|
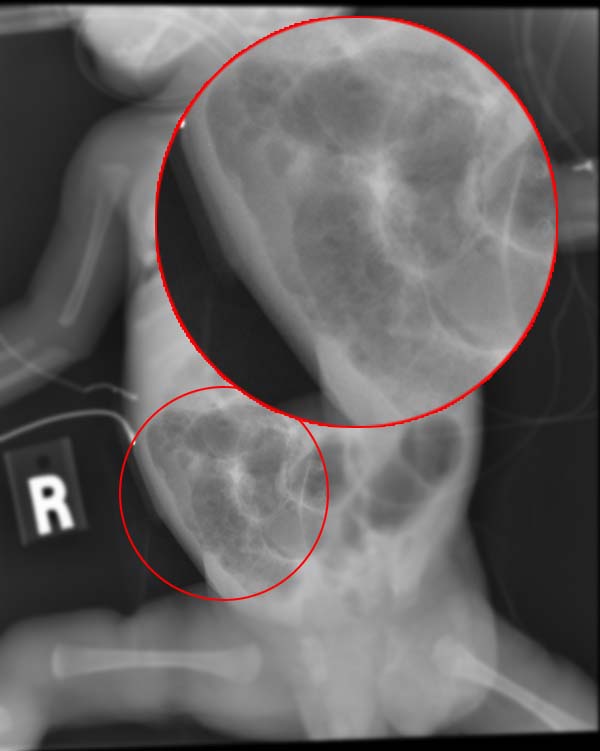
Pneumatosis Intestinalis
Pneumatosis intestinalis (also called intestinal pneumatosis, pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis, pneumatosis coli, or intramural bowel gas) is pneumatosis of an intestine, that is, gas cysts in the bowel wall. As a radiological sign it is highly suggestive for necrotizing enterocolitis. This is in contrast to gas in the intestinal lumen (which is relieved by flatulence). In newborns, pneumatosis intestinalis is considered diagnostic for necrotizing enterocolitis, and the gas is produced by bacteria in the bowel wall. The pathogenesis of pneumatosis intestinalis is poorly understood and is likely multifactorial. PI itself is not a disease, but rather a clinical sign. In some cases, PI is an incidental finding, whereas in others, it portends a life-threatening intra-abdominal condition. __TOC__ Additional images File:Pneumatosis intestinalis CT LF Darmischaemie cor.jpg, Pneumatosis intestinalis at computed tomography in intestinal ischemia. Lung window for better representation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumatosis
Pneumatosis is the abnormal presence of air or other gas within tissues. In the lungs, emphysema involves enlargement of the distal airspaces,page 64 in: and is a major feature of (COPD). Other pneumatoses in the lungs are focal (localized) blebs and bullae, pulmonary cysts and cavities. |
Intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cells divide incessantly and become cancerous, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavian Journal Of Surgery
''Scandinavian Journal of Surgery'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes papers in the field of surgery. The journal's editor-in-chief is Ari Leppäniemi (Meilahti Hospital, Finland). It has been in publication since 1919 and is currently published by SAGE Publications on behalf of the Finnish Surgical Society. Abstracting and indexing ''Scandinavian Journal of Surgery'' is abstracted and indexed in, among other databases: SCOPUS, and the Social Sciences Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', its 2012 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... is 1.169, ranking it 118 out of 199 journals in the category ‘Surgery’. References External links * {{Official website, 1=http://sjs.sagepub.com/ Finnish Surgical Socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiological Sign
A radiologic sign is an objective indication of some medical fact (that is, a medical sign) that is detected by a physician during radiologic examination with medical imaging (for example, via an X-ray, CT scan, MRI scan, or sonographic scan). Examples * Double decidual sac sign * Face of the giant panda sign * Football sign * Golden S sign * Hampton's hump * Hilum overlay sign * Kerley lines * Mickey Mouse sign * Omental cake * Peribronchial cuffing * Pneumatosis intestinalis * Rigler's sign * Westermark sign In chest radiography, the Westermark sign is a sign that represents a focus of oligemia (hypovolemia) (leading to collapse of vessel) seen distal to a pulmonary embolism (PE). While the chest x-ray is normal in the majority of PE cases, the Westerm ... References See also List of radiologic signs {{Radiologic signs * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating intestinal disease that affects premature or very low birth weight infants.Gephart S.M., Quinn M. A call to action to fight for equity and end necrotizing enterocolitis disparities. ''Adv. Neonatal Care.'' 2021;21(5):333-335. doi:10.1097/ANC.0000000000000940 Symptoms may include poor feeding, bloating, decreased activity, blood in the stool, vomiting of bile, bowel death, multiorgan failure, and even death. The exact cause is unclear. However, several risk factors have been identified. Consistently described risk factors include formula feeding, intestinal dysbiosis, low birth weight, and prematurity. Maternal factors such as chorioamnionitis, cocaine abuse, ''in utero'' growth restriction, intrahepatic cholestasis during pregnancy, increased body mass index, lack of prenatal steroids, mode of delivery, placental abruption, preeclampsia, and smoking have not been consistently implicated with the development of NEC. Other risk fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Lumen
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatulence
Flatulence, in humans, is the expulsion of gas from the intestines via the anus, commonly referred to as farting. "Flatus" is the medical word for gas generated in the stomach or bowels. A proportion of intestinal gas may be swallowed environmental air, and hence flatus is not entirely generated in the stomach or bowels. The scientific study of this area of medicine is termed flatology. Flatus is brought to the rectum and pressurized by muscles in the intestines. It is normal to pass flatus ("to fart"), though volume and frequency vary greatly among individuals. It is also normal for intestinal gas to have a feculent or unpleasant odor, which may be intense. The noise commonly associated with flatulence (" blowing a raspberry") is produced by the anus and buttocks, which act together in a manner similar to that of an embouchure. Both the sound and odor are sources of embarrassment, annoyance or amusement ( flatulence humor). There are several general symptoms related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neonates
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, an infant who is only hours, days, or up to one month old. In medical contexts, a newborn or neonate (from Latin, ''neonatus'', newborn) is an infant in the first 28 days after birth; the term applies to premature, full term, and postmature infants. Before birth, the offspring is called a fetus. The term ''infant'' is typically applied to very young children under one year of age; however, definitions may vary and may include children up to two years of age. When a human child learns to walk, they are called a toddler instead. Other uses In British English, an ''infant school'' is for children aged between four and seven. As a legal term, ''infancy'' is more li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathognomonic
Pathognomonic (rare synonym ''pathognomic'') is a term, often used in medicine, that means "characteristic for a particular disease". A pathognomonic sign is a particular sign whose presence means that a particular disease is present beyond any doubt. Labelling a sign or symptom "pathognomonic" represents a marked intensification of a "diagnostic" sign or symptom. The word is an adjective of Greek origin derived from πάθος ''pathos'' "disease" and γνώμων ''gnomon'' "indicator" (from γιγνώσκω ''gignosko'' "I know, I recognize"). Practical use While some findings may be classic, typical or highly suggestive in a certain condition, they may not occur ''uniquely'' in this condition and therefore may not directly imply a specific diagnosis. A pathognomonic sign or symptom has very high positive predictive value but does not need to have high sensitivity: for example it can sometimes be absent in a certain disease, since the term only implies that, when it is presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |