|
Pawned The Shetland Islands
The History of Shetland concerns the subarctic archipelago of Shetland in Scotland. The early history of the islands is dominated by the influence of the Vikings. From the 14th century, it was incorporated into the Kingdom of Scotland, and later into the United Kingdom. Prehistory Due to building in stone on virtually treeless islands—a practice dating to at least the early Neolithic Period—Shetland is extremely rich in physical remains of the prehistoric era, and there are over 5,000 archaeological sites. A midden site at West Voe on the south coast of Mainland, dated to 4320–4030 BC, has provided the first evidence of Mesolithic human activity in Shetland. The same site provides dates for early Neolithic activity, and finds at Scourd of Brouster in Walls have been dated to 3400 BC. "Shetland knives" are stone tools that date from this period made from felsite from Northmavine.Schei (2006) p. 10 Brochs were built in Shetland until 150-200 AD: in the case of Old Scatn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of humid continental regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Scandinavia, Siberia, and the Cairngorms. Generally, subarctic regions fall between 50°N and 70°N latitude, depending on local climates. Precipitation is usually low, and vegetation is characteristic of the taiga. Daylight at these latitudes is quite extreme between summer and winter due to its high latitude. Near the summer solstice for instance, subarctic regions can experience an all-night period of either civil, nautical, or astronomical twilight (or in the northern reaches full daylight), but without true night, since the sun never dips more than 18 degrees below the horizon. Noctilucent clouds are best observed within this range of latitude. Climate and soils Subarctic temperatures are above for at least one and at most three months of the year. Precipitation tends to be l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Scatness
Old Scatness is an archeological site on the Ness of Burgi, near the village of Scatness, parish of Dunrossness in the south end of Mainland, Shetland, near Sumburgh Airport and consists of medieval, Viking, Pictish, and Iron Age remains. It has been a settlement for thousands of years, each new generation adding buildings, and leveling off old ones. Among the discoveries is an Iron Age broch, the Ness of Burgi fort. Discovery and excavation The site was first unearthed during construction work for airport improvements in the late 1970s. An arc of the broch wall was exposed in one side of a green mound during the building of the perimeter road at the airport at Sumburgh Head. Since 1995, University of Bradford staff and students, professional archaeologists and local volunteers have been excavating the site and cataloging the finds. Excavations have uncovered a multi-period settlement with broch, wheelhouses and later dwellings. The site is managed by the Shetland Amenity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Conquest Of Britain
The Roman conquest of Britain refers to the conquest of the island of Britain by occupying Roman forces. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by 87 when the Stanegate was established. Conquest of the far north and Scotland took longer with fluctuating success. The Roman army was generally recruited in Italia, Hispania, and Gaul. To control the English Channel they used the newly formed fleet. The Romans under their general Aulus Plautius first forced their way inland in several battles against British tribes, including the Battle of the Medway, the Battle of the Thames, and in later years Caratacus's last battle and the Roman conquest of Anglesey. Following a widespread uprising in AD 60 in which Boudica sacked Camulodunum, VerulamiumChurchill, ''A History of the English-Speaking Peoples'', p. 7 and Londinium, the Romans suppressed the rebellion in the Defeat of Boudica. They went on ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Drusus and Antonia Minor at Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, where his father was stationed as a military legate. He was the first Roman emperor to be born outside Italy. Nonetheless, Claudius was an Italian of Sabine origins. As he had a limp and slight deafness due to sickness at a young age, he was ostracized by his family and was excluded from public office until his consulship (which was shared with his nephew, Caligula, in 37). Claudius's infirmity probably saved him from the fate of many other nobles during the purges throughout the reigns of Tiberius and Caligula, as potential enemies did not see him as a serious threat. His survival led to him being declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard after Caligula's assassination, at which point he was the last adult m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
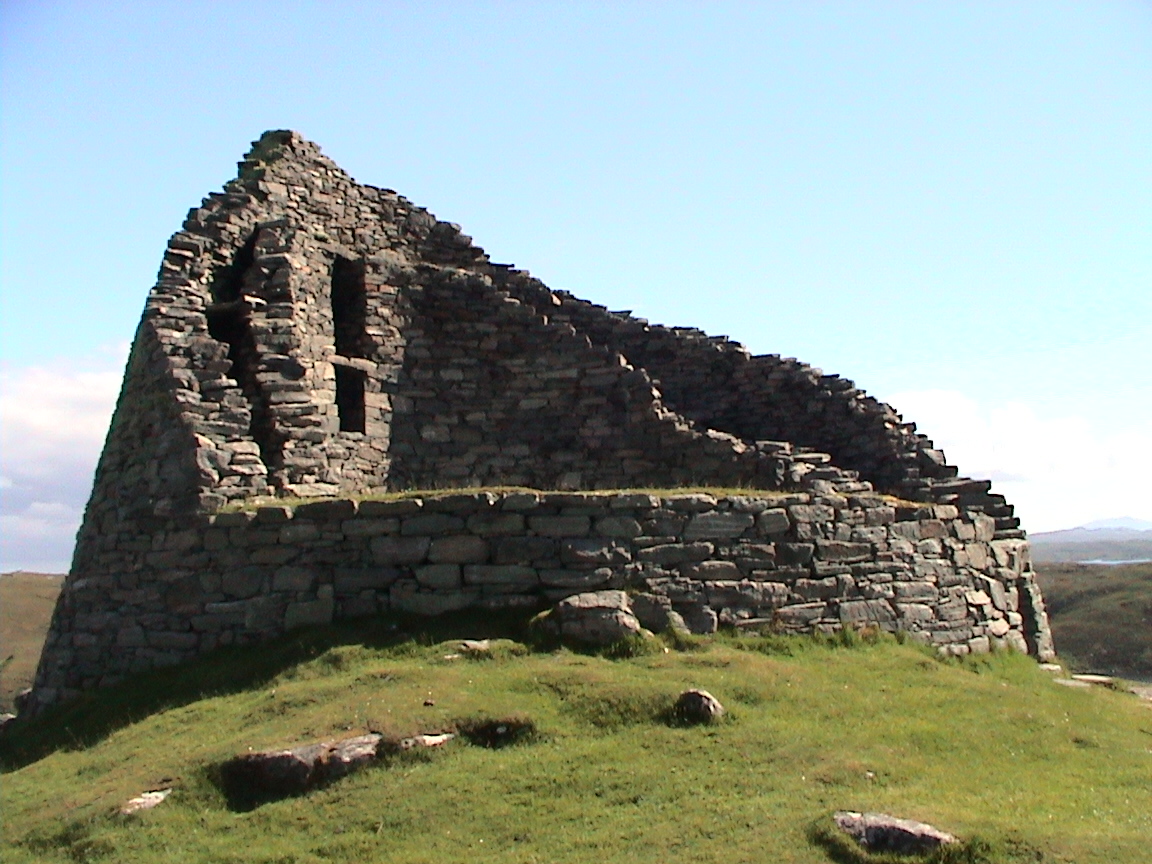
Brochs
A broch is an Iron Age drystone hollow-walled structure found in Scotland. Brochs belong to the classification "complex Atlantic roundhouse" devised by Scottish archaeologists in the 1980s. Their origin is a matter of some controversy. Origin and definition The word ''broch'' is derived from Lowland Scots 'brough', meaning (among other things) fort. In the mid-19th century Scottish antiquaries called brochs 'burgs', after Old Norse ', with the same meaning. Place names in Scandinavian Scotland such as Burgawater and Burgan show that Old Norse ' is the older word used for these structures in the north. Brochs are often referred to as '' duns'' in the west. Antiquarians began to use the spelling ''broch'' in the 1870s. A precise definition for the word has proved elusive. Brochs are the most spectacular of a complex class of roundhouse buildings found throughout Atlantic Scotland. The Shetland Amenity Trust lists about 120 sites in Shetland as candidate brochs, while the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars. The surviving portions of his two major works—the ''Annals'' (Latin: ''Annales'') and the ''Histories'' (Latin: ''Historiae'')—examine the reigns of the emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). These two works span the history of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the death of Domitian (96 AD), although there are substantial lacunae in the surviving texts. Tacitus's other writings discuss oratory (in dialogue format, see '' Dialogus de oratoribus''), Germania (in ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Agricola (the general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain), mainly focusing on his campaign in Britannia ('' De vita et moribus Iulii Agricol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thule
Thule ( grc-gre, Θούλη, Thoúlē; la, Thūlē) is the most northerly location mentioned in ancient Greek and Roman literature and cartography. Modern interpretations have included Orkney, Shetland, northern Scotland, the island of Saaremaa (Ösel) in Estonia, and the Norwegian island of Smøla.Andreas Kleineberg, Christian Marx, Eberhard Knobloch und Dieter Lelgemann: ''Germania und die Insel Thule. Die Entschlüsselung von Ptolemaios' "Atlas der Oikumene".'' Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft, Darmstadt 2010. In classical and medieval literature, ''ultima Thule'' (Latin "farthest Thule") acquired a metaphorical meaning of any distant place located beyond the "borders of the known world". By the Late Middle Ages and early modern period, the Greco-Roman Thule was often identified with the real Iceland or Greenland. Sometimes ''Ultima Thule'' was a Latin name for Greenland, when ''Thule'' was used for Iceland. By the late 19th century, however, ''Thule'' was frequentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
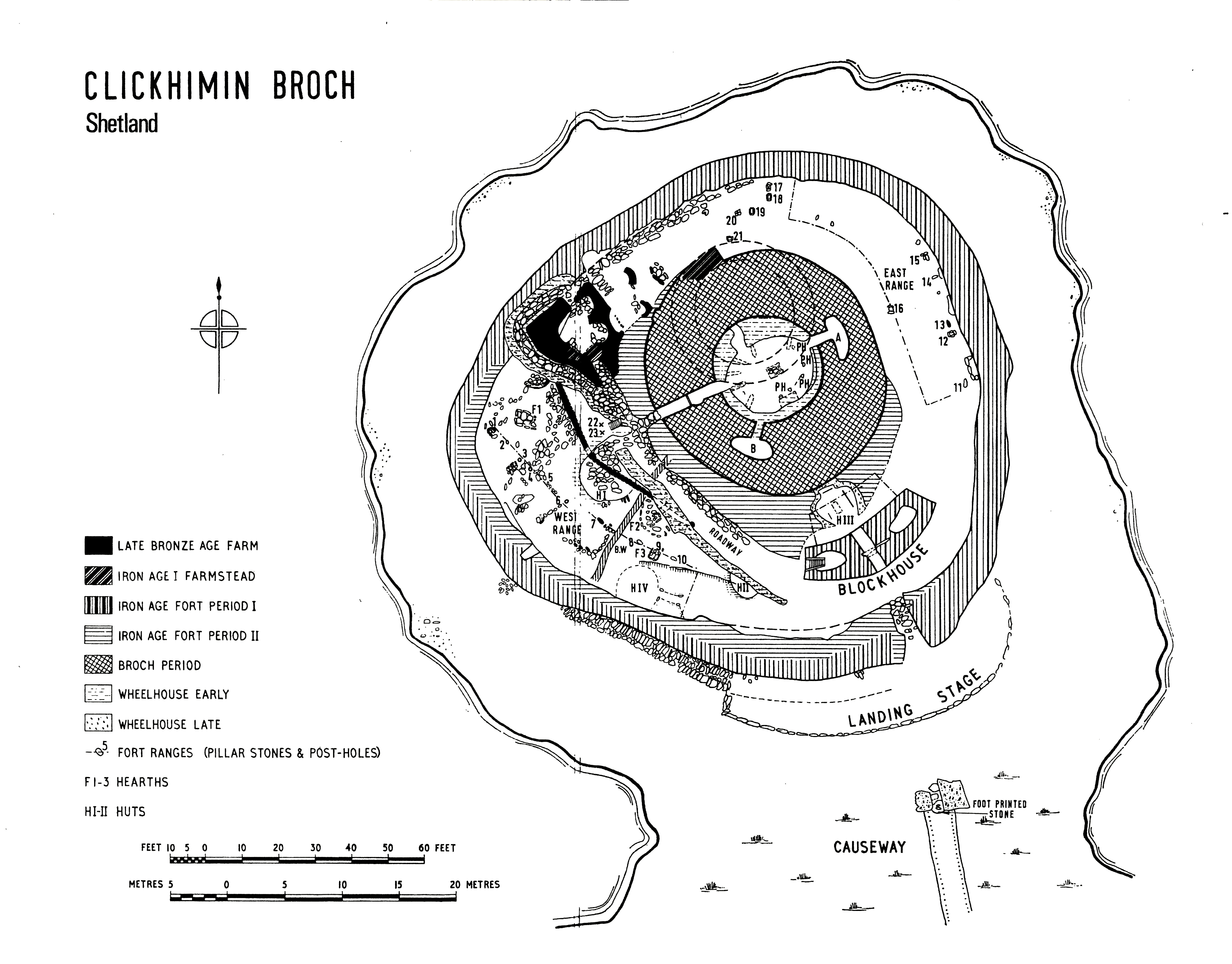
Clickimin
The Broch of Clickimin (also Clickimin or Clickhimin Broch) is a large, well-preserved but restored broch in Lerwick in Shetland, Scotland (). Originally built on an island in Clickimin Loch, it was approached by a stone causeway. The broch is situated within a walled enclosure and, unusually for brochs, features a large "forework" or "blockhouse" between the opening in the enclosure and the broch itself. The site is maintained by Historic Scotland. According to its excavator, John R.C. Hamilton, there were several periods of occupation of the site: Late Bronze Age farmstead, Early Iron Age farmstead, Iron Age fort, broch period, and wheelhouse settlement. Location Clickimin Broch is situated on the south shore of the Clickimin Loch Clickimin Loch is a loch in Shetland, Scotland, west of Lerwick Lerwick (; non, Leirvik; nrn, Larvik) is the main town and port of the Shetland archipelago, Scotland. Shetland's only burgh, Lerwick had a population of about 7,000 reside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochs
''Loch'' () is the Scottish Gaelic, Scots and Irish word for a lake or sea inlet. It is cognate with the Manx lough, Cornish logh, and one of the Welsh words for lake, llwch. In English English and Hiberno-English, the anglicised spelling lough is commonly found in place names; in Lowland Scots and Scottish English, the spelling "loch" is always used. Many loughs are connected to stories of lake-bursts, signifying their mythical origin. Sea-inlet lochs are often called sea lochs or sea loughs. Some such bodies of water could also be called firths, fjords, estuaries, straits or bays. Background This name for a body of water is Insular CelticThe current form has currency in the following languages: Scottish Gaelic, Irish, Manx, and has been borrowed into Lowland Scots, Scottish English, Irish English and Standard English. in origin and is applied to most lakes in Scotland and to many sea inlets in the west and north of Scotland. The word comes from Proto-Indo-European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culswick
The Broch of Culswick (also Culswick Broch) is an unexcavated coastal broch in the Shetland Islands of Scotland (). It has good views all around, including Foula and Vaila isles, and Fitful Head and Fair Isle in the south. The broch stands on the top of a rock platform and is about 3 metres high at its tallest point. Much rubble has fallen into the centre. This broch has a massive triangular lintel stone over the entrance, which is partly filled with rubble. Drawings by Low in 1774 and Skene in 1805 reveal that the structure survived very well up to those dates. Location The Broch of Culswick is located a kilometre west of Culswick in the parish of Sandsting Sandsting is a parish in the West Mainland of Shetland, Scotland, forming a southern arm of the Walls Peninsula. After the parish of Aithsting was annexed into Sandsting in the sixteenth century, it became known as Sandsting and Aithsting pari .... It is on top of a steep, smooth knoll near cliffs and the sea. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levenwick
Levenwick is a small village about south of Lerwick, on the east side of the South Mainland of Shetland, Scotland. It is part of the parish of Dunrossness and the Levenwick Health Centre provides medical support for the Dunrossness area.It contains a local hall that you can hire and a campsite.As well as a small Sandy beach that has otters at it In the literature of the isles, it is associated with George Stewart, author of the pioneering '' Shetland Fireside Tales'', who lived here in his youth. Today Levenwick is home to a number of artists, including Amy Moncrieff, Neil McLean, Anne Bain and James Bruce Thomason. It was also where musician Ian Bairnson grew up. Notable people Ian Bairnson Ian Bairnson (born 3 August 1953 as ''John Bairnson'') is a Scottish musician, best known for being one of the core members of The Alan Parsons Project. He is a multi-instrumentalist, who has played saxophone and keyboards, although he is best ... George Stewart Neil Mclean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |