|
Neon-burning Process
The neon-burning process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in evolved massive stars with at least 8 Solar masses. Neon burning requires high temperatures and densities (around 1.2 billion K or 100 keV and 4 billion kg/m3). At such high temperatures photodisintegration becomes a significant effect, so some neon nuclei decompose, absorbing 4.73 MeV and releasing alpha particles. This free helium nucleus can then fuse with neon to produce magnesium, releasing 9.316 MeV. : Alternatively: Ne-21 + y Ne-21 + He -> Mg-24 + n -->: where the neutron consumed in the first step is regenerated in the second. A secondary reaction causes helium to fuse with magnesium to produce silicon: : + → + γ Contraction of the core leads to an increase of temperature, allowing neon to fuse directly as follows: : + → + Neon burning takes place after carbon burning has consumed all carbon in the core and built up a new oxygen–neon–sodium–magnesium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei, nuclei/neutrons, neutron by-products. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of energy. This difference in mass arises as a result of the difference in nuclear binding energy between the atomic nuclei before and after the fusion reaction. Nuclear fusion is the process that powers all active stars, via many Stellar nucleosynthesis, reaction pathways. Fusion processes require an extremely large Lawson criterion, triple product of temperature, density, and confinement time. These conditions occur only in Stellar core, stellar cores, advanced Nuclear weapon design, nuclear weapons, and are approached in List of fusion experiments, fusion power experiments. A nuclear fusion process that produces atomic nuclei lighter than nickel-62 is generally exothermic, due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
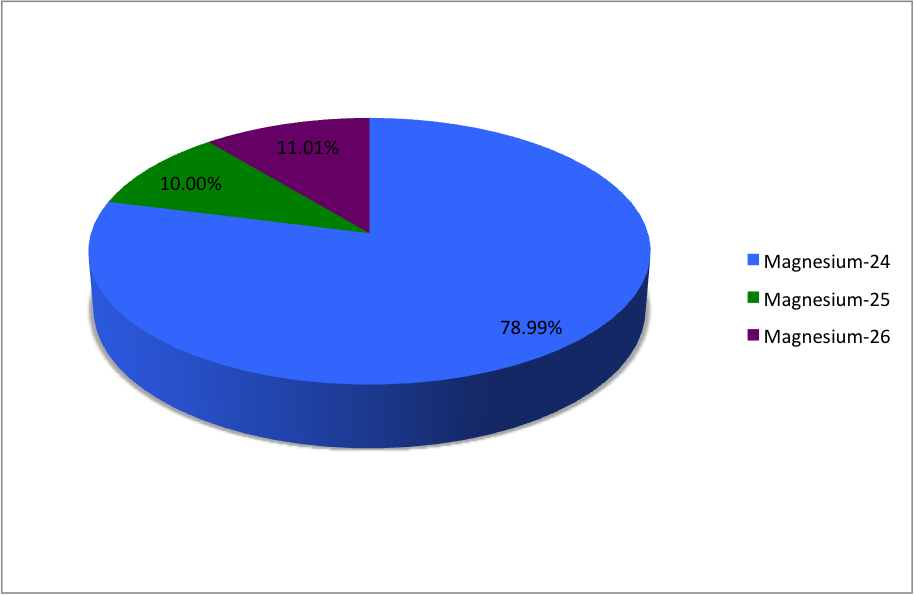
Magnesium-24
Magnesium (12Mg) naturally occurs in three stable isotopes: , , and . There are 19 radioisotopes that have been discovered, ranging from to (with the exception of ). The longest-lived radioisotope is with a half-life of . The lighter isotopes mostly decay to isotopes of sodium while the heavier isotopes decay to isotopes of aluminium. The shortest-lived is proton-unbound with a half-life of . A precise measurement of the neutron-rich 40Mg in 2019 showed the unexpected difference in its nuclear structure, compared to the lighter neighboring isotopes. List of isotopes , -id=Magnesium-18 , , style="text-align:right" , 12 , style="text-align:right" , 6 , , , 2p , , 0+ , , , -id=Magnesium-19 , , style="text-align:right" , 12 , style="text-align:right" , 7 , , , 2p , , 1/2−# , , , - , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 12 , rowspan=2 style="text-align:right" , 8 , rowspan=2, , rowspan=2, , β+ () , , rowsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table), it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin Passivation (chemistry), passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium Salt (chemistry), salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight magnesium alloy, alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three Helium nucleus, helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been Leaching (chemistry), leached by the action of water from the Earth, Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in Soap, soap manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neon
Neon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is the second noble gas in the periodic table. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with approximately two-thirds the density of air. Neon was discovered in 1898 alongside krypton and xenon, identified as one of the three remaining rare inert elements in dry air after the removal of nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide. Its discovery was marked by the distinctive bright red emission spectrum it exhibited, leading to its immediate recognition as a new element. The name ''neon'' originates from the Greek word , a neuter singular form of (), meaning 'new'. Neon is a chemically inert gas; although neon compounds do exist, they are primarily ionic molecules or fragile molecules held together by van der Waals forces. The synthesis of most neon in the cosmos resulted from the nuclear fusion within stars of oxygen and helium through the alpha-capture proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon-burning Process
The carbon-burning process or carbon fusion is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in the cores of massive stars (at least 4 \beginM_\odot\end at birth) that combines carbon into other elements. It requires high temperatures (> 5×108 K or 50 keV) and densities (> 3×109 kg/m3). These figures for temperature and density are only a guide. More massive stars burn their nuclear fuel more quickly, since they have to offset greater gravitational forces to stay in (approximate) hydrostatic equilibrium. That generally means higher temperatures, although lower densities, than for less massive stars. To get the right figures for a particular mass, and a particular stage of evolution, it is necessary to use a numerical stellar model computed with computer algorithms. Such models are continually being refined based on nuclear physics experiments (which measure nuclear reaction rates) and astronomical observations (which include direct observation of mass loss, det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Silicon is a significant element that is essential for several physiological and metabolic processes in plants. Silicon is widely regarded as the predominant semiconductor material due to its versatile applications in various electrical devices such as transistors, solar cells, integrated circuits, and others. These may be due to its significant band gap, expansive optical transmission range, extensive absorption spectrum, surface roughening, and effective anti-reflection coating. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neon-21
Neon (10Ne) possesses three stable isotopes: , , and . In addition, 17 radioactive isotopes have been discovered, ranging from to , all short-lived. The longest-lived is with a half-life of . All others are under a minute, most under a second. The least stable is with a half-life of (). See isotopes of carbon for notes about the measurement. Light radioactive neon isotopes usually decay to fluorine or oxygen, while heavier ones decay to sodium. List of isotopes , -id=Neon-15 , , style="text-align:right" , 10 , style="text-align:right" , 5 , , [] , proton emission, 2p , , (3/2−) , , , -id=Neon-16 , , style="text-align:right" , 10 , style="text-align:right" , 6 , , > [ , -id=Neon-21 , , style="text-align:right" , 10 , style="text-align:right" , 11 , , colspan=3 align=center, Stable , 3/2+ , , ref name="Isotopic Composition of Elements" /> , -id=Neon-22 , , style="text-align:right" , 10 , style="text-align:right" , 12 , , c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , that has no electric charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. The Discovery of the neutron, neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932, leading to the discovery of nuclear fission in 1938, the first self-sustaining nuclear reactor (Chicago Pile-1, 1942) and the first nuclear weapon (Trinity (nuclear test), Trinity, 1945). Neutrons are found, together with a similar number of protons in the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. Atoms of a chemical element that differ only in neutron number are called isotopes. Free neutrons are produced copiously in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion, fusion. They are a primary contributor to the nucleosynthesis of chemical elements within stars through fission, fusion, and neutron capture processes. Neutron stars, formed from massive collapsing stars, consist of neutrons at the density of atomic nuclei but a total mass more than the Sun. Neutron properties and interactions ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |