Brainstem on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the

 The
The
Midbrain - superior colliculus.svg, Cross-section of the midbrain at the level of the superior colliculus
Midbrain - inferior colliculus.svg, Cross-section of the midbrain at the level of the inferior colliculus
Pons - Middle.svg, Cross-section of the middle pons (at the level of cranial nerve V)
Pons - Inferior.svg, Cross-section of the inferior pons (at the level of the facial genu)
Medulla - Rostral level cross section.svg, Cross-section of the rostral (superior) medulla
Medulla - Middle level cross section.svg, Cross-section of the middle medulla
Medulla - Inferior level cross section.svg, Cross-section of the inferior medulla
 In the medial part of the
In the medial part of the  The most medial part of the
The most medial part of the
 The main supply of blood to the brainstem is provided by the basilar arteries and the
The main supply of blood to the brainstem is provided by the basilar arteries and the
 Ten of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves either target or are sourced from the brainstem nuclei. The nuclei of the oculomotor nerve (III) and trochlear nerve (IV) are located in the midbrain. The nuclei of the trigeminal nerve (V), abducens nerve (VI), facial nerve (VII) and vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) are located in the pons. The nuclei of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), vagus nerve (X), accessory nerve (XI) and hypoglossal nerve (XII) are located in the medulla. The fibers of these cranial nerves exit the brainstem from these nuclei.
Ten of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves either target or are sourced from the brainstem nuclei. The nuclei of the oculomotor nerve (III) and trochlear nerve (IV) are located in the midbrain. The nuclei of the trigeminal nerve (V), abducens nerve (VI), facial nerve (VII) and vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) are located in the pons. The nuclei of the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), vagus nerve (X), accessory nerve (XI) and hypoglossal nerve (XII) are located in the medulla. The fibers of these cranial nerves exit the brainstem from these nuclei.
File:Human brain frontal (coronal) section description.JPG, The midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata are labelled on this coronal section of the human brain.
File:Human brainstem.gif, 3D visualization of the brainstem in an average human brain
 The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
that connects the cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb ...
with the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
. In the human brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the act ...
the brainstem is composed of the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
, the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Va ...
, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, ...
of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem.
The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating cardiac
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
, and respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gre ...
function, helping to control heart rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excr ...
and breathing rate
The respiratory rate is the rate at which breathing occurs; it is set and controlled by the respiratory center of the brain. A person's respiratory rate is usually measured in breaths per minute.
Measurement
The respiratory rate in humans is me ...
. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may aff ...
and neck via the cranial nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and f ...
. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
and the body's sleep cycle
The sleep cycle is an oscillation between the slow-wave and REM (paradoxical) phases of sleep. It is sometimes called the ultradian sleep cycle, sleep–dream cycle, or REM-NREM cycle, to distinguish it from the circadian alternation between sle ...
. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the body back to the brain. These pathways include the corticospinal tract
The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway starting at the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord, controlling movements of the limbs and trunk. There are more than one million neur ...
(motor function), the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal c ...
(fine touch
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch (haptic perception), as well as temperature (thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It i ...
, vibration sensation, and proprioception
Proprioception ( ), also referred to as kinaesthesia (or kinesthesia), is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. It is sometimes described as the "sixth sense".
Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, mechanosensory neurons ...
), and the spinothalamic tract
The spinothalamic tract is a part of the anterolateral system or the ventrolateral system, a sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory co ...
( pain, temperature, itch, and crude touch).
Structure
The parts of the brainstem are the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata, and sometimes the diencephalon.Midbrain

 The
The midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
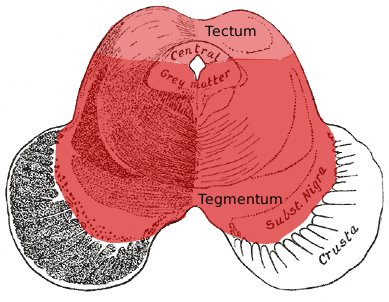
is further subdivided into three parts: tectum
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal ( alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
, tegmentum
The tegmentum (from Latin for "covering") is a general area within the brainstem. The tegmentum is the ventral part of the midbrain and the tectum is the dorsal part of the midbrain. It is located between the ventricular system and distinctive ba ...
, and the ventral tegmental area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is th ...
. The tectum
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal ( alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
forms the ceiling. The tectum comprises the paired structure of the superior and inferior colliculi
The inferior colliculus (IC) (Latin for ''lower hill'') is the principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex. Th ...
and is the dorsal covering of the cerebral aqueduct
The cerebral aqueduct (aqueductus mesencephali, mesencephalic duct, sylvian aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius) is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the br ...
. The inferior colliculus
The inferior colliculus (IC) (Latin for ''lower hill'') is the principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex. T ...
is the principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex. Its inferior brachium (arm-like process) reaches to the medial geniculate nucleus
The medial geniculate nucleus (MGN) or medial geniculate body (MGB) is part of the auditory thalamus and represents the thalamic relay between the inferior colliculus (IC) and the auditory cortex (AC). It is made up of a number of sub-nuclei that ...
of the diencephalon. The superior colliculus is positioned above the inferior colliculus, and marks the rostral midbrain. It is involved in the special sense of vision and sends its superior brachium to the lateral geniculate body
In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN; also called the lateral geniculate body or lateral geniculate complex) is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, ventral project ...
of the diencephalon.
The tegmentum
The tegmentum (from Latin for "covering") is a general area within the brainstem. The tegmentum is the ventral part of the midbrain and the tectum is the dorsal part of the midbrain. It is located between the ventricular system and distinctive ba ...
which forms the floor of the midbrain, is ventral to the cerebral aqueduct
The cerebral aqueduct (aqueductus mesencephali, mesencephalic duct, sylvian aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius) is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the br ...
. Several nuclei, tracts, and the reticular formation are contained here.
The ventral tegmental area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is th ...
(VTA) is composed of paired cerebral peduncle
The cerebral peduncles are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) nerve tract ...
s. These transmit axons of upper motor neuron
Upper motor neurons (UMNs) is a term introduced by William Gowers in 1886. They are found in the cerebral cortex and brainstem and carry information down to activate interneurons and lower motor neurons, which in turn directly signal muscles t ...
s.
Midbrain nuclei
The midbrain consists of: *Periaqueductal gray
The periaqueductal gray (PAG, also known as the central gray) is a brain region that plays a critical role in autonomic function, motivated behavior and behavioural responses to threatening stimuli. PAG is also the primary control center for d ...
: The area of gray matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is distingui ...
around the cerebral aqueduct
The cerebral aqueduct (aqueductus mesencephali, mesencephalic duct, sylvian aqueduct or aqueduct of Sylvius) is a conduit for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle of the ventricular system of the br ...
, which contains various neurons involved in the pain desensitization pathway. Neurons synapse here and, when stimulated, cause activation of neurons in the nucleus raphe magnus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
, which then project down into the posterior grey column
The posterior grey column (posterior cornu, dorsal horn, spinal dorsal horn, posterior horn, sensory horn) of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord. It receives several types of sensory information from the body, incl ...
of the spinal cord and prevent pain sensation transmission.
* Oculomotor nerve nucleus: This is the third cranial nerve nucleus
A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neurons (gray matter) in the brain stem that is associated with one or more of the cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei. Lesions ...
.
*Trochlear nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates just one muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye, which operates through the pu ...
nucleus: This is the fourth cranial nerve.
*Red nucleus
The red nucleus or nucleus ruber is a structure in the rostral midbrain involved in motor coordination. The red nucleus is pale pink, which is believed to be due to the presence of iron in at least two different forms: hemoglobin and ferritin. ...
: This is a motor nucleus that sends a descending tract to the lower motor neuron
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are motor neurons located in either the anterior grey column, anterior nerve roots (spinal lower motor neurons) or the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and cranial nerves with motor function (cranial nerve low ...
s.
* Substantia nigra pars compacta: This is a concentration of neurons in the ventral portion of the midbrain that uses dopamine as its neurotransmitter and is involved in both motor function and emotion. Its dysfunction is implicated in Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
.
* Reticular formation: This is a large area in the midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', " ...
that is involved in various important functions of the midbrain. In particular, it contains lower motor neurons, is involved in the pain desensitization pathway, is involved in the arousal and consciousness systems, and contains the locus coeruleus, which is involved in intensive alertness
Alertness is the state of active attention by high sensory awareness such as being watchful and prompt to meet danger or emergency, or being quick to perceive and act. It is related for psychology . A lack of alertness is a symptom of a ...
modulation and in autonomic reflexes.
*Central tegmental tract
The central tegmental tractKamali A, Kramer LA, Butler IJ, Hasan KM. Diffusion tensor tractography of the somatosensory system in the human brainstem: initial findings using high isotropic spatial resolution at 3.0 T. Eur Radiol. 2009 19:1480-8. do ...
: Directly anterior to the floor of the fourth ventricle
The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ve ...
, this is a pathway by which many tracts project up to the cortex and down to the spinal cord.
*Ventral tegmental area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is th ...
: A dopaminergic nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
, known as group A10 cells is located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain.
*Rostromedial tegmental nucleus The rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg), also known as the tail of the ventral tegmental area (tVTA), is a GABAergic nucleus which functions as a "master brake" for the midbrain dopamine system. It is poorly differentiated from the rest of the v ...
: A GABAergic nucleus located adjacent to the ventral tegmental area.
Pons
The pons lies between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata. It is separated from the midbrain by the superior pontine sulcus, and from the medulla by the inferior pontine sulcus. It contains tracts that carry signals from thecerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb ...
to the medulla and to the cerebellum and also tracts that carry sensory signals to the thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, ...
. The pons is connected to the cerebellum by the cerebellar peduncles. The pons houses the respiratory pneumotaxic center
The respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata and pons, in the brainstem. The respiratory center is made up of three major respiratory groups of neurons, two in the medulla and one in the pons. In the medulla they are the dorsal res ...
and apneustic center that make up the pontine respiratory group in the respiratory center
The respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata and pons, in the brainstem. The respiratory center is made up of three major respiratory groups of neurons, two in the medulla and one in the pons. In the medulla they are the dorsal ...
. The pons co-ordinates activities of the cerebellar hemispheres
The cerebellum consists of three parts, a median and two lateral, which are continuous with each other, and are substantially the same in structure. The median portion is constricted, and is called the vermis, from its annulated appearance which ...
.
The pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Va ...
and medulla oblongata are parts of the hindbrain
The hindbrain or rhombencephalon or lower brain is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephal ...
that form much of the brainstem.
Medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata, often just referred to as the medulla, is the lower half of the brainstem continuous with the spinal cord. Its upper part is continuous with the pons. The medulla contains thecardiac
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
, dorsal and ventral respiratory group
The respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata and pons, in the brainstem. The respiratory center is made up of three major respiratory groups of neurons, two in the medulla and one in the pons. In the medulla they are the dorsal r ...
s, and vasomotor
Vasomotor refers to actions upon a blood vessel which alter its diameter. More specifically, it can refer to vasodilator action and vasoconstrictor action.
Control Sympathetic innervation
Sympathetic nerve fibers travel around the tunica media of ...
centres, dealing with heart rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excr ...
, breathing and blood pressure. Another important medullary structure is the area postrema
The area postrema, a paired structure in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem, is a circumventricular organ having permeable capillaries and sensory neurons that enable its dual role to detect circulating chemical messengers in the blood and t ...
whose functions include the control of vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteri ...
.
Appearance
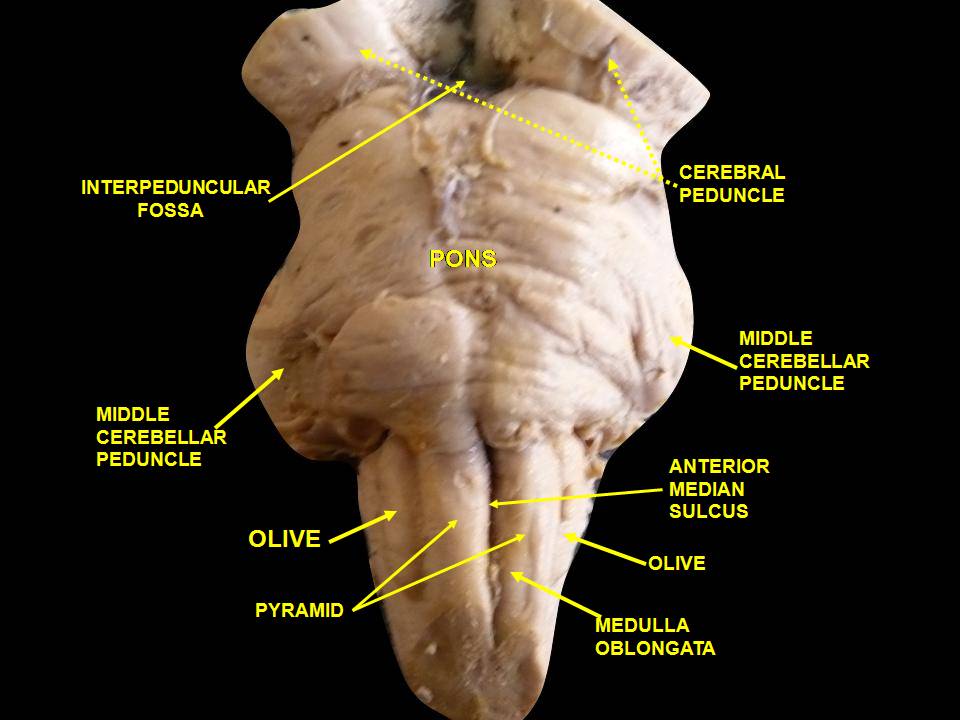
;From the frontmedulla
Medulla or Medullary may refer to:
Science
* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem
* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney
* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland
* Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary
* Medulla of t ...
is the anterior median fissure. Moving laterally on each side are the medullary pyramids. The pyramids contain the fibers of the corticospinal
The pyramidal tracts include both the corticobulbar tract and the corticospinal tract. These are aggregations of efferent nerve fibers from the upper motor neurons that travel from the cerebral cortex and terminate either in the brainstem (''co ...
tract (also called the pyramidal tract), or the upper motor neuronal axons as they head inferiorly to synapse on lower motor neuronal cell bodies within the anterior grey column
The anterior grey column (also called the anterior cornu, anterior horn of spinal cord, motor horn or ventral horn) is the front column of grey matter in the spinal cord. It is one of the three grey columns. The anterior grey column contains motor ...
of the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
.
The anterolateral sulcus is lateral to the pyramids. Emerging from the anterolateral sulci are the CN XII (hypoglossal nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by ...
) rootlets. Lateral to these rootlets and the anterolateral sulci are the olives
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' 'M ...
. The olives are swellings in the medulla containing underlying inferior nucleary nuclei (containing various nuclei and afferent fibers). Lateral (and dorsal) to the olives are the rootlets for CN IX (glossopharyngeal
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. B ...
), CN X (vagus
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right v ...
) and CN XI (accessory nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerv ...
). The pyramids end at the pontine medulla
Medulla or Medullary may refer to:
Science
* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem
* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney
* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland
* Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary
* Medulla of t ...
junction, noted most obviously by the large basal pons. From this junction, CN VI (abducens nerve
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocul ...
), CN VII (facial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste ...
) and CN VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the bra ...
) emerge. At the level of the midpons, CN V (the trigeminal nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve ( lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chew ...
) emerges. Cranial nerve III (the oculomotor nerve) emerges ventrally from the midbrain, while the CN IV (the trochlear nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates just one muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye, which operates through the pu ...
) emerges out from the dorsal aspect of the midbrain.
Between the two pyramids can be seen a decussation
Decussation is used in biological contexts to describe a crossing (due to the shape of the Roman numeral for ten, an uppercase 'X' (), ). In Latin anatomical terms, the form is used, e.g. .
Similarly, the anatomical term chiasma is named aft ...
of fibers which marks the transition from the medulla to the spinal cord. The medulla is above the decussation and the spinal cord below.
;From behind
medulla
Medulla or Medullary may refer to:
Science
* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem
* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney
* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland
* Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary
* Medulla of t ...
is the posterior median sulcus. Moving laterally on each side is the gracile fasciculus, and lateral to that is the cuneate fasciculus
Cuneate means "wedge-shaped", and can apply to:
* Cuneate leaf, a leaf shape
* Cuneate nucleus, a part of the brainstem
* Cuneate fasciculus
Cuneate means "wedge-shaped", and can apply to:
* Cuneate leaf
The following is a list of terms which ...
. Superior to each of these, and directly inferior to the obex
OBEX (abbreviation of OBject EXchange, also termed IrOBEX) is a communications protocol that facilitates the exchange of binary objects between devices. It is maintained by the Infrared Data Association but has also been adopted by the Bluetooth S ...
, are the gracile and cuneate tubercles, respectively. Underlying these are their respective nuclei. The obex marks the end of the fourth ventricle
The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ve ...
and the beginning of the central canal
The central canal (also known as spinal foramen or ependymal canal) is the cerebrospinal fluid-filled space that runs through the spinal cord. The central canal lies below and is connected to the ventricular system of the brain, from which it r ...
. The posterior intermediate sulcus separates the gracile fasciculus from the cuneate fasciculus. Lateral to the cuneate fasciculus is the lateral funiculus
The most lateral of the bundles of the anterior nerve roots is generally taken as a dividing line that separates the anterolateral system
The spinothalamic tract is a part of the anterolateral system or the ventrolateral system, a sensory path ...
.
Superior to the obex is the floor of the fourth ventricle. In the floor of the fourth ventricle, various nuclei can be visualized by the small bumps that they make in the overlying tissue. In the midline and directly superior to the obex is the vagal trigone
The cells of the dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve are spindle-shaped, like those of the posterior column of the spinal cord, and the nucleus is usually considered as representing the base of the posterior column. It measures about 2 cm. in lengt ...
and superior to that it the hypoglossal trigone
In the upper part of the medulla oblongata, the hypoglossal nucleus approaches the rhomboid fossa
The rhomboid fossa is a rhombus-shaped depression that is the anterior part of the fourth ventricle. Its anterior wall, formed by the back of the p ...
. Underlying each of these are motor nuclei for the respective cranial nerves. Superior to these trigones are fibers running laterally in both directions. These fibers are known collectively as the striae medullares. Continuing in a rostral direction, the large bumps are called the facial colliculi. Each facial colliculus
The facial colliculus is an elevated area located in the pontine tegmentum (dorsal pons), within the floor of the fourth ventricle (i.e. the rhomboid fossa). It is formed by fibres from the facial motor nucleus looping over the abducens nucleus. ...
, contrary to their names, do not contain the facial nerve nuclei. Instead, they have facial nerve axons traversing superficial to underlying abducens (CN VI) nuclei. Lateral to all these bumps previously discussed is an indented line, or sulcus that runs rostrally, and is known as the sulcus limitans
The sulcus limitans is found in the fourth ventricle of the brain. It separates the cranial nerve motor nuclei (medial) from the sensory nuclei (lateral).Nolte, John. The Human Brain 6th ed. p.685. Mosby Inc. It can also be located by searching ...
. This separates the medial motor neurons from the lateral sensory neurons. Lateral to the sulcus limitans is the area of the vestibular system, which is involved in special sensation. Moving rostrally, the inferior, middle, and superior cerebellar peduncles are found connecting the midbrain to the cerebellum. Directly rostral to the superior cerebellar peduncle, there is the superior medullary velum and then the two trochlear nerves. This marks the end of the pons as the inferior colliculus
The inferior colliculus (IC) (Latin for ''lower hill'') is the principal midbrain nucleus of the auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex. T ...
is directly rostral and marks the caudal midbrain. Middle cerebellar peduncle is located inferior and lateral to the superior cerebellar peduncle, connecting pons to the cerebellum. Likewise, inferior cerebellar peduncle is found connecting the medulla oblongata to the cerebellum.
Blood supply
 The main supply of blood to the brainstem is provided by the basilar arteries and the
The main supply of blood to the brainstem is provided by the basilar arteries and the vertebral arteries
The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline ...
.
Development
The human brainstem emerges from two of the threeprimary brain vesicles
Brain vesicles are the bulge-like features of the early development of the neural tube in vertebrates. Vesicle formation begins shortly after anterior neural tube closure at about embryonic day 9.0 in the mouse and the fourth and fifth gestational ...
formed of the neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, ...
. The mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "m ...
is the second of the three primary vesicles, and does not further differentiate into a secondary brain vesicle. This will become the midbrain. The third primary vesicle, the rhombencephalon
The hindbrain or rhombencephalon or lower brain is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates. It includes the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. Together they support vital bodily processes. Metencephal ...
(hindbrain) will further differentiate into two secondary vesicles, the metencephalon
The metencephalon is the embryonic part of the hindbrain that differentiates into the pons and the cerebellum. It contains a portion of the fourth ventricle and the trigeminal nerve (CN V), abducens nerve (CN VI), facial nerve (CN VII), and a port ...
and the myelencephalon
The myelencephalon or afterbrain is the most posterior region of the embryonic hindbrain, from which the medulla oblongata develops.
Development
Neural tube to myelencephalon
During fetal development, divisions of the neural tube that give ...
. The metencephalon will become the cerebellum and the pons. The more caudal myelencephalon will become the medulla
Medulla or Medullary may refer to:
Science
* Medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem
* Renal medulla, a part of the kidney
* Adrenal medulla, a part of the adrenal gland
* Medulla of ovary, a stroma in the center of the ovary
* Medulla of t ...
.
Function
There are three main functions of the brainstem: # The brainstem plays a role in conduction. That is, all information relayed from the body to the cerebrum and cerebellum and vice versa must traverse the brainstem. The ascending pathways coming from the body to the brain are the sensory pathways and include thespinothalamic tract
The spinothalamic tract is a part of the anterolateral system or the ventrolateral system, a sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory co ...
for pain and temperature sensation and the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal c ...
(DCML) including the gracile fasciculus and the cuneate fasciculus
Cuneate means "wedge-shaped", and can apply to:
* Cuneate leaf, a leaf shape
* Cuneate nucleus, a part of the brainstem
* Cuneate fasciculus
Cuneate means "wedge-shaped", and can apply to:
* Cuneate leaf
The following is a list of terms which ...
for touch, proprioception
Proprioception ( ), also referred to as kinaesthesia (or kinesthesia), is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. It is sometimes described as the "sixth sense".
Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, mechanosensory neurons ...
, and pressure sensation. The facial sensations have similar pathways and will travel in the spinothalamic tract and the DCML. Descending tracts are the axons of upper motor neurons destined to synapse on lower motor neurons in the ventral horn and posterior horn. In addition, there are upper motor neurons that originate in the brainstem's vestibular, red, tectal, and reticular nuclei, which also descend and synapse in the spinal cord.
# The cranial nerves III-XII emerge from the brainstem. These cranial nerves supply the face, head, and viscera. (The first two pairs of cranial nerves arise from the cerebrum).
# The brainstem has integrative functions being involved in cardiovascular system control, respiratory control, pain sensitivity control, alertness, awareness, and consciousness. Thus, brainstem damage is a very serious and often life-threatening problem.
Cranial nerves
Clinical significance
Diseases of the brainstem can result in abnormalities in the function of cranial nerves that may lead to visual disturbances, pupil abnormalities, changes in sensation, muscle weakness, hearing problems, vertigo, swallowing and speech difficulty, voice change, and co-ordination problems. Localizing neurological lesions in the brainstem may be very precise, although it relies on a clear understanding on the functions of brainstem anatomical structures and how to test them. Brainstem stroke syndrome can cause a range of impairments includinglocked-in syndrome
Locked-in syndrome (LIS), also known as pseudocoma, is a condition in which a patient is aware but cannot move or communicate verbally due to complete paralysis of nearly all voluntary muscles in the body except for vertical eye movements and bli ...
.
Duret haemorrhages are areas of bleeding in the midbrain and upper pons due to a downward traumatic displacement of the brainstem.
Cysts known as syrinxes can affect the brainstem, in a condition, called syringobulbia. These fluid-filled cavities can be congenital, acquired or the result of a tumor.
Criteria for claiming brainstem death in the UK have developed in order to make the decision of when to stop ventilation of somebody who could not otherwise sustain life. These determining factors are that the patient is irreversibly unconscious and incapable of breathing unaided. All other possible causes must be ruled out that might otherwise indicate a temporary condition. The state of irreversible brain damage has to be unequivocal. There are brainstem reflexes that are checked for by two senior doctors so that imaging technology
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
is unnecessary. The absence of the cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three ph ...
and gag reflex The pharyngeal reflex or gag reflex is a reflex muscular contraction of the back of the throat, evoked by touching the roof of the mouth, the back of the tongue, the area around the tonsils, the uvula, and the back of the throat. It, along with ot ...
es, of the corneal reflex
The corneal reflex, also known as the blink reflex or eyelid reflex, is an involuntary blinking of the eyelids elicited by stimulation of the cornea (such as by touching or by a foreign body), though it could result from any peripheral stimulus. S ...
and the vestibulo–ocular reflex
The vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is a reflex acting to stabilize gaze during head movement, with eye movement due to activation of the vestibular system. The reflex acts to stabilize images on the retinas of the eye during head movement. Gaze ...
need to be established; the pupils of the eyes must be fixed and dilated; there must be an absence of motor response to stimulation and an absence of breathing marked by concentrations of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood. All of these tests must be repeated after a certain time before death can be declared.Black's Medical Dictionary 39th edition 1999
Additional images
See also
*Triune brain
The triune brain is a model of the evolution of the vertebrate forebrain and behavior, proposed by the American physician and neuroscientist Paul D. MacLean in the 1960s. The triune brain consists of the reptilian complex (basal ganglia), the p ...
- reptilian brain
References
External links
* Comparative Neuroscience atWikiversity
Wikiversity is a Wikimedia Foundation project that supports learning communities, their learning materials, and resulting activities. It differs from Wikipedia in that it offers tutorials and other materials for the fostering of learning, rather ...
{{Authority control
Neurophysiology