|
Rogernomics
In February 1985, journalists at the '' New Zealand Listener'' coined the term Rogernomics, a portmanteau of "Roger" and "economics" (by analogy with " Reaganomics"), to describe the neoliberal economic policies followed by Roger Douglas. Douglas served as Minister of Finance (1984–1988) in the Fourth Labour Government of New Zealand of 26 July 1984 to 2 November 1990. Rogernomics featured market-led restructuring and deregulation and the control of inflation through tight monetary policy, accompanied by a floating exchange-rate and reductions in the fiscal deficit. Dalziel, Paul in Easton, Brian ed ''The Making of Rogernomics'' Auckland University Press 1989 p. 53 Douglas came from a background of Labour Party politics. His adoption of policies more usually associated with the political right (or New Right), and their implementation by the Fourth Labour Government, became the subject of lasting controversy. Douglas and the development of economic policy, 1969–1983 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Douglas
Sir Roger Owen Douglas (born 5 December 1937) is a retired New Zealand politician who served as a minister in two Labour governments. He became arguably best known for his prominent role in New Zealand's radical economic restructuring in the 1980s, when the Fourth Labour Government's economic policy became known as " Rogernomics". Douglas served as a Labour Member of Parliament from 1969 to 1990. During his time as Minister of Finance (1984 to 1988), the government floated the New Zealand dollar, introduced corporate practices to state services, sold off state assets, and removed a swathe of regulations and subsidies. Some Labour Party supporters regarded Douglas's economic policies as a betrayal of Labour's left-wing policy-platform, and the moves became deeply unpopular with the public and with ordinary party members. His supporters defended the reforms as necessary to revive the economy, which had been tightly regulated under National's Muldoon (Minister of Finance from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Labour Government Of New Zealand
The Fourth Labour Government of New Zealand governed New Zealand from 26 July 1984 to 2 November 1990. It was the first Labour government to win a second consecutive term since the First Labour Government of 1935 to 1949. The policy agenda of the Fourth Labour Government differed significantly from that of previous Labour governments: it enacted major social reforms (such as legalising homosexual relations) and economic reforms (including corporatisation of state services and reform of the tax system). The economic reforms became known as "Rogernomics", after Finance Minister Roger Douglas. According to one political scientist: The Labour government also enacted nuclear-free legislation, which led to the United States suspending its treaty obligations to New Zealand under the ANZUS alliance. David Lange led the government for most of its two three-year terms in office. Lange and Douglas had a falling out that divided the party. The government suffered a defeat at the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand National Party
The New Zealand National Party ( mi, Rōpū Nāhinara o Aotearoa), shortened to National () or the Nats, is a centre-right political party in New Zealand. It is one of two major parties that dominate contemporary New Zealand politics, alongside its traditional rival, the Labour Party. National formed in 1936 through amalgamation of conservative and liberal parties, Reform and United respectively, and subsequently became New Zealand's second-oldest extant political party. National's predecessors had previously formed a coalition against the growing labour movement. National has governed for five periods during the 20th and 21st centuries, and has spent more time in government than any other New Zealand party. After the 1949 general election, Sidney Holland became the first prime minister from the National Party, and remained in office until 1957. Keith Holyoake succeeded Holland, and was defeated some months later at a general election by the Labour Party in 1957. Hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Labour Party
The New Zealand Labour Party ( mi, Rōpū Reipa o Aotearoa), or simply Labour (), is a centre-left political party in New Zealand. The party's platform programme describes its founding principle as democratic socialism, while observers describe Labour as social-democratic and pragmatic in practice. The party participates in the international Progressive Alliance. It is one of two major political parties in New Zealand, alongside its traditional rival, the National Party. The New Zealand Labour Party formed in 1916 out of various socialist parties and trade unions. It is the country's oldest political party still in existence. Alongside the National Party, Labour has alternated in leading governments of New Zealand since the 1930s. , there have been six periods of Labour government under ten Labour prime ministers. The party has traditionally been supported by working class, urban, Māori, Pasifika, immigrant and trade unionist New Zealanders, and has had strongholds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Muldoon
Sir Robert David Muldoon (; 25 September 19215 August 1992) was a New Zealand politician who served as the 31st Prime Minister of New Zealand, from 1975 to 1984, while leader of the National Party. Serving as a corporal and sergeant in the army in the Second World War, Muldoon completed his training as an accountant and returned to New Zealand as its first fully qualified cost accountant. He was first elected to the House of Representatives at the 1960 general election as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Tamaki, representing the National Party. In this time of political stability, Muldoon served successively as Minister of Tourism (1967), Minister of Finance (1967–1972), and Deputy Prime Minister (1972). Over this time he built up an informal but solid backing amongst National's mostly rural right faction, which he labelled "Rob's Mob"—possibly in imitation of gangs such as the Mongrel Mob. National were then expelled from office in 1972, beginning the tenure of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Lange
David Russell Lange ( ; 4 August 1942 – 13 August 2005) was a New Zealand politician who served as the 32nd prime minister of New Zealand from 1984 to 1989. Lange was born and brought up in Otahuhu, the son of a medical doctor. He became a lawyer by profession, and represented poor and struggling people in civil rights causes in the rapidly changing Auckland of the 1970s. After serving as legal advisor to the Polynesian Panthers, Lange was first elected to the New Zealand Parliament in the Mangere by-election of 1977. He became a prominent debater within parliament, and soon gained a reputation for cutting wit (sometimes directed against himself) and eloquence. Lange became the Leader of the Labour Party and Leader of the Opposition in 1983, succeeding Bill Rowling. When Prime Minister Robert Muldoon called an election for July 1984 Lange led his party to a landslide victory, becoming, at the age of 41, New Zealand's youngest prime minister of the 20th century. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoliberal
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent factor in the rise of conservative and libertarian organizations, political parties, and think tanks, and predominantly advocated by them, it is generally associated with policies of economic liberalization, including privatization, deregulation, globalization, free trade, monetarism, austerity, and reductions in government spending in order to increase the role of the private sector in the economy and society. The defining features of neoliberalism in both thought and practice have been the subject of substantial scholarly debate. As an economic philosophy, neoliberalism emerged among European liberal scholars in the 1930s as they attempted to revive and renew central ideas from classical liberalism as they saw these ideas diminish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Reform
Microeconomic reform (or often just economic reform) comprises policies directed to achieve improvements in economic efficiency, either by eliminating or reducing distortions in individual sectors of the economy or by reforming economy-wide policies such as tax policy and competition policy with an emphasis on economic efficiency, rather than other goals such as equity or employment growth. "Economic reform" usually refers to deregulation, or at times to reduction in the size of government, to remove distortions caused by regulations or the presence of government, rather than new or increased regulations or government programs to reduce distortions caused by market failure. As such, these reform policies are in the tradition of laissez faire, emphasizing the distortions caused by government, rather than in ordoliberalism, which emphasizes the need for state regulation to maximize efficiency. Microeconomic reform in Australia Microeconomic reform dominated Australian economic polic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mike Moore (New Zealand Politician)
Michael Kenneth Moore (28 January 1949 – 2 February 2020) was a New Zealand politician, union organiser, and author. In the Fourth Labour Government he served in several portfolios including minister of Foreign Affairs, and was the 34th prime minister of New Zealand for 59 days before the 1990 general election elected a new parliament. Following Labour's defeat in that election, Moore served as Leader of the Opposition until the 1993 election, after which Helen Clark successfully challenged him for the Labour Party leadership. Following his retirement from New Zealand politics, Moore was Director-General of the World Trade Organization from 1999 to 2002. He also held the post of New Zealand Ambassador to the United States from 2010 to 2015. Early life Moore was born in 1949 in Whakatāne, Bay of Plenty, New Zealand, the son of Audrey Evelyn (née Goodall) and Alan George Moore. He was raised in Moerewa and while aged only two his mother pushed him around town in a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Rowling
Sir Wallace Edward Rowling (; 15 November 1927 – 31 October 1995), commonly known as Bill Rowling, was a New Zealand politician who was the 30th prime minister of New Zealand from 1974 to 1975. He held office as the parliamentary leader of the Labour Party. Rowling was a lecturer in economics when he entered politics; he became a Member of Parliament in the 1962 Buller by-election. Not long after entering parliament Rowling began to rise through Labour's internal hierarchy, and he was Party President from 1970 to 1973. He was serving as Minister of Finance (1972–1974) when he was appointed Prime Minister following the death of the highly popular Norman Kirk. His Labour Government's effort to retrieve the economy ended with an upset victory by the National Party in November 1975. Rowling continued to lead the Labour Party but lost two more general elections. Upon retiring from the party's leadership in 1983, he was knighted. He served as Ambassador to the United States f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Right
New Right is a term for various right-wing political groups or policies in different countries during different periods. One prominent usage was to describe the emergence of certain Eastern European parties after the collapse of the Soviet Union. In the United States, the Second New Right campaigned against abortion, homosexuality, the Equal Rights Amendment (ERA), the Panama Canal Treaty, affirmative action, and most forms of taxation. History ''New Right'' appeared during the 1964 presidential campaign of Barry Goldwater to designate the emergence, in response to American-style liberalism (i.e., social liberalism), of a more combative, anti-egalitarian, and uninhibited right. Popularized by Richard Viguerie, the term became later used to describe a broader movement in the English-speaking world: those proponents of the night-watchman state but who also tended to be socially conservative, such as Ronald Reagan, Margaret Thatcher, Turgut Özal, Augusto Pinochet or New Zeal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
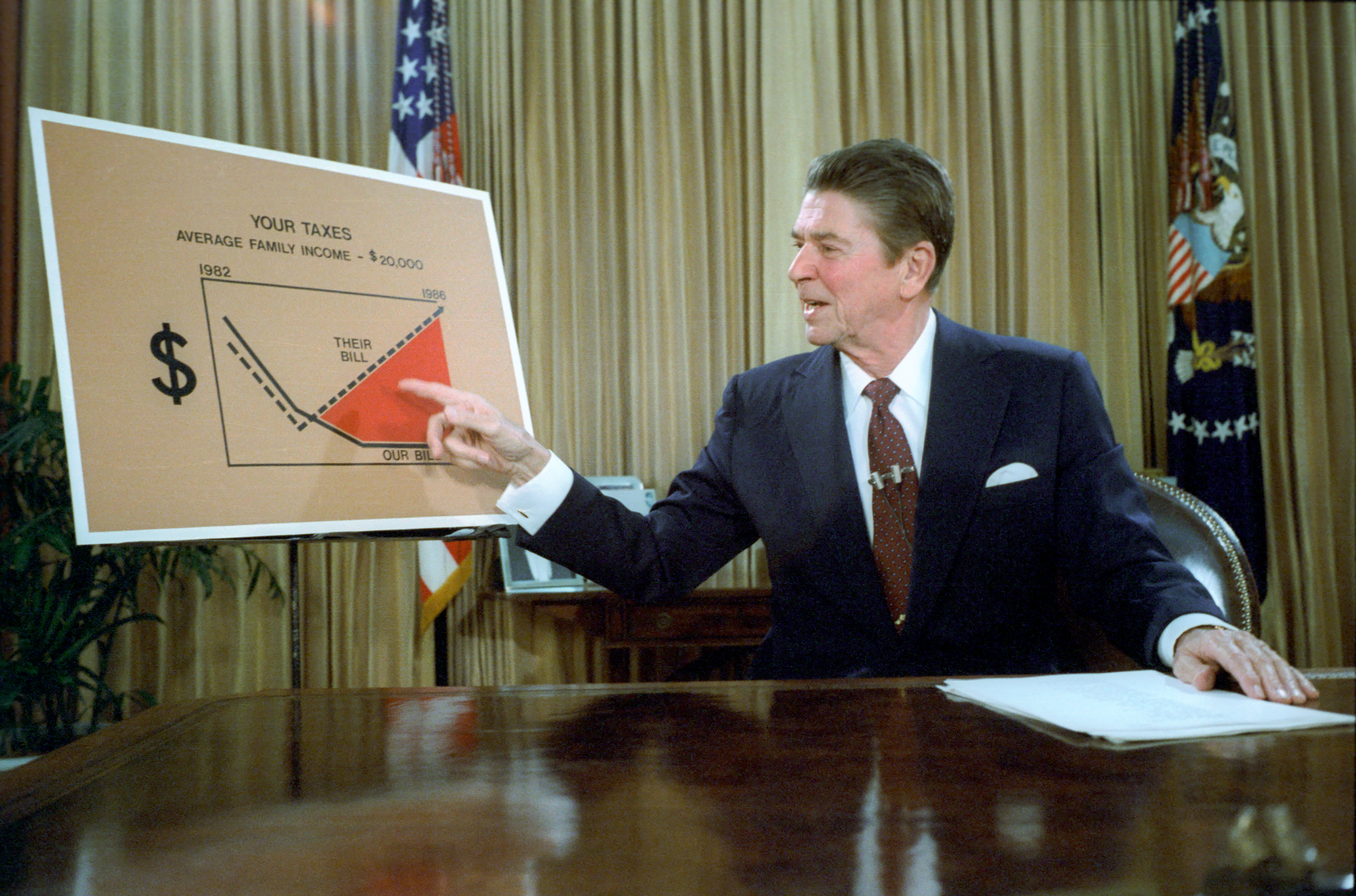
Reaganomics
Reaganomics (; a portmanteau of ''Reagan'' and ''economics'' attributed to Paul Harvey), or Reaganism, refers to the neoliberal economic policies promoted by U.S. President Ronald Reagan during the 1980s. These policies are commonly associated with and characterized as supply-side economics, trickle-down economics, or "voodoo economics" by opponents, while Reagan and his advocates preferred to call it free-market economics. The pillars of Reagan's economic policy included increasing defense spending, balancing the federal budget and slowing the growth of government spending, reducing the federal income tax and capital gains tax, reducing government regulation, and tightening the money supply in order to reduce inflation. The results of Reaganomics are still debated. Supporters point to the end of stagflation, stronger GDP growth, and an entrepreneurial revolution in the decades that followed. Critics point to the widening income gap, what they described as an atmosphere of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)