Oncovirus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming
 Tumor viruses come in a variety of forms: Viruses with a DNA
Tumor viruses come in a variety of forms: Viruses with a DNA
 A direct oncogenic viral mechanism involves either insertion of additional viral oncogenic genes into the host cell or to enhance already existing oncogenic genes ( proto-oncogenes) in the genome. For example, it has been shown that vFLIP and vCyclin interfere with the TGF-β signaling pathway indirectly by inducing oncogenic host mir17-92 cluster.
Indirect viral oncogenicity involves chronic nonspecific inflammation occurring over decades of infection, as is the case for HCV-induced liver cancer. These two mechanisms differ in their biology and epidemiology: direct tumor viruses must have at least one virus copy in every tumor cell expressing at least one protein or RNA that is causing the cell to become cancerous. Because foreign virus
A direct oncogenic viral mechanism involves either insertion of additional viral oncogenic genes into the host cell or to enhance already existing oncogenic genes ( proto-oncogenes) in the genome. For example, it has been shown that vFLIP and vCyclin interfere with the TGF-β signaling pathway indirectly by inducing oncogenic host mir17-92 cluster.
Indirect viral oncogenicity involves chronic nonspecific inflammation occurring over decades of infection, as is the case for HCV-induced liver cancer. These two mechanisms differ in their biology and epidemiology: direct tumor viruses must have at least one virus copy in every tumor cell expressing at least one protein or RNA that is causing the cell to become cancerous. Because foreign virus
 DNA oncoviruses typically impair two families of tumor suppressor proteins: tumor proteins p53 and the retinoblastoma proteins (Rb). It is evolutionarily advantageous for viruses to inactivate p53 because p53 can trigger cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in infected cells when the virus attempts to replicate its DNA. Similarly, Rb proteins regulate many essential cell functions, including but not limited to a crucial cell cycle checkpoint, making them a target for viruses attempting to interrupt regular cell function.
While several DNA oncoviruses have been discovered, three have been studied extensively. Adenoviruses can lead to tumors in rodent models but do not cause cancer in humans; however, they have been exploited as delivery vehicles in gene therapy for diseases such as cystic fibrosis and cancer. Simian virus 40 (SV40), a polyomavirus, can cause tumors in rodent models but is not oncogenic in humans. This phenomenon has been one of the major controversies of oncogenesis in the 20th century because an estimated 100 million people were inadvertently exposed to SV40 through polio vaccines. The
DNA oncoviruses typically impair two families of tumor suppressor proteins: tumor proteins p53 and the retinoblastoma proteins (Rb). It is evolutionarily advantageous for viruses to inactivate p53 because p53 can trigger cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in infected cells when the virus attempts to replicate its DNA. Similarly, Rb proteins regulate many essential cell functions, including but not limited to a crucial cell cycle checkpoint, making them a target for viruses attempting to interrupt regular cell function.
While several DNA oncoviruses have been discovered, three have been studied extensively. Adenoviruses can lead to tumors in rodent models but do not cause cancer in humans; however, they have been exploited as delivery vehicles in gene therapy for diseases such as cystic fibrosis and cancer. Simian virus 40 (SV40), a polyomavirus, can cause tumors in rodent models but is not oncogenic in humans. This phenomenon has been one of the major controversies of oncogenesis in the 20th century because an estimated 100 million people were inadvertently exposed to SV40 through polio vaccines. The

 The main viruses associated with human cancers are the
The main viruses associated with human cancers are the
 The theory that cancer could be caused by a virus began with the experiments of Oluf Bang and Vilhelm Ellerman in 1908 at the
The theory that cancer could be caused by a virus began with the experiments of Oluf Bang and Vilhelm Ellerman in 1908 at the
 Between 1984 and 1986
Between 1984 and 1986
 An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptas ...
es in the 1950–60s, when the term "oncornaviruses" was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the letters "RNA" removed, it now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with "tumor virus" or "cancer virus". The vast majority of human and animal viruses do not cause cancer, probably because of longstanding co-evolution between the virus and its host. Oncoviruses have been important not only in epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evi ...
, but also in investigations of cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
control mechanisms such as the retinoblastoma protein.
The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
's International Agency for Research on Cancer
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC; french: Centre International de Recherche sur le Cancer, CIRC) is an intergovernmental agency forming part of the World Health Organization of the United Nations.
Its role is to conduct and ...
estimated that in 2002, infection caused 17.8% of human cancers, with 11.9% caused by one of seven viruses. A 2020 study of 2,658 samples from 38 different types of cancer found that 16% were associated with a virus. These cancers might be easily prevented through vaccination (e.g., papillomavirus vaccines), diagnosed with simple blood tests, and treated with less-toxic antiviral compounds.
Causality
Generally, tumor viruses cause little or no disease after infection in their hosts, or cause non- neoplastic diseases such as acute hepatitis for hepatitis B virus or mononucleosis forEpstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
It is ...
. A minority of persons (or animals) will go on to develop cancers after infection. This has complicated efforts to determine whether or not a given virus causes cancer. The well-known Koch's postulates, 19th-century constructs developed by Robert Koch to establish the likelihood that '' Bacillus anthracis'' will cause anthrax
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The s ...
disease, are not applicable to viral diseases. Firstly, this is because viruses cannot truly be isolated in pure culture—even stringent isolation techniques cannot exclude undetected contaminating viruses with similar density characteristics, and viruses must be grown on cells. Secondly, asymptomatic virus infection and carriage is the norm for most tumor viruses, which violates Koch's third principle. Relman and Fredericks have described the difficulties in applying Koch's postulates to virus-induced cancers. Finally, the host restriction for human viruses makes it unethical to experimentally transmit a suspected cancer virus. Other measures, such as A. B. Hill's criteria, are more relevant to cancer virology but also have some limitations in determining causality.
genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
, such as adenovirus, and viruses with an RNA genome, like the hepatitis C virus (HCV), can cause cancers, as can retroviruses having both DNA and RNA genomes (Human T-lymphotropic virus
The human T-lymphotropic virus, human T-cell lymphotropic virus, or human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus (HTLV) family of viruses are a group of human retroviruses that are known to cause a type of cancer called adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and ...
and hepatitis B virus, which normally replicates as a mixed double and single-stranded DNA virus but also has a retroviral replication component). In many cases, tumor viruses do not cause cancer in their native hosts but only in dead-end species. For example, adenoviruses do not cause cancer in humans but are instead responsible for colds, conjunctivitis and other acute illnesses. They only become tumorigenic when infected into certain rodent species, such as Syrian hamsters. Some viruses are tumorigenic when they infect a cell and persist as circular episomes or plasmids, replicating separately from host cell DNA (Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
It is ...
and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus). Other viruses are only carcinogenic when they integrate into the host cell genome as part of a biological accident, such as polyomaviruses and papillomaviruses.
Oncogenic viral mechanism
 A direct oncogenic viral mechanism involves either insertion of additional viral oncogenic genes into the host cell or to enhance already existing oncogenic genes ( proto-oncogenes) in the genome. For example, it has been shown that vFLIP and vCyclin interfere with the TGF-β signaling pathway indirectly by inducing oncogenic host mir17-92 cluster.
Indirect viral oncogenicity involves chronic nonspecific inflammation occurring over decades of infection, as is the case for HCV-induced liver cancer. These two mechanisms differ in their biology and epidemiology: direct tumor viruses must have at least one virus copy in every tumor cell expressing at least one protein or RNA that is causing the cell to become cancerous. Because foreign virus
A direct oncogenic viral mechanism involves either insertion of additional viral oncogenic genes into the host cell or to enhance already existing oncogenic genes ( proto-oncogenes) in the genome. For example, it has been shown that vFLIP and vCyclin interfere with the TGF-β signaling pathway indirectly by inducing oncogenic host mir17-92 cluster.
Indirect viral oncogenicity involves chronic nonspecific inflammation occurring over decades of infection, as is the case for HCV-induced liver cancer. These two mechanisms differ in their biology and epidemiology: direct tumor viruses must have at least one virus copy in every tumor cell expressing at least one protein or RNA that is causing the cell to become cancerous. Because foreign virus antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
s are expressed in these tumors, persons who are immunosuppressed such as AIDS or transplant patients are at higher risk for these types of cancers.
Chronic indirect tumor viruses, on the other hand, can be lost (at least theoretically) from a mature tumor that has accumulated sufficient mutations and growth conditions (hyperplasia) from the chronic inflammation of viral infection. In this latter case, it is controversial but at least theoretically possible that an indirect tumor virus could undergo "hit-and-run" and so the virus would be lost from the clinically diagnosed tumor. In practical terms, this is an uncommon occurrence if it does occur.
DNA oncoviruses
 DNA oncoviruses typically impair two families of tumor suppressor proteins: tumor proteins p53 and the retinoblastoma proteins (Rb). It is evolutionarily advantageous for viruses to inactivate p53 because p53 can trigger cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in infected cells when the virus attempts to replicate its DNA. Similarly, Rb proteins regulate many essential cell functions, including but not limited to a crucial cell cycle checkpoint, making them a target for viruses attempting to interrupt regular cell function.
While several DNA oncoviruses have been discovered, three have been studied extensively. Adenoviruses can lead to tumors in rodent models but do not cause cancer in humans; however, they have been exploited as delivery vehicles in gene therapy for diseases such as cystic fibrosis and cancer. Simian virus 40 (SV40), a polyomavirus, can cause tumors in rodent models but is not oncogenic in humans. This phenomenon has been one of the major controversies of oncogenesis in the 20th century because an estimated 100 million people were inadvertently exposed to SV40 through polio vaccines. The
DNA oncoviruses typically impair two families of tumor suppressor proteins: tumor proteins p53 and the retinoblastoma proteins (Rb). It is evolutionarily advantageous for viruses to inactivate p53 because p53 can trigger cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in infected cells when the virus attempts to replicate its DNA. Similarly, Rb proteins regulate many essential cell functions, including but not limited to a crucial cell cycle checkpoint, making them a target for viruses attempting to interrupt regular cell function.
While several DNA oncoviruses have been discovered, three have been studied extensively. Adenoviruses can lead to tumors in rodent models but do not cause cancer in humans; however, they have been exploited as delivery vehicles in gene therapy for diseases such as cystic fibrosis and cancer. Simian virus 40 (SV40), a polyomavirus, can cause tumors in rodent models but is not oncogenic in humans. This phenomenon has been one of the major controversies of oncogenesis in the 20th century because an estimated 100 million people were inadvertently exposed to SV40 through polio vaccines. The human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
-16 (HPV-16) has been shown to lead to cervical cancer and other cancers, including head and neck cancer. These three viruses have parallel mechanisms of action, forming an archetype for DNA oncoviruses. All three of these DNA oncoviruses are able to integrate their DNA into the host cell, and use this to transcribe it and transform cells by bypassing the G1/S checkpoint of the cell cycle.
Integration of viral DNA
DNA oncoviruses transform infected cells by integrating their DNA into the host cell's genome. The DNA is believed to be inserted during transcription or replication, when the two annealed strands are separated. This event is relatively rare and generally unpredictable; there seems to be no deterministic predictor of the site of integration. After integration, the host's cell cycle loses regulation from Rb and p53, and the cell begins cloning to form a tumor.G1/S Checkpoint
Rb and p53 regulate the transition between G1 andS phase
S phase (Synthesis Phase) is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Since accurate duplication of the genome is critical to successful cell division, the processes that occur during ...
, arresting the cell cycle before DNA replication until the appropriate checkpoint inputs, such as DNA damage repair, are completed. p53 regulates the p21 gene, which produces a protein which binds to the Cyclin D-Cdk4/6 complex. This prevents Rb phosphorylation and prevents the cell from entering S phase. In mammals, when Rb is active (unphosphorylated), it inhibits the E2F
E2F is a group of genes that encodes a family of transcription factors (TF) in higher eukaryotes. Three of them are activators: E2F1, 2 and E2F3a. Six others act as suppressors: E2F3b, E2F4-8. All of them are involved in the cell cycle regulation a ...
family of transcription factors, which regulate the Cyclin E
Cyclin E is a member of the cyclin family.
Cyclin E binds to G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase of the cell cycle that determines initiation of DNA duplication. The Cyclin E/CDK2 complex phosphorylates p27 ...
- Cdk2 complex, which inhibits Rb, forming a positive feedback loop, keeping the cell in G1 until the input crosses a threshold. To drive the cell into S phase prematurely, the viruses must inactivate p53, which plays a central role in the G1/S checkpoint, as well as Rb, which, though downstream of it, is typically kept active by a positive feedback loop.
Inactivation of p53
Viruses employ various methods of inactivating p53. The adenovirus E1B protein (55K) prevents p53 from regulating genes by binding to the site on p53 which binds to the genome. In SV40, thelarge T antigen
The large tumor antigen (also called the large T-antigen and abbreviated LTag or LT) is a protein encoded in the genomes of polyomaviruses, which are small double-stranded DNA viruses. LTag is expressed early in the infectious cycle and is ess ...
(LT) is an analogue; LT also binds to several other cellular proteins, such as p107 and p130, on the same residues. LT binds to p53's binding domain on the DNA (rather than on the protein), again preventing p53 from appropriately regulating genes. HPV instead degrades p53: the HPV protein E6 binds to a cellular protein called the E6-associated protein (E6-AP, also known as UBE3A), forming a complex which causes the rapid and specific ubiquitination of p53.
Inactivation of Rb
Rb is inactivated (thereby allowing the G1/S transition to progress unimpeded) by different but analogous viral oncoproteins. Theadenovirus early region 1A Adenovirus early region 1A (''E1A'') is a gene expressed during adenovirus replication to produce a variety of E1A proteins. It is expressed during the early phase of the viral life span.
''E1A'' encodes two major proteins in Ad5, translated after ...
(E1A) is an oncoprotein which binds to Rb and can stimulate transcription and transform cells. SV40 uses the same protein for inactivating Rb, LT, to inactivate p53. HPV contains a protein, E7, which can bind to Rb in much the same way. Rb can be inactivated by phosphorylation, or by being bound to a viral oncoprotein, or by mutations—mutations which prevent oncoprotein binding are also associated with cancer.
Variations
DNA oncoviruses typically cause cancer by inactivating p53 and Rb, thereby allowing unregulated cell division and creating tumors. There may be many different mechanisms which have evolved separately; in addition to those described above, for example, theHuman Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
inactivates p53 by sequestering it in the cytoplasm.
SV40 has been well studied and does not cause cancer in humans, but a recently discovered analogue called Merkel cell polyomavirus
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV or MCPyV) was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called ...
has been associated with Merkel cell carcinoma, a form of skin cancer. The Rb binding feature is believed to be the same between the two viruses.
RNA oncoviruses
In the 1960s, the replication process of RNA virus was believed to be similar to other single-stranded RNA. Single-stranded RNA replication involves RNA-dependent RNA synthesis which meant that virus-coding enzymes would make partial double-stranded RNA. This belief was proven to be incorrect because there were no double-stranded RNA found in the retrovirus cell. In 1964, Howard Temin proposed a provirus hypothesis, but shortly after reverse transcription in the retrovirus genome was discovered.Description of virus
All retroviruses have three major coding domains; '' gag'', ''pol'' and ''env
env is a shell command for Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is used to either print a list of environment variables or run another utility in an altered environment without having to modify the currently existing environment. Using env, ...
''. In the ''gag'' region of the virus, the synthesis of the internal virion proteins are maintained which make up the matrix, capsid and nucleocapsid proteins. In ''pol'', the information for the reverse transcription and integration enzymes are stored. In ''env'', it is derived from the surface and transmembrane for the viral envelope protein. There is a fourth coding domain which is smaller, but exists in all retroviruses. ''Pol'' is the domain that encodes the virion protease.
Retrovirus enters host cell
The retrovirus begins the journey into a host cell by attaching a surface glycoprotein to the cell's plasma membrane receptor. Once inside the cell, the retrovirus goes through reverse transcription in the cytoplasm and generates a double-stranded DNA copy of the RNA genome. Reverse transcription also produces identical structures known as long terminal repeats (LTRs). Long terminal repeats are at the ends of the DNA strands and regulates viral gene expression. The viral DNA is then translocated into the nucleus where one strand of the retroviral genome is put into the chromosomal DNA by the help of the virion intergrase. At this point the retrovirus is referred to as provirus. Once in the chromosomal DNA, the provirus is transcribed by the cellular RNA polymerase II. The transcription leads to the splicing and full-length mRNAs and full-length progeny virion RNA. The virion protein and progeny RNA assemble in the cytoplasm and leave the cell, whereas the other copies send translated viral messages in the cytoplasm.Classification

DNA viruses
*Human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
(HPV), a DNA virus, causes transformation in cells through interfering with tumor suppressor proteins such as p53. Interfering with the action of p53 allows a cell infected with the virus to move into a different stage of the cell cycle, enabling the virus genome to be replicated. Forcing the cell into the S phase of the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
could cause the cell to become transformed. Human papillomavirus infection is a major cause of cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer
Vaginal cancer is an extraordinarily rare form of cancer that develops in the tissue of the vagina. Primary vaginal cancer originates from the vaginal tissue – most frequently squamous cell carcinoma, but primary vaginal adenocarcinoma, sarcoma ...
, penis cancer
Penile cancer is cancer that develops in the skin or tissues of the penis. Symptoms may include abnormal growth, an ulcer or sore on the skin of the penis, and bleeding or foul smelling discharge.
Risk factors include phimosis (inability to retra ...
, anal cancer, and HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer (OPC), also known as oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) and tonsil cancer, is a disease in which abnormal cells with the potential to both grow locally and spread to other parts of the body are found in the oral ca ...
s. There are nearly 200 distinct human papillomaviruses (HPVs), and many HPV types are carcinogenic.
* Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is associated with Hepatocarcinoma
* Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
It is ...
(EBV or HHV-4) is associated with four types of cancers
* Human cytomegalovirus
''Human betaherpesvirus 5'', also called human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), is species of virus in the genus '' Cytomegalovirus'', which in turn is a member of the viral family known as '' Herpesviridae'' or herpesviruses. It is also commonly cal ...
(CMV or HHV-5) is associated with mucoepidermoid carcinoma and possibly other malignancies.
* Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV or HHV-8) is associated with Kaposi's sarcoma, a type of skin cancer.
*Merkel cell polyomavirus
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV or MCPyV) was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called ...
a polyoma virusis associated with the development of Merkel cell carcinoma
RNA viruses
Not all oncoviruses are DNA viruses. SomeRNA virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid ( RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA virus ...
es have also been associated such as the hepatitis C virus as well as certain retroviruses, e.g., human T-lymphotropic virus
The human T-lymphotropic virus, human T-cell lymphotropic virus, or human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus (HTLV) family of viruses are a group of human retroviruses that are known to cause a type of cancer called adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and ...
(HTLV-1) and Rous sarcoma virus (RSV).
Overview table
Estimated percent of new cancers attributable to the virus worldwide in 2002. NA indicates not available. The association of other viruses with human cancer is continually under research.Main viruses associated with human cancer

 The main viruses associated with human cancers are the
The main viruses associated with human cancers are the human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
, the hepatitis B and hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, ...
viruses, the Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
It is ...
, the human T-lymphotropic virus
The human T-lymphotropic virus, human T-cell lymphotropic virus, or human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus (HTLV) family of viruses are a group of human retroviruses that are known to cause a type of cancer called adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and ...
, the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) and the Merkel cell polyomavirus
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV or MCPyV) was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called ...
. Experimental and epidemiological data imply a causative role for viruses and they appear to be the second most important risk factor for cancer development in humans, exceeded only by tobacco usage. The mode of virally induced tumors can be divided into two, ''acutely transforming'' or ''slowly transforming''. In acutely transforming viruses, the viral particles carry a gene that encodes for an overactive oncogene called viral-oncogene (v-onc), and the infected cell is transformed as soon as v-onc is expressed. In contrast, in slowly transforming viruses, the virus genome is inserted, especially as viral genome insertion is an obligatory part of retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptas ...
es, near a proto-oncogene in the host genome. The viral promoter or other transcription regulation elements in turn cause overexpression of that proto-oncogene, which in turn induces uncontrolled cellular proliferation. Because viral genome insertion is not specific to proto-oncogenes and the chance of insertion near that proto-oncogene is low, slowly transforming viruses have very long tumor latency compared to acutely transforming viruses, which already carry the viral oncogene.
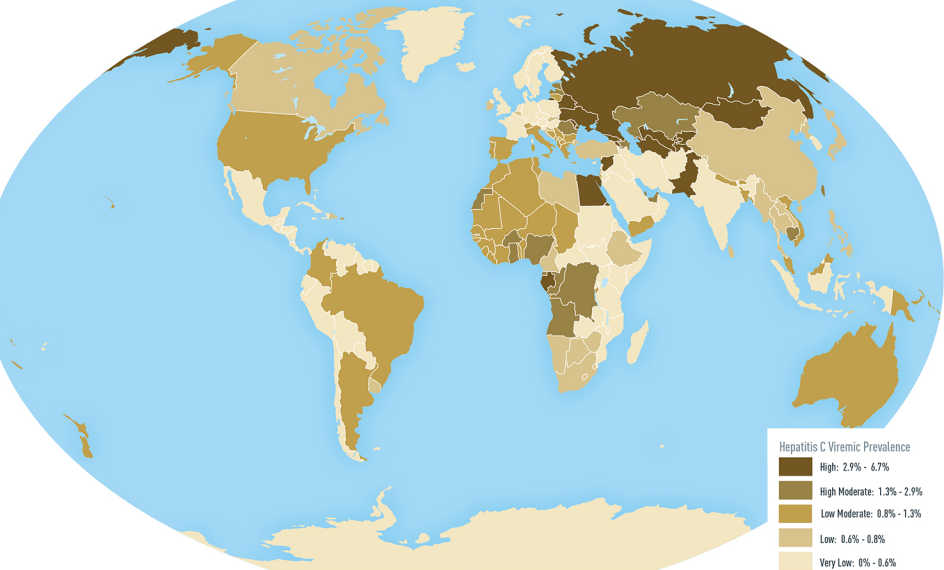
Hepatitis viruses, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, ...
, can induce a chronic viral infection that leads to liver cancer
Liver cancer (also known as hepatic cancer, primary hepatic cancer, or primary hepatic malignancy) is cancer that starts in the liver. Liver cancer can be primary (starts in liver) or secondary (meaning cancer which has spread from elsewhere to th ...
in 0.47% of hepatitis B patients per year (especially in Asia, less so in North America), and in 1.4% of hepatitis C carriers per year. Liver cirrhosis, whether from chronic viral hepatitis infection or alcoholism, is associated with the development of liver cancer, and the combination of cirrhosis and viral hepatitis presents the highest risk of liver cancer development. Worldwide, liver cancer is one of the most common, and most deadly, cancers due to a huge burden of viral hepatitis transmission and disease.
Through advances in cancer research, vaccines designed to prevent cancer have been created. The hepatitis B vaccine is the first vaccine that has been established to prevent cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
It occurs in t ...
) by preventing infection with the causative virus. In 2006, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a human papilloma virus vaccine, called Gardasil. The vaccine protects against four HPV types, which together cause 70% of cervical cancers and 90% of genital warts. In March 2007, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
(CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) officially recommended that females aged 11–12 receive the vaccine, and indicated that females as young as age 9 and as old as age 26 are also candidates for immunization.
History
The history of cancer virus discovery is intertwined with theHistory of cancer
The history of cancer describes the development of the field of oncology and its role in the history of medicine.
Early diagnosis
The earliest known descriptions of cancer appear in several papyri from Ancient Egypt. The Edwin Smith Papyrus was ...
research and the history of virology. The oldest surviving record of a human cancer is the Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
n Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a Babylonian legal text composed 1755–1750 BC. It is the longest, best-organised, and best-preserved legal text from the ancient Near East. It is written in the Old Babylonian dialect of Akkadian, purportedly by Hamm ...
(dated ca. 1754 BC) but scientific oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ó ...
could only emerge in the 19th century, when tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s were studied at microscopic level with the help of the compound microscope and achromatic lenses. 19th century microbiology
Microbiology () is the scientific study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, ...
accumulated evidence that implicated bacteria, yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
s, fungi, and protozoa in the development of cancer. In 1926 the Nobel Prize was awarded for documenting that a nematode worm could provoke stomach cancer in rats. But it was not recognized that cancer could have infectious origins until much later as virus had first been discovered by Dmitri Ivanovsky and Martinus Beijerinck at the close of the 19th century.
History of non-human oncoviruses
 The theory that cancer could be caused by a virus began with the experiments of Oluf Bang and Vilhelm Ellerman in 1908 at the
The theory that cancer could be caused by a virus began with the experiments of Oluf Bang and Vilhelm Ellerman in 1908 at the University of Copenhagen
The University of Copenhagen ( da, Københavns Universitet, KU) is a prestigious public university, public research university in Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark. Founded in 1479, the University of Copenhagen is the second-oldest university in ...
. Bang and Ellerman demonstrated that avian sarcoma leukosis virus could be transmitted between chickens after cell-free filtration and subsequently cause leukemia. This was subsequently confirmed for solid tumors in chickens in 1910–1911 by Peyton Rous
Francis Peyton Rous () (October 5, 1879 – February 16, 1970) was an American pathologist at the Rockefeller University known for his works in oncoviruses, blood transfusion and physiology of digestion. A medical graduate from the Johns Hopk ...
. Rous at the Rockefeller University extended Bang and Ellerman's experiments to show cell-free transmission of a solid tumor sarcoma to chickens (now known as ''Rous sarcoma''). The reasons why chickens are so receptive to such transmission may involve unusual characteristics of stability or instability as they relate to endogenous retroviruses. Charlotte Friend
Charlotte Friend (March 11, 1921 – January 13, 1987) was an American virologist. She is best known for her discovery of the Friend leukemia virus. She helped to establish the concept of the oncovirus, studied the role of the host immune respon ...
confirmed Bang and Ellerman findings for liquid tumor in mice by . In 1933 Richard Shope and Edward Weston Hurst showed that warts from wild cottontail rabbit
Cottontail rabbits are the leporid species in the genus ''Sylvilagus'', found in the Americas. Most ''Sylvilagus'' species have stub tails with white undersides that show when they retreat, giving them their characteristic name. However, this ...
s contained the Shope papilloma virus. In 1936 John Joseph Bittner identified the mouse mammary tumor virus, an "extrachromosomal factor" (i.e. virus) that could be transmitted between laboratory strains of mice by breast feeding.
By the early 1950s, it was known that viruses could remove and incorporate genes and genetic material in cells. It was suggested that such types of viruses could cause cancer by introducing new genes into the genome. Genetic analysis of mice infected with Friend virus confirmed that retroviral
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
integration could disrupt tumor suppressor genes, causing cancer. Viral oncogenes
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.
were subsequently discovered and identified to cause cancer. Ludwik Gross identified the first mouse leukemia virus ( murine leukemia virus) in 1951 and in 1953 reported on a component of mouse leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
extract capable of causing solid tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s in mice. This compound was subsequently identified as a virus by Sarah Stewart and Bernice Eddy
Bernice Eddy (September 30, 1903–May 24, 1989) was an American virologist and epidemiologist. She and Sarah Elizabeth Stewart are known for their discoveries related to polyomavirus, particularly SV40 polyomavirus.
Personal life and education ...
at the National Cancer Institute
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) coordinates the United States National Cancer Program and is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which is one of eleven agencies that are part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. T ...
, after whom it was once called "SE polyoma". In 1957 Charlotte Friend
Charlotte Friend (March 11, 1921 – January 13, 1987) was an American virologist. She is best known for her discovery of the Friend leukemia virus. She helped to establish the concept of the oncovirus, studied the role of the host immune respon ...
discovered the Friend virus, a strain of murine leukemia virus capable of causing cancers in immunocompetent mice. Though her findings received significant backlash, they were eventually accepted by the field and cemented the validity of viral oncogenesis.
In 1961 Eddy discovered the simian vacuolating virus 40 ( SV40). Merck Laboratory also confirmed the existence of a rhesus macaque virus contaminating cells used to make Salk and Sabin polio vaccines. Several years later, it was shown to cause cancer in Syrian hamsters, raising concern about possible human health implications. Scientific consensus now strongly agrees that this is not likely to cause human cancer.
History of human oncoviruses
In 1964Anthony Epstein
Sir Michael Anthony Epstein (born 18 May 1921) is a British pathologist and academic. He is one of the discoverers of the Epstein–Barr virus, along with Yvonne Barr and Bert Achong.
Personal life
Epstein was born on 18 May 1921, and educ ...
, Bert Achong
Bert Geoffrey Achong (6 December 1928 – 28 November 1996) was a Trinidadian-born pathologist
known for co-discovering the Epstein–Barr virus through use of electron microscopy.
Career
Achong was born in Trinidad and Tobago and was of Chin ...
and Yvonne Barr identified the first human oncovirus from Burkitt's lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, particularly B lymphocytes found in the germinal center. It is named after Denis Parsons Burkitt, the Irish surgeon who first described the disease in 1958 while working in equatorial Africa. ...
cells. A herpesvirus, this virus is formally known as human herpesvirus 4 but more commonly called Epstein–Barr virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), formally called ''Human gammaherpesvirus 4'', is one of the nine known human herpesvirus types in the herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus.
It is ...
or EBV. In the mid-1960s Baruch Blumberg
Baruch Samuel Blumberg (July 28, 1925 April 5, 2011), known as Barry Blumberg, was an American physician, geneticist, and co-recipient of the 1976 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (with Daniel Carleton Gajdusek), for his work on the hepat ...
first physically isolated and characterized Hepatitis B while working at the National Institute of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
(NIH) and later the Fox Chase Cancer Center
Fox Chase Cancer Center is a National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center research facility and hospital located in the Fox Chase section of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. The main facilities of the center are loca ...
. Although this agent was the clear cause of hepatitis and might contribute to liver cancer hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
It occurs in t ...
, this link was not firmly established until epidemiologic studies were performed in the 1980s by R. Palmer Beasley and others.
In 1980 the first human retrovirus, Human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-I), was discovered by Bernard Poiesz and Robert Gallo at NIH, and independently by Mitsuaki Yoshida
was a Japanese virologist known for identifying the molecular structure of Human T-lymphotropic virus 1 responsible for Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.
Life
Yoshida was born in Toyama, Japan and received his Ph.D. in 1967 from the University of ...
and coworkers in Japan. But it was not certain whether HTLV-I promoted leukemia. In 1981 Yorio Hinuma and his colleagues at Kyoto University
, mottoeng = Freedom of academic culture
, established =
, type = Public (National)
, endowment = ¥ 316 billion (2.4 billion USD)
, faculty = 3,480 (Teaching Staff)
, administrative_staff = 3,978 (Total Staff)
, students = ...
reported visualization of retroviral particles produced by a leukemia cell line derived from patients with Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. This virus turned out to be HTLV-1 and the research established the causal role of the HTLV-1 virus to ATL.
 Between 1984 and 1986
Between 1984 and 1986 Harald zur Hausen
Harald zur Hausen NAS EASA APS (; born 11 March 1936) is a German virologist and professor emeritus. He has done research on cervical cancer and discovered the role of papilloma viruses in cervical cancer, for which he received the Nobel ...
and Lutz Gissmann
Lutz Gissmann (born September 18, 1949 in Kaufbeuren, Germany) is a German virologist and was head of the Division “Genome Modifications and Carcinogenesis” at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) in Heidelberg until his retirement in 201 ...
discovered HPV16 and HPV18, together these Papillomaviridae viruses (HPV) are responsible for approximately 70% of human papillomavirus infections that cause cervical cancers. For the discovery that HPV cause human cancer the 2008 Nobel Prize was awarded. In 1987 the Hepatitis C virus (HCV) was discovered by panning a cDNA library made from diseased tissues for foreign antigens recognized by patient sera. This work was performed by Michael Houghton at Chiron, a biotechnology company, and Daniel W. Bradley at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
(CDC). HCV was subsequently shown to be a major contributor to Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
It occurs in t ...
(liver cancer) worldwide.
In 1994 Patrick S. Moore
Patrick S. Moore (born October 21, 1956) is an Irish and American virologist and epidemiologist who co-discovered together with his wife, Yuan Chang, two different human viruses causing the AIDS-related cancer Kaposi's sarcoma and the skin cance ...
and Yuan Chang at Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
), working together with Ethel Cesarman, isolated Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV or HHV8) using representational difference analysis. This search was prompted by work from Valerie Beral and colleagues who inferred from the epidemic of Kaposi's sarcoma among patients with AIDS that this cancer must be caused by another infectious agent besides HIV, and that this was likely to be a second virus. Subsequent studies revealed that KSHV is the "KS agent" and is responsible for the epidemiologic patterns of KS and related cancers.
In 2008 Yuan Chang and Patrick S. Moore
Patrick S. Moore (born October 21, 1956) is an Irish and American virologist and epidemiologist who co-discovered together with his wife, Yuan Chang, two different human viruses causing the AIDS-related cancer Kaposi's sarcoma and the skin cance ...
developed a new method to identify cancer viruses based on computer subtraction of human sequences from a tumor transcriptome, called digital transcriptome subtraction (DTS). DTS was used to isolate DNA fragments of Merkel cell polyomavirus
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV or MCPyV) was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called ...
from a Merkel cell carcinoma and it is now believed that this virus causes 70–80% of these cancers.
See also
* Infectious causes of cancer *Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive sub ...
* Oncogenic
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnor ...
* Oncogene
* Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
* Cancer bacteria
Cancer bacteria are bacteria infectious organisms that are known or suspected to cause cancer. While cancer-associated bacteria have long been considered to be opportunistic (i.e., infecting healthy tissues after cancer has already established ...
* Oncolytic virus
An oncolytic virus is a virus that preferentially infects and kills cancer cells. As the infected cancer cells are destroyed by oncolysis, they release new infectious virus particles or virions to help destroy the remaining tumour. Oncolytic viru ...
, a virus that infects and kills cancer cells
* Gag-onc fusion protein
* List of infectious diseases
This is a list of infectious diseases arranged by name, along with the infectious agents that cause them and the vaccines that can prevent or cure them when they exist.
List
See also
*
* List of oncogenic bacteria
* − including specific i ...
References
External links
* {{Authority control Carcinogenesis Virology Viruses Infectious causes of cancer