|
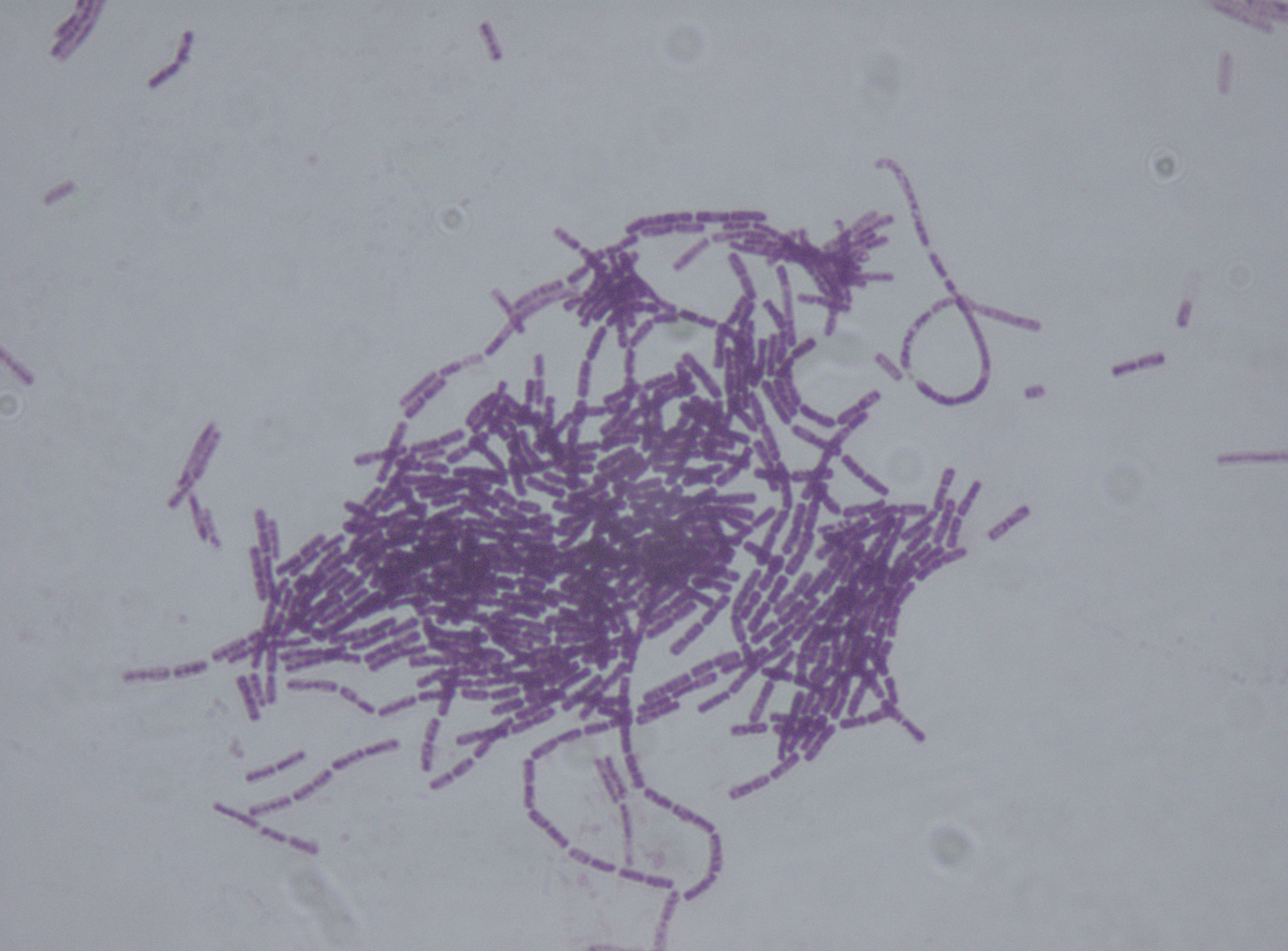
PlcR
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness due to their spore-forming nature, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals, and even exhibit mutualism with certain plants. ''B. cereus'' bacteria may be aerobes or facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus ''Bacillus'', can produce protective endospores. They have a wide range of virulence factors, including phospholipase C, cereulide, sphingomyelinase, metalloproteases, and cytotoxin K, many of which are regulated via quorum sensing. ''B. cereus'' strains exhibit flagellar motility. The ''Bacillus cereus'' group comprises seven closely related species: ''B. cereus'' ''sensu stricto'' (referred to herein as ''B. cereus''), '' B. anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Anthracis
''Bacillus anthracis'' is a gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium that causes anthrax, a deadly disease to livestock and, occasionally, to humans. It is the only permanent (obligate) pathogen within the genus ''Bacillus''. Its infection is a type of zoonosis, as it is transmitted from animals to humans. It was discovered by a German physician Robert Koch in 1876, and became the first bacterium to be experimentally shown as a pathogen. The discovery was also the first scientific evidence for the germ theory of diseases. ''B. anthracis'' measures about 3 to 5 μm long and 1 to 1.2 μm wide. The reference genome consists of a 5,227,419 bp circular chromosome and two extrachromosomal DNA plasmids, pXO1 and pXO2, of 181,677 and 94,830 bp respectively, which are responsible for the pathogenicity. It forms a protective layer called endospore by which it can remain inactive for many years and suddenly becomes infective under suitable environmental conditions. Because of the resilience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive bacteria, gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterfly, butterflies, as well as on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize moths such as ''Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During Endospore, sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have Insecticide, insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Genetically modified maize#Bt corn, Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strain (biology), strains, though, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agar Plate
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to Microbiological culture, culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics. Individual microorganisms placed on the plate will grow into individual colony (biology), colonies, each a cloning, clone genetically identical to the individual ancestor organism (except for the low, unavoidable rate of mutation). Thus, the plate can be used either to estimate the concentration of organisms in a Microbiological culture, liquid culture or a suitable dilution of that culture using a colony counter, or to generate genetically pure cultures from a mixed culture of genetically different organisms. Several methods are available to plate out cells. One technique is known as "Streaking (microbiology), streaking". In this technique, a drop of the culture on the end of a thin, sterilization (microbiology), sterile loop of wire, sometimes known as an inocu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxin K
Cytotoxin-K (CytK) is a protein toxin produced by the gram-positive bacteria ''Bacillus cereus''. It was first discovered in a certain ''Bacillus cereus'' strain which was isolated from a food poisoning epidemic that occurred in a French nursing home in 1998. There were six cases of bloody diarrhea, three of which were fatal. None of the known enterotoxins from ''B. cereus'' could be detected at this time. Later, this ''B. cereus'' strain and its relatives were classified as a brand-new species called Bacillus cytotoxicus, which is the thermo-tolerant member of the Bacillus genus. The cytotoxin-K gene is present in approximately 50% of ''Bacillus cereus'' isolates, and its expression is regulated by several factors, including temperature and nutrient availability. Further studies showed that Cytotoxin-K is a pore-forming toxin that can create small holes in cell membranes, leading to cell death. It has been shown to cause damage to intestinal epithelial cells, indicating its poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Sciences
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including observation, experimentation, and mathematical modeling. Modern biology is grounded in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |