune system and enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inf ...
and designed to reduce side effects of cardiac surgery
* C6.5, a diabody targeting HER2/neu
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that normally resides in the membranes of cells and is encoded by the ''ERBB2'' gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The ...
found in some breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
s
* Brolucizumab, a scFV binding to VEGF-A and used to treat wet age-related macular degeneration
* G6A, a scFV binding to human Hsp70.1 and can be used to target this protein as a potential marker in vast cancers.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Single-Chain Variable Fragment .