|
Oncogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and organs. According to the prevailing accepted theory of carcinogenesis, the somatic mutation theory, mutations in DNA and epimutations that lead to cancer disrupt these orderly processes by interfering with the programming regulating the processes, upsetting the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells by natural selection in the body. Only certain mutations lead to cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Transformation
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as ''malignant degeneration'' of a previously existing benign tumor. Causes There are many causes of primary malignant transformation, or tumorigenesis. Most human cancers in the United States are caused by external factors, and these factors are largely avoidable. These factors were summarized by Doll and Peto in 1981, and were still considered to be valid in 2015. These factors are listed in the table. a Reproductive and sexual behaviors include: number of partners; age at first menstruation; zero versus one or more live births Examples of diet-related malignant transformation Diet and colon cancer Colon cancer provides one example of the mechanisms by which diet, the top factor listed in the table, is an external factor in cancer. The Western diet of African Americans in the United States is associated with a ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
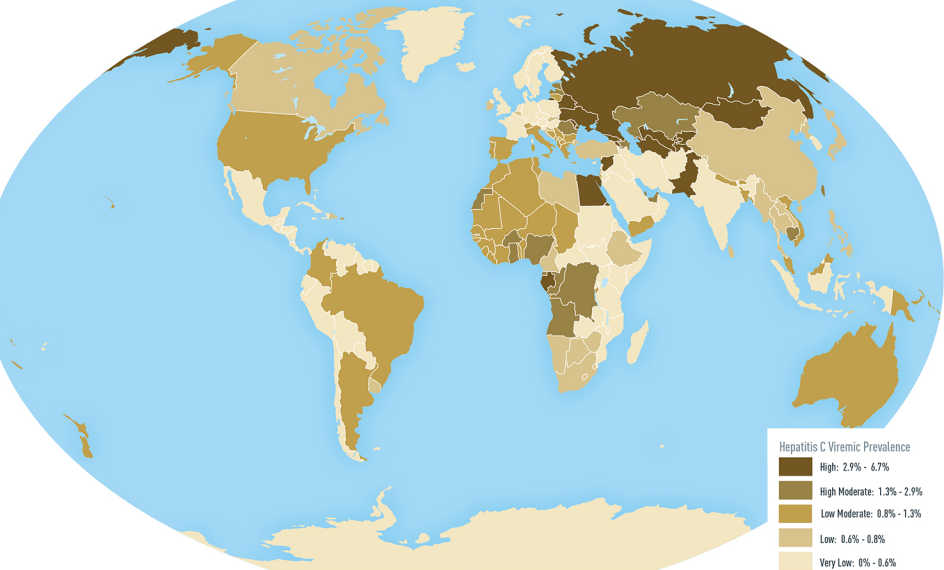
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified in Cell (biology), cells, by internal metabolism, metabolic by-products, and by external ionizing radiation, ultraviolet light, and medicines, resulting in spontaneous DNA damage involving tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. DNA modifications can also be programmed. Molecular lesions can cause structural damage to the DNA molecule, and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability for Transcription (biology), transcription and gene expression. Other lesions may induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells following mitosis. Consequently, DNA repair as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) is constantly active. When normal repair proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Suppressor Gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell (biology), cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or reduction in its function. In combination with other genetic mutations, this could allow the cell to grow abnormally. The Loss-of-function mutation, loss of function for these genes may be even more significant in the development of human cancers, compared to the activation of oncogenes. TSGs can be grouped into the following categories: caretaker genes, gatekeeper genes, and more recently landscaper genes. Caretaker genes ensure stability of the genome via DNA repair and subsequently when mutated allow mutations to accumulate. Meanwhile, gatekeeper genes directly regulate cell growth by either inhibiting cell cycle progression or inducing apoptosis. Lastly, landscaper genes regulate growth by contributing to the surrounding e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Requires Multiple Mutations From NIHen
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor causing approximately 16–18% of cancers worldwide. These infectious agents include '' Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HPV, Epstein–Barr virus, Human T-lymphotropic virus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogenes
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.Kimball's Biology Pages. "Oncogenes" Free full text Most normal cells undergo a preprogrammed rapid cell death () if critical functions are altered and then malfunction. Activated oncogenes can cause those cells designated for apoptosis to survive and proliferate instead. Most oncogenes began as proto-oncogenes: normal genes involved in cell growth and proliferation or inhibition of apoptosis. If, through mutation, normal genes promoting cellular growth are up-regulated (gain-of-function mutation), they predispose the cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncovirus
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term ''oncornaviruses'' was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the letters ''RNA'' removed, it now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with ''tumor virus'' or ''cancer virus''. The vast majority of human and animal viruses do not cause cancer, probably because of longstanding co-evolution between the virus and its host. Oncoviruses have been important not only in epidemiology, but also in investigations of cell cycle control mechanisms such as the retinoblastoma protein. The World Health Organization's International Agency for Research on Cancer estimated that in 2002, infection caused 17.8% of human cancers, with 11.9% caused by one of seven viruses. A 2020 study of 2,658 samples from 38 different types of cancer found that 16% were associated with a virus. These ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.Kimball's Biology Pages. "Oncogenes" Free full text Most normal cells undergo a preprogrammed rapid cell death () if critical functions are altered and then malfunction. Activated oncogenes can cause those cells designated for apoptosis to survive and proliferate instead. Most oncogenes began as proto-oncogenes: normal genes involved in cell growth and proliferation or inhibition of apoptosis. If, through mutation, normal genes promoting cellular growth are up-regulated (gain-of-function mutation), they predispose the cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, a G nucleotide present at a specific location in a reference genome may be replaced by an A in a minority of individuals. The two possible nucleotide variations of this SNP – G or A – are called alleles. SNPs can help explain differences in susceptibility to a wide range of diseases across a population. For example, a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of age-related macular degeneration. Differences in the severity of an illness or response to treatments may also be manifestations of genetic variations caused by SNPs. For example, two common SNPs in the ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genes
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |