|
Pseudocholinesterase Deficiency
Pseudocholinesterase deficiency is an autosomal recessive inherited blood plasma enzyme abnormality in which the body's production of butyrylcholinesterase (BCHE; pseudocholinesterase aka PCE) is impaired. People who have this abnormality may be sensitive to certain anesthetic drugs, including the muscle relaxants succinylcholine and mivacurium as well as other ester local anesthetics. Signs and symptoms The effects are varied depending on the particular drug given. When anesthetists administer standard doses of these anesthetic drugs to a person with pseudocholinesterase deficiency, the patient experiences prolonged paralysis of the respiratory muscles, requiring an extended period of time during which the patient must be mechanically ventilated. Eventually the muscle-paralyzing effects of these drugs will wear off despite the deficiency of the pseudocholinesterase enzyme. If the patient is maintained on a mechanical respirator until normal breathing function returns, there i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise require physical restraint in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * ''General anesthesia'' suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of Sensation (psychology), sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * ''Sedation'' suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiolysis, anxiety and creation of long-term memory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, a Guanine, G nucleotide present at a specific location in a reference genome may be replaced by an Adenine, A in a minority of individuals. The two possible nucleotide variations of this SNP – G or A – are called alleles. SNPs can help explain differences in susceptibility to a wide range of diseases across a population. For example, a common SNP in the Factor H, CFH gene is associated with increased risk of age-related macular degeneration. Differences in the severity of an illness or response to treatments may also be manifestations of genetic variations caused by SNPs. For example, two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
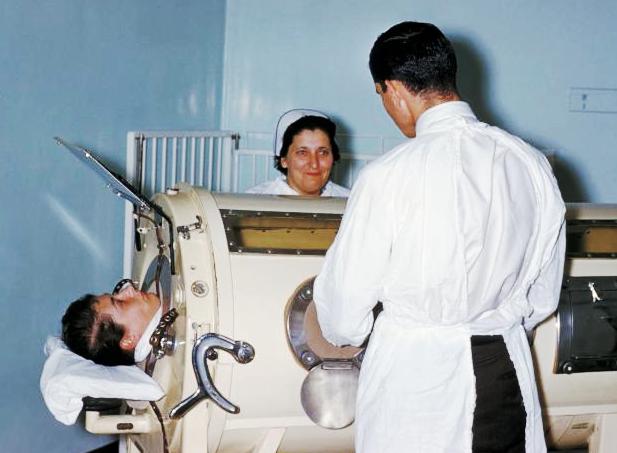
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal masks are used. The two main types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinylcholine
Suxamethonium chloride (brand names Scoline and Sucostrin, among others), also known as suxamethonium or succinylcholine, or simply sux in medical abbreviation, is a medication used to cause short-term paralysis as part of general anesthesia. This is done to help with tracheal intubation or electroconvulsive therapy. It is administered by injection, either intravenous, into a vein or intramuscular, into a muscle. When used in a vein, onset of action is generally within one minute and effects last for up to 10 minutes. Common side effects include low blood pressure, increased saliva production, muscle pain, and rash. Serious side effects include malignant hyperthermia, hyperkalemia and allergic reactions. It is not recommended in people who are at risk of high blood potassium or a history of myopathy. Use during pregnancy appears to be safe for the baby. Suxamethonium is in the neuromuscular-blocking drugs, neuromuscular blocker family of medications and is of the depolarizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetracaine
Tetracaine, also known as amethocaine, is an ester local anesthetic used to numb the eyes, nose, or throat. It may also be applied to the skin before starting intravenous therapy to decrease pain from the procedure. Typically it is applied as a liquid to the area. Onset of effects when used in the eyes is within 30 seconds and last for less than 15 minutes. Common side effects include a brief period of burning at the site of use. Allergic reactions may uncommonly occur. Long-term use is generally not recommended as it may slow healing of the eye. It is unclear if use during pregnancy is safe for the baby. Tetracaine is in the ester-type local anesthetic family of medications. It works by blocking the sending of nerve impulses. Tetracaine was patented in 1930 and came into medical use in 1941. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines Medical uses A systematic review investigated tetracaine for use in emergency departments, especially for starting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroprocaine
Chloroprocaine, sold under the brand name Nesacaine among others is a local anesthetic given by injection. It is used as the hydrochloride salt. Chloroprocaine is a local anesthetic. Medical uses Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine) is indicated for the production of local anesthesia by infiltration and peripheral nerve block; and for the production of local anesthesia by infiltration, peripheral and central nerve block, including lumbar and caudal epidural blocks. Chloroprocaine (Clorotekal) is indicated for intrathecal injection in adults for the production of subarachnoid block (spinal anesthesia). Chloroprocaine is used for regional anesthesia including spinal anesthesia, caudal anesthesia and epidural anesthesia. It is also indicated for local anesthesia including brachial plexus block, cervical nerve block, occipital nerve block. mandibular nerve block or maxillary nerve block for dental anesthesia, ophthalmic anesthesia via infraorbital nerve block, ulnar nerve block, para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procaine
Procaine is a local anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is most commonly used in dental procedures to numb the area around a tooth and is also used to reduce the pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin. Owing to the ubiquity of the trade name Novocain (without the "e" in the original German patent) or Novocaine (with the "e" in the US patent), in some regions, procaine is referred to generically as novocaine. It acts mainly as a sodium channel blocker. Today, it is used therapeutically in some countries due to its sympatholytic, anti-inflammatory, perfusion-enhancing, and mood-enhancing effects. Procaine was first synthesized in 1905, shortly after amylocaine. It was created by the chemist Alfred Einhorn who gave the chemical the trade name Novocain, from the Latin ''nov-'' (meaning "new") and ''-caine'', a common ending for alkaloids used as anesthetics. It was introduced into medical use by surgeon Heinrich Braun. Prior to the discovery of amylocaine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyrylcholine
Butyrylcholine is a choline-based ester that can function as a neurotransmitter. It is similar to acetylcholine, with activation of some of the same receptors as acetylcholine. Butyrylcholine is a synthetic compound and does not occur in the body naturally. Usage It is used as a clinical laboratory tool to distinguish between the cholinesterase The enzyme cholinesterase (EC 3.1.1.8, choline esterase; systematic name acylcholine acylhydrolase) catalyses the hydrolysis of choline-based esters: : an acylcholine + H2O = choline + a carboxylate Several of these serve as neurotransmitte ...s; acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase preferentially lyse acetylcholine and butyrylcholine, respectively. References Quaternary ammonium compounds Butyrate esters {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body's unconscious actions. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed-and-breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion, and defecation. Its action is described as being complementary to that of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for stimulating activities associated with the fight-or-flight response. Nerve fibres of the parasympathetic nervous system arise from the central nervous system. Specific nerves include several cranial nerves, specifically the oculomotor nerve, facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, and vagus nerve. Three spinal nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholinergic
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word " choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the ''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethylethanolammonium cation. Found in most animal tissues, choline is a primary component of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and functions with inositol as a basic constituent of lecithin. Choline also prevents fat deposits in the liver and facilitates the movement of fats into cells. The parasympathetic nervous system, which uses acetylcholine almost exclusively to send its messages, is said to be almost entirely cholinergic. Neuromuscular junctions, preganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, the basal forebrain, and brain stem complexes are also cholinergic, as are the receptor for the merocrine sweat glands. In neuroscience and related fields, the term cholinergic is used in these related contexts: * A substance (or ligand) is cholinergic if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule. Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), but they can also have insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs. Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function or amount of the gene product(s) they code or regulate for. However, sometimes different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation. A notable example of this is Gregor Mendel's discovery that the white and purple flower colors in pea plants were the result of a single gene with two alleles. Nearly all multicellular organisms have two sets of chromosomes at some point in their biological life cycle; that is, they are diploid. For a given locus, if the two chromosomes contain the same allele, they, and the organism, are homozygous with re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |