|
Peripheral Chemoreceptor
Peripheral chemoreceptors (of the carotid and aortic bodies) are so named because they are sensory extensions of the peripheral nervous system into blood vessels where they detect changes in chemical concentrations. As transducers of patterns of variability in the surrounding environment, carotid and aortic bodies count as chemosensors in a similar way as taste buds and photoreceptors. However, because carotid and aortic bodies detect variation within the body's internal organs, they are considered interoceptors. Taste buds, olfactory bulbs, photoreceptors, and other receptors associated with the five traditional sensory modalities, by contrast, are exteroceptors in that they respond to stimuli outside the body. The body also contains proprioceptors, which respond to the amount of stretch within the organ, usually muscle, that they occupy. As for their particular function, peripheral chemoreceptors help maintain homeostasis in the cardiorespiratory system by monitoring concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
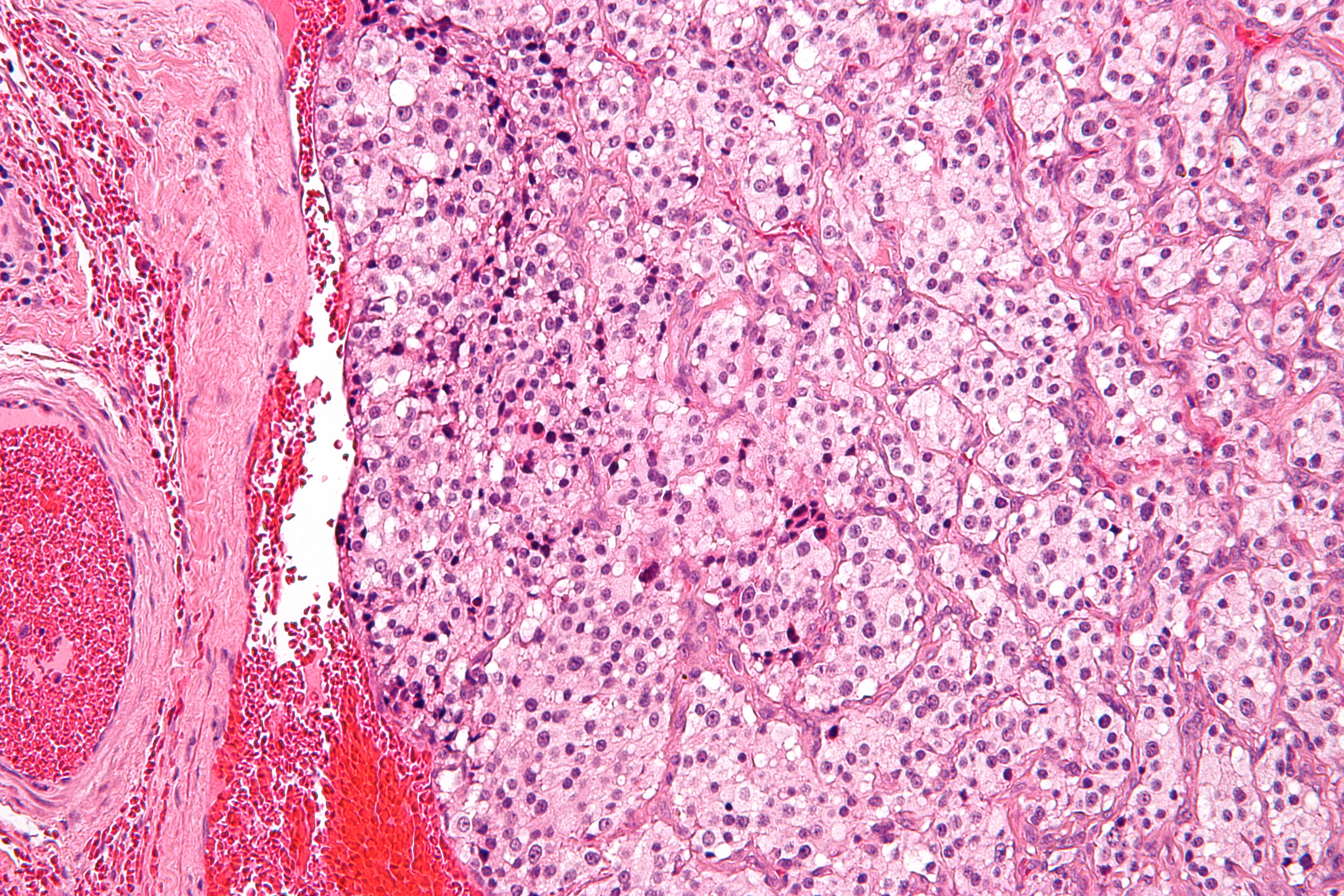
Carotid Body
The carotid body is a small cluster of peripheral chemoreceptor cells and supporting sustentacular cells situated at the bifurcation of each common carotid artery in its tunica externa. The carotid body detects changes in the composition of arterial blood flowing through it, mainly the partial pressure of arterial oxygen, but also of carbon dioxide. It is also sensitive to changes in blood pH, and temperature. Structure The carotid body is situated on the posterior aspect of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. The carotid body is made up of two types of cells, called glomus cells: glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors, and glomus type II cells are sustentacular supportive cells. * Glomus type I cells are derived from the neural crest. They release a variety of neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine, ATP, and dopamine that trigger EPSPs in synapsed neurons leading to the respiratory center. They are innervated by axons of the glossopharyngeal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of an adequate oxygen supply at the tissue (biology), tissue level. Hypoxia may be classified as either ''Generalized hypoxia, generalized'', affecting the whole body, or ''local'', affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological condition, variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise. Hypoxia differs from hypoxemia and anoxemia, in that hypoxia refers to a state in which oxygen present in a tissue or the whole body is insufficient, whereas hypoxemia and anoxemia refer specifically to states that have low or no Oxygen saturation (medicine), oxygen in the blood. Hypoxia in which there is complete absence of oxygen supply is referred to as anoxia. Hypoxia can be due to external causes, when the breathing gas is hypoxic, or internal causes, such as reduced effectiveness of gas transfer in the lung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the thorax, chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right Atrium (heart), atria and lower left and right Ventricle (heart), ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent cardiac regurgitation, backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
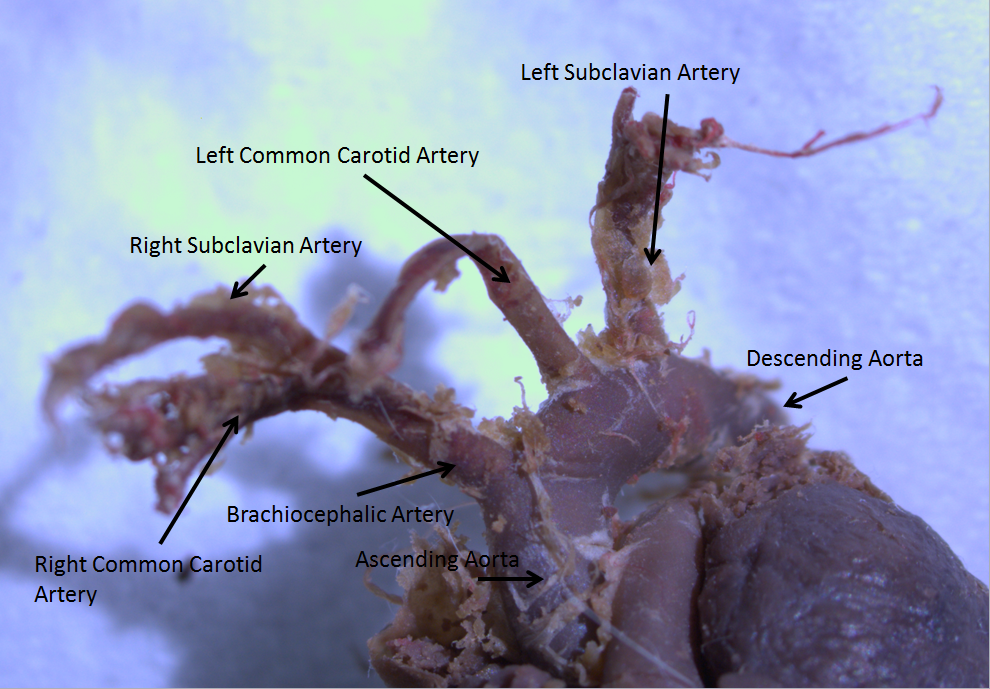
Aortic Arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea. Structure The aorta begins at the level of the upper border of the second/third sternocostal articulation of the right side, behind the ventricular outflow tract and pulmonary trunk. The right atrial appendage overlaps it. The first few centimeters of the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk lies in the same pericardial sheath and runs at first upward, arches over the pulmonary trunk, right pulmonary artery, and right main bronchus to lie behind the right second coastal cartilage. The right lung and sternum lies anterior to the aorta at this point. The aorta then passes posteriorly and to the left, anterior to the trachea, and arches over left main bronchus and left pulmonary artery, and reaches to the left side of the T4 vertebral body. Apart from T4 vertebral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture (Dalton's Law). In respiratory physiology, the partial pressure of a dissolved gas in liquid (such as oxygen in arterial blood) is also defined as the partial pressure of that gas as it would be undissolved in gas phase yet in equilibrium with the liquid. This concept is also known as blood gas tension. In this sense, the diffusion of a gas liquid is said to be driven by differences in partial pressure (not concentration). In chemistry and thermodynamics, this concept is generalized to non-ideal gases and instead called fugacity. The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of its Thermodynamic activity, thermodynamic activity. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Additionally, the neck is highly flexible, allowing the head to turn and move in all directions. Anatomically, the human neck is divided into four compartments: vertebral, visceral, and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae, the cervical portion of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. The muscles of the neck, which are separate from the compartments, form the boundaries of the neck triangles. In anatomy, the neck is also referred to as the or . However, when the term ''cervix'' is used alone, it often refers to the uterine cervix, the neck of the uterus. Therefore, the adjective ''cervical'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in the pulmonary circulation that carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the umbilical arteries in the fetal circulation that carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. It consists of a multi-layered artery wall wrapped into a tube-shaped channel. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry deoxygenated blood back towards the heart; or in the pulmonary and fetal circulations carry oxygenated blood to the lungs and fetus respectively. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic scale, macroscopic level, and histology, microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscope. The arterial system of the human body is divided into systemic circulation, systemic arteries, carrying blood from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand (biochemistry), ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a Cell signaling#Signaling pathways, signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription (biology), transcription or translation (biology), translation of genes, and post-translational modification, post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Body
The aortic bodies are one of several small clusters of peripheral chemoreceptors located along the aortic arch. They are important in measuring partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, and blood pH. Structure The aortic bodies are collections of chemoreceptors present on the aortic arch. Most are located above the aortic arch, while some are located on the posterior side of the aortic arch between it and the pulmonary artery below. They consist of glomus cells and sustentacular cells. Some sources equate the "aortic bodies" and " paraaortic bodies", while other sources explicitly distinguish between the two. When a distinction is made, the "aortic bodies" are chemoreceptors which regulate the circulatory system, while the "paraaortic bodies" are the chromaffin cells which manufacture catecholamines. Function The aortic bodies measure partial gas pressures and the composition of arterial blood flowing past it. These changes may include: * oxygen par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventilation (physiology)
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into ( inhalation) and out of ( exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or external respiration, brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where cellular respiration takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating heart and respiratory system, respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afferent Nerves
A sensory nerve, or afferent nerve, is a nerve that contains exclusively afferent nerve fibers. Nerves containing also motor fibers are called mixed. Afferent nerve fibers in a sensory nerve carry sensory information toward the central nervous system (CNS) from different sensory receptors of sensory neurons in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). A motor nerve carries information from the CNS to the PNS. Afferent nerve fibers link the sensory neurons throughout the body, in pathways to the relevant processing circuits in the central nervous system. Afferent nerve fibers are often paired with efferent nerve fibers from the motor neurons (that travel from the CNS to the PNS), in mixed nerves. Stimuli cause nerve impulses in the receptors and alter the potentials, which is known as sensory transduction. Spinal cord entry Afferent nerve fibers leave the sensory neuron from the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord, and motor commands carried by the efferent fibers leave the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |