|
Repeating Circle
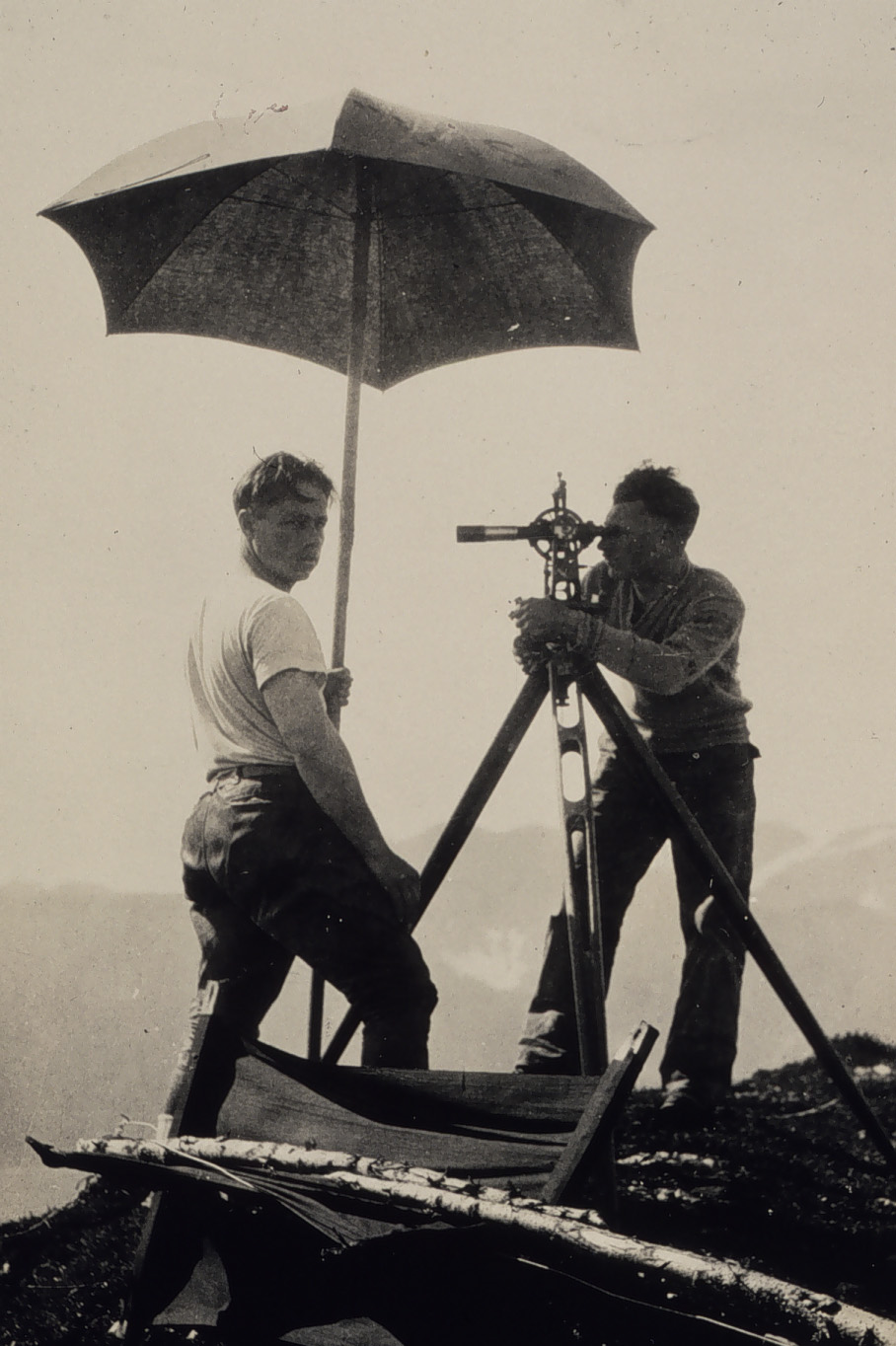
The repeating circle is an instrument for geodetic surveying, developed from the Reflecting instrument#reflecting circle, reflecting circle by Étienne Lenoir (instrument maker), Étienne Lenoir in 1784. He invented it while an assistant of Jean-Charles de Borda, who later improved the instrument. It was notable as being the equal of the Ramsden surveying instruments#great theodolite, great theodolite created by the renowned instrument maker, Jesse Ramsden. It was used to arc measurement, measure the meridian arc from Dunkirk to Barcelona by Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre, Jean Baptiste Delambre and Pierre Méchain (see: meridian arc of Delambre and Méchain). Construction and operation The repeating circle is made of two telescopes mounted on a shared axis with scales to measure the angle between the two. The instrument combines multiple measurements to increase accuracy with the following procedure: At this stage, the angle on the instrument is double the angle of interest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
12in Repeating Circle
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes with glass lenses and were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy. The reflecting telescope, which uses mirrors to collect and focus light, was invented within a few decades of the first refracting telescope. In the 20th century, many new types of telescopes were invented, including radio telescopes in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Meridional Definition
During the French Revolution, the traditional units of measure were to be replaced by consistent measures based on natural phenomena. As a base unit of length, scientists had favoured the seconds pendulum (a pendulum with a half-period of one second) one century earlier, but this was rejected as it had been discovered that this length varied from place to place with local gravity. A new unit of length, the ''metre'' was introduced – defined as one ten-millionth of the shortest distance from the North Pole to the equator passing through Paris, assuming an Earth flattening of . Following the arc measurement of Delambre and Méchain, the historical French official standard of the metre was made available in the form of the , a platinum bar held in Paris. During the mid nineteenth century, following the American Revolution and independence of Latin America, the metre gained adoption in Americas, particularly in scientific usage, and it was officially established as an intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reflecting Circles
Reflecting instruments are those that use mirrors to enhance their ability to make measurements. In particular, the use of mirrors permits one to observe two objects simultaneously while measuring the angular distance between the objects. While reflecting instruments are used in many professions, they are primarily associated with celestial navigation as the need to solve navigation problems, in particular the problem of the longitude, was the primary motivation in their development. Objectives of the instruments The purpose of reflecting instruments is to allow an observer to measure the altitude of a celestial object or the angular distance between two objects. The driving force behind the developments discussed here was the solution to the problem of finding one's longitude at sea. The solution to this problem was seen to require an accurate means of measuring angles and the accuracy was seen to rely on the observer's ability to measure this angle by simultaneously observing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Observational Error
Observational error (or measurement error) is the difference between a measured value of a quantity and its unknown true value.Dodge, Y. (2003) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', OUP. Such errors are inherent in the measurement process; for example lengths measured with a ruler calibrated in whole centimeters will have a measurement error of several millimeters. The error or uncertainty of a measurement can be estimated, and is specified with the measurement as, for example, 32.3 ± 0.5 cm. Scientific observations are marred by two distinct types of errors, systematic errors on the one hand, and random, on the other hand. The effects of random errors can be mitigated by the repeated measurements. Constant or systematic errors on the contrary must be carefully avoided, because they arise from one or more causes which constantly act in the same way, and have the effect of always altering the result of the experiment in the same direction. They therefore alter the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zenith
The zenith (, ) is the imaginary point on the celestial sphere directly "above" a particular location. "Above" means in the vertical direction (Vertical and horizontal, plumb line) opposite to the gravity direction at that location (nadir). The zenith is the "highest" point on the celestial sphere. The direction opposite of the zenith is the nadir. Origin The word ''zenith'' derives from an inaccurate reading of the Arabic language, Arabic expression (), meaning "direction of the head" or "path above the head", by Medieval Latin scribes in the Middle Ages (during the 14th century), possibly through Old Spanish. It was reduced to ''samt'' ("direction") and miswritten as ''senit''/''cenit'', the ''m'' being misread as ''ni''. Through the Old French ''cenith'', ''zenith'' first appeared in the 17th century. Relevance and use The term ''zenith'' sometimes means the culmination, highest point, way, or level reached by a celestial body on its daily apparent path around a given poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of a second, where the second is defined by a hyperfine transition frequency of caesium. The metre was originally defined in 1791 by the French National Assembly as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's polar circumference is approximately . In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar. The bar used was changed in 1889, and in 1960 the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paris Meridian
The Paris meridian is a meridian line running through the Paris Observatory in Paris, France – now longitude 2°20′14.02500″ East. It was a long-standing rival to the Greenwich meridian as the prime meridian of the world. The "Paris meridian arc" or "French meridian arc" (French: ''la Méridienne de France'') is the name of the meridian arc measured along the Paris meridian. The French meridian arc was important for French cartography, since the triangulations of France began with the measurement of the French meridian arc. Moreover, the French meridian arc was important for geodesy as it was one of the meridian arcs which were measured to determine the figure of the Earth via the arc measurement method. The determination of the figure of the Earth was a problem of the highest importance in astronomy, as the diameter of the Earth was the unit to which all celestial distances had to be referred. History French cartography and the figure of the Earth In the ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arc Measurement Of Delambre And Méchain
The arc measurement of Delambre and Méchain was a geodetic survey carried out by Jean-Baptiste Delambre and Pierre Méchain in 1792–1798 to measure an arc section of the Paris meridian between Dunkirk and Barcelona. This arc measurement served as the basis for the original definition of the metre. Until the French Revolution of 1789, France was particularly affected by the proliferation of length measures; the conflicts related to units helped precipitate the revolution. In addition to rejecting standards inherited from feudalism, linking determination of a decimal unit of length with the figure of the Earth was an explicit goal. This project culminated in an immense effort to measure a meridian passing through Paris in order to define the metre. When question of measurement reform was placed in the hands of the French Academy of Sciences, a commission, whose members included Jean-Charles de Borda, Joseph-Louis Lagrange, Pierre-Simon Laplace, Gaspard Monge and the Marquis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
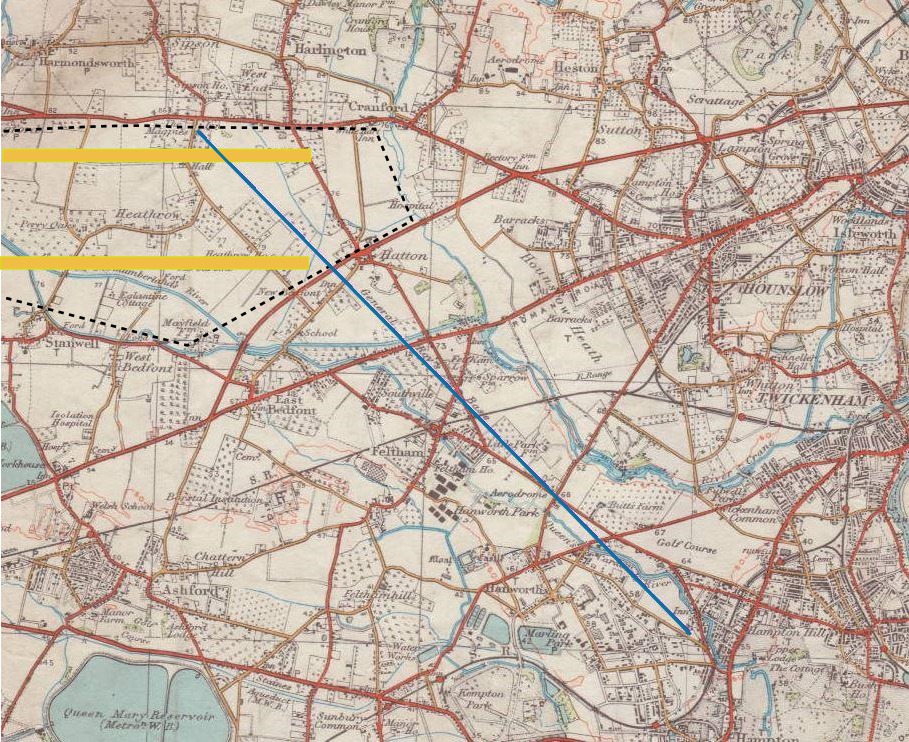
Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790)
The Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790) was the geodetic survey to measure the relative position of the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, Royal Greenwich Observatory and the Paris Observatory via triangulation (surveying), triangulation. The English operations, executed by William Roy, consisted of the measurements of bases at Hounslow Heath (1784) and Romney Marsh (1787), the measurements of the angles of the triangles (1787–1788) and finally the calculation of all the triangles (1788–1790). The survey is very significant as the first precise survey within Britain, and the forerunner of the work of the Ordnance Survey which was founded in 1791, one year after Roy's death. Cassini's memoir Late in life, when he was 57, Roy was granted the opportunity to establish his lasting reputation in the world of geodesy. The opening came from a completely unexpected direction. In 1783 the director of the Paris Observatory, César-François Cassini de Thury, Cassini de Thury, addressed a me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Triangulation (surveying)
In surveying, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by measuring only angles to it from known points at either end of a fixed baseline by using trigonometry, rather than measuring distances to the point directly as in trilateration. The point can then be fixed as the third point of a triangle with one known side and two known angles. Triangulation can also refer to the accurate surveying of systems of very large triangles, called triangulation networks. This followed from the work of Willebrord Snellius, Willebrord Snell in 1615–17, who showed how a point could be located from the angles subtended from ''three'' known points, but measured at the new unknown point rather than the previously fixed points, a problem called Position resection and intersection, resectioning. Surveying error is minimized if a mesh of triangles at the largest appropriate scale is established first. Points inside the triangles can all then be accurately located with refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
César-François Cassini De Thury
César-François Cassini de Thury (17 June 1714 – 4 September 1784), also called Cassini III or Cassini de Thury, was a French astronomer and cartographer. Biography Cassini de Thury was born in Thury-sous-Clermont, in the Oise department, the second son of Jacques Cassini and Suzanne Françoise Charpentier de Charmois. He was a grandson of Giovanni Domenico Cassini, and would become the father of Jean-Dominique Cassini, Comte de Cassini. In 1739, he became a member of the French Academy of Sciences as a supernumerary adjunct astronomer, in 1741 as an adjunct astronomer, and in 1745 as a full member astronomer. In January 1751, he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society. Cassini de Thury succeeded his father's official position in 1756 and continued the hereditary surveying operations.Jonathan Powell, ''From Cave Art to Hubble: A History of Astronomical Record Keeping'', (Springer Nature Switzerland AG, 2019), 115 In 1744, he began the construction of a great to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |