|
Primes In Arithmetic Progressions
In number theory, primes in arithmetic progression are any sequence of at least three prime numbers that are consecutive terms in an arithmetic progression. An example is the sequence of primes (3, 7, 11), which is given by a_n = 3 + 4n for 0 \le n \le 2. According to the Green–Tao theorem, there exist arbitrarily long arithmetic progressions in the sequence of primes. Sometimes the phrase may also be used about primes which belong to an arithmetic progression which also contains composite numbers. For example, it can be used about primes in an arithmetic progression of the form an + b, where ''a'' and ''b'' are coprime which according to Dirichlet's theorem on arithmetic progressions contains infinitely many primes, along with infinitely many composites. For any integer k\geq 3, an AP-''k'' (also called PAP-''k'') is any sequence of k primes in arithmetic progression. An AP-k can be written as k primes of the form an+b, for fixed integers a (called the common difference) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and arithmetic functions. Number theorists study prime numbers as well as the properties of mathematical objects constructed from integers (for example, rational numbers), or defined as generalizations of the integers (for example, algebraic integers). Integers can be considered either in themselves or as solutions to equations (Diophantine geometry). Questions in number theory can often be understood through the study of Complex analysis, analytical objects, such as the Riemann zeta function, that encode properties of the integers, primes or other number-theoretic objects in some fashion (analytic number theory). One may also study real numbers in relation to rational numbers, as for instance how irrational numbers can be approximated by fractions (Diophantine approximation). Number theory is one of the oldest branches of mathematics alongside geometry. One quirk of number theory is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexy Prime
In number theory, sexy primes are prime numbers that differ from each other by . For example, the numbers and are a pair of sexy primes, because both are prime and 11 - 5 = 6. The term "sexy prime" is a pun stemming from the Latin word for six: . If or (where is the lower prime) is also prime, then the sexy prime is part of a prime triplet. In August 2014, the Polymath group, seeking the proof of the twin prime conjecture, showed that if the generalized Elliott–Halberstam conjecture is proven, one can show the existence of infinitely many pairs of consecutive primes that differ by at most 6 and as such they are either twin, cousin A cousin is a relative who is the child of a parent's sibling; this is more specifically referred to as a first cousin. A parent of a first cousin is an aunt or uncle. More generally, in the kinship system used in the English-speaking world, ... or sexy primes. The sexy primes (sequences and in OEIS) below 500 are: :(5,11), (7,13) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Computing
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers. The components of a distributed system communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from SOA-based systems to microservices to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer applications. Distributed systems cost significantly more than monolithic architectures, primarily due to increased needs for additional hardware, servers, gateways, firewalls, new subnets, proxies, and so on. Also, distributed systems are prone to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanced Prime
In number theory, a balanced prime is a prime number with equal-sized prime gaps above and below it, so that it is equal to the arithmetic mean of the nearest primes above and below. Or to put it algebraically, the nth prime number p_n is a balanced prime if :p_n = . For example, 53 is the sixteenth prime; the fifteenth and seventeenth primes, 47 and 59, add up to 106, and half of that is 53; thus 53 is a balanced prime. Examples The first few balanced primes are 5, 53, 157, 173, 211, 257, 263, 373, 563, 593, 607, 653, 733, 947, 977, 1103, 1123, 1187, 1223, 1367, 1511, 1747, 1753, 1907, 2287, 2417, 2677, 2903 . Infinitude It is conjecture In mathematics, a conjecture is a conclusion or a proposition that is proffered on a tentative basis without proof. Some conjectures, such as the Riemann hypothesis or Fermat's conjecture (now a theorem, proven in 1995 by Andrew Wiles), ha ...d that there are infinitely many balanced primes. Three consecutive primes in arithm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
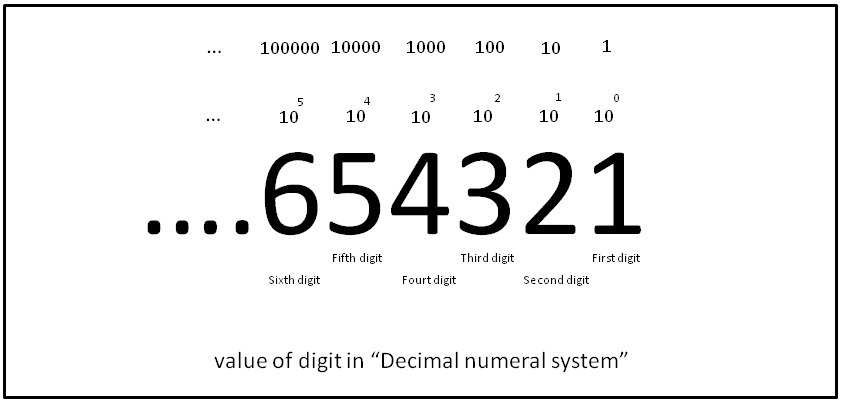
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duron
Duron is a line of budget x86-compatible microprocessors manufactured by Advanced Micro Devices, AMD and released on June 19, 2000. Duron was intended to be a lower-cost offering to complement AMD's then mainstream performance Athlon processor line, and it also competed with rival chipmaker Intel's Pentium III and Celeron processor offerings. The Duron brand name was retired in 2004, succeeded by AMD's Sempron line of processors as their budget offering. Performance The original Duron processors were derived from AMD's mainstream ''Athlon'' Athlon#Athlon Thunderbird, Thunderbird processors, the primary difference being a reduction in L2 cache size to 64 Binary prefix, KB from the Athlon's 256 KB. This was a relatively severe reduction, making it even smaller than the 128 KB L2 available on Intel's competing budget Celeron line. However, the originating Thunderbird architecture already featured one of the largest L1 caches at 128 KB (which was not reduced i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentium D
Pentium D is a range of desktop 64-bit x86-64 processors based on the NetBurst microarchitecture, which is the Multi-core processor, dual-core variant of the Pentium 4 manufactured by Intel. Each CPU comprised two cores. The brand's first processor, codenamed Smithfield and manufactured on the 90 nm process, was released on May 25, 2005, followed by the 65 nm Presler nine months later. The core implementation on the 90 nm Smithfield and later 65 nm Presler are designed differently but are functionally the same. The 90 nm Smithfield contains a single Die (integrated circuit), die, with two adjoined but functionally separate CPU cores cut from the same wafer (electronics), wafer. The later 65 nm Presler utilized a multi-chip module package, where two discrete dies each containing a single core reside on the CPU substrate. Neither the 90 nm Smithfield nor the 65 nm Presler were capable of direct core to core communication, relying instead on the Northbridge (computing), northbridge li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlon
AMD Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86, x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by AMD, Advanced Micro Devices. The original Athlon (now called Athlon Classic) was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and the first desktop processor to reach speeds of one gigahertz (GHz). It made its debut as AMD's high-end processor brand on June 23, 1999. Over the years AMD has used the Athlon name with the 64-bit Athlon 64 architecture, the Athlon II, and Accelerated Processing Unit (APU) chips targeting the Socket AM1 desktop System on a chip, SoC architecture, and Socket AM4 Zen (microarchitecture). The modern Zen-based Athlon with a Radeon, Radeon Graphics processor was introduced in 2019 as AMD's highest-performance entry-level processor. Brand history K7 design and development The first Athlon processor was a result of AMD's development of K7 processors in the 1990s. AMD founder and then-CEO Jerry Sanders (businessman), Jerry Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlon 64
The Athlon 64 is a ninth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name ''Athlon'', and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. The Athlon 64 was the second processor to implement the AMD64 architecture (after the Opteron) and the first 64-bit processor targeted at the average consumer. Variants of the Athlon 64 have been produced for Socket 754, Socket 939, Socket 940, and Socket AM2. It was AMD's primary consumer CPU, and primarily competed with Intel's Pentium 4, especially the ''Prescott'' and ''Cedar Mill'' core revisions. The Athlon 64 is AMD's first K8, eighth-generation processor core for desktop and mobile computers. Despite being natively 64-bit, the AMD64 architecture is backward-compatible with 32-bit x86 instructions. The Athlon 64 line was succeeded by the dual-core Athlon 64 X2 and Athlon X2 lines. Background The Athlon 64 was originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Microprocessor
The Cell Broadband Engine (Cell/B.E.) is a 64-bit multi-core processor and microarchitecture developed by Sony, Toshiba, and IBM—an alliance known as "STI". It combines a general-purpose PowerPC core, called the Power Processing Element (PPE), with multiple specialized coprocessors, known as Synergistic Processing Elements (SPEs), which accelerate tasks such as multimedia and vector processing. The architecture was developed over a four-year period beginning in March 2001, with Sony reporting a development budget of approximately . Its first major commercial application was in Sony's PlayStation 3 home video game console, released in 2006. In 2008, a modified version of the Cell processor powered IBM's Roadrunner, the first supercomputer to sustain one petaFLOPS. Other applications include high-performance computing systems from Mercury Computer Systems and specialized arcade system boards. Cell emphasizes memory coherence, power efficiency, and peak computational throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CUDA
In computing, CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a proprietary parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) that allows software to use certain types of graphics processing units (GPUs) for accelerated general-purpose processing, an approach called general-purpose computing on GPUs. CUDA was created by Nvidia in 2006. When it was first introduced, the name was an acronym for ''Compute Unified Device Architecture'', but Nvidia later dropped the common use of the acronym and now rarely expands it. CUDA is a software layer that gives direct access to the GPU's virtual instruction set and parallel computational elements for the execution of compute kernels. In addition to drivers and runtime kernels, the CUDA platform includes compilers, libraries and developer tools to help programmers accelerate their applications. CUDA is designed to work with programming languages such as C, C++, Fortran, Python and Julia. This accessibility makes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nvidia
Nvidia Corporation ( ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and incorporated in Delaware. Founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang (president and CEO), Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem, it designs and supplies graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interfaces (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing, and system on a chip units (SoCs) for mobile computing and the automotive market. Nvidia is also a leading supplier of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware and software. Nvidia outsources the manufacturing of the hardware it designs. Nvidia's professional line of GPUs are used for edge-to-cloud computing and in supercomputers and workstations for applications in fields such as architecture, engineering and construction, media and entertainment, automotive, scientific research, and manufacturing design. Its GeForce line of GPUs are aimed at the consumer market and are used in ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |