|
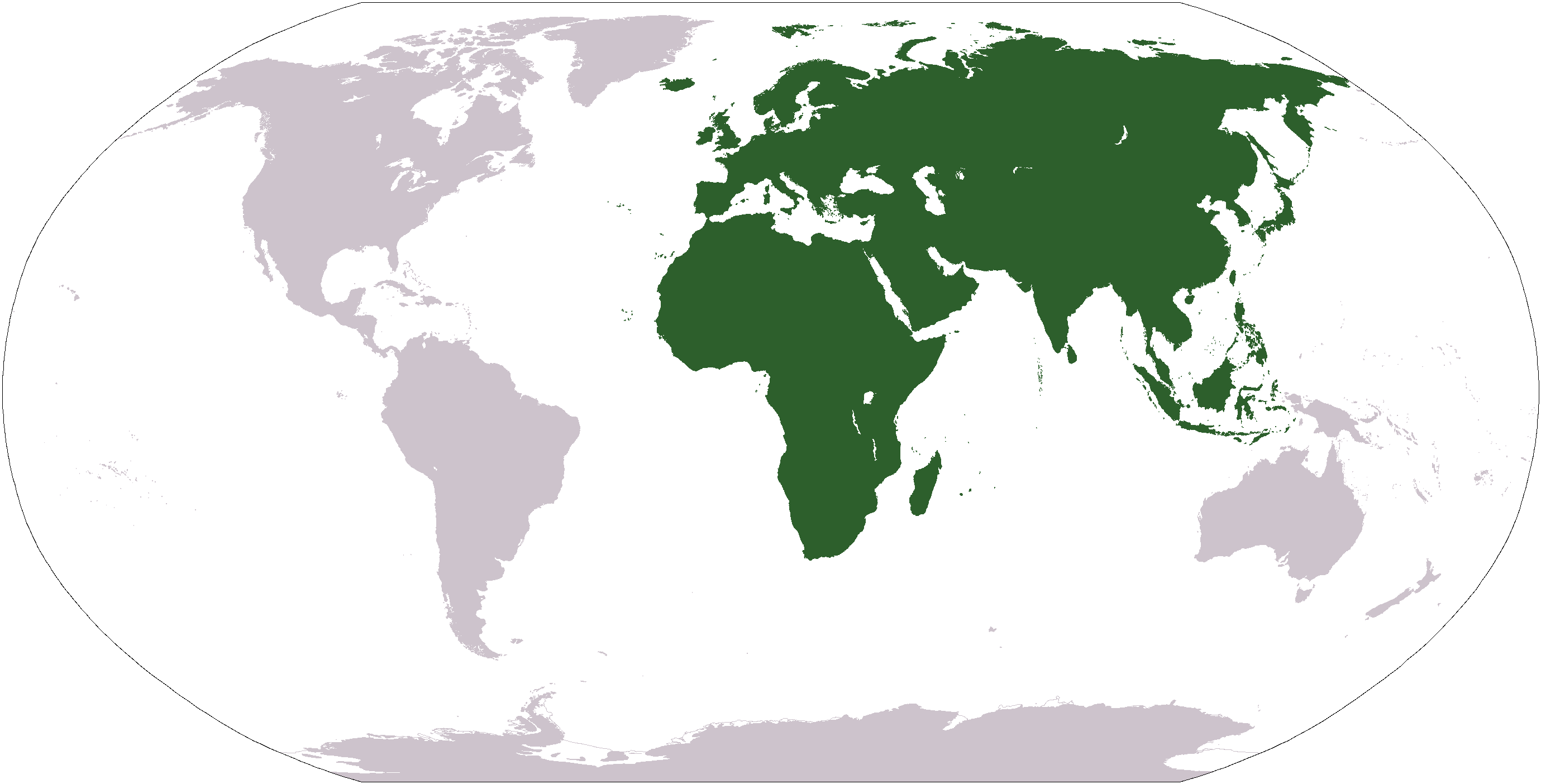
Merlin (bird)
The merlin (''Falco columbarius'') is a small species of falcon from the Northern Hemisphere, with numerous subspecies throughout North America and Eurasia. A bird of prey, the merlin breeds in the northern Holarctic; some migrate to subtropical and northern tropical regions in winter. Males typically have wingspans of , with females being slightly larger. They are swift fliers and skilled hunters which specialize in preying on small birds in the size range of sparrows to doves and medium-sized shorebirds. In recent decades merlin populations in North America have been significantly increasing, with some merlins becoming so well adapted to city life that they forgo migration; in Europe, populations increased up to about 2000 but have been steady subsequently. The merlin has for centuries been well regarded as a falconry bird. Nomenclature The merlin was described and illustrated by the English naturalist Mark Catesby (as the "pigeon hawk") in his ''Natural history of Carolina, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive with a respective county. The city is the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the United States by both population and urban area. New York is a global center of finance and commerce, culture, technology, entertainment and media, academics, and scientific output, the arts and fashion, and, as home to the headquarters of the United Nations, international diplomacy. With an estimated population in 2024 of 8,478,072 distributed over , the city is the most densely populated major city in the United States. New York City has more than double the population of Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the Orthographic ligature, ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Sweden, Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomenclature, was partially developed by the Bauhin brothers, Gaspard Bauhin, Gaspard and Johann Bauhin, Johann, Linnaeus was the first to use it consistently throughout his book. The first edition was published in 1735. The full title of the 10th edition (1758), which was the most important one, was ', which appeared in English in 1806 with the title: "A General System of Nature, Through the Three Grand Kingdoms of Animals, Vegetables, and Minerals, Systematically Divided Into their Several Classes, Orders, Genera, Species, and Varieties, with their Habitations, Manners, Economy, Structure and Peculiarities". The 10th edition of Systema Naturae, tenth edition of this book (1758) is considered the starting point of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; ) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally identified as the period from around 500/750 to 1050. Rather than representing a single supra-regional form of German, Old High German encompasses the numerous West Germanic languages, West Germanic dialects that had undergone the set of sound change, consonantal changes called the High German consonant shift, Second Sound Shift. At the start of this period, dialect areas reflected the territories of largely independent tribal kingdoms, but by 788 the conquests of Charlemagne had brought all OHG dialect areas into a single polity. The period also saw the development of a stable linguistic border between German and Gallo-Romance languages, Gallo-Romance, later French language, French. Old High German largely preserved the synthetic language, synthetic inflectional system inherited from its ancestral Germanic forms. The eventual disruption of these patterns, which led to the more analytic language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects whose ancestor was Old Dutch. It was spoken and written between 1150 and 1500. Until the advent of Modern Dutch after 1500 or , there was no overarching standard language, but all dialects were mutually intelligible. During that period, a rich Medieval Dutch literature developed, which had not yet existed during Old Dutch. The various literary works of the time are often very readable for speakers of Modern Dutch since Dutch is a rather conservative language. Phonology Differences with Old Dutch Several phonological changes occurred leading up to the Middle Dutch period. * Earlier Old Dutch , , merge into already in Old Dutch. * Voiceless fricatives become voiced syllable-initially: > , > (merging with from Proto-Germanic ), > . (10th or 11th century) * > * > or . The outcome is dialect-specific, with found in more western dialects and further east. This results in later pairs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anglo-Norman Language
Anglo-Norman (; ), also known as Anglo-Norman French, was a dialect of Old Norman that was used in Kingdom of England, England and, to a lesser extent, other places in Great Britain and Ireland during the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman period. Origin The term "Anglo-Norman" harks back to the time when the language was regarded as being primarily the regional dialect of the Norman settlers. Today the generic term "Anglo-French" is used instead to reflect not only the broader origin of the settlers who came with William the Conqueror, but also the continued influence of Parisian French from the House of Plantagenet, Plantagenet period onwards. According to some linguists, the name Insular French might be more suitable, because "Anglo-Norman" is constantly associated with the notion of a mixed language based on English and Norman. According to some, such a mixed language never existed. Other sources, however, indicate that such a language did exist, and that it was the language desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Old French
Old French (, , ; ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France approximately between the late 8th [2-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it was deemed no longer make to think of the varieties spoken in Gaul as Latin. Although a precise date can't be given, there is a general consensus (see Wright 1982, 1991, Lodge 1993) that an awareness of a vernacular, distinct from Latin, emerged at the end of the eighth century.] and mid-14th centuries. Rather than a unified Dialect#Dialect or language, language, Old French was a Dialect cluster, group of Romance languages, Romance dialects, Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible yet Dialect continuum, diverse. These dialects came to be collectively known as the , contrasting with the , the emerging Occitano-Romance languages of Occitania, now the south of France. The mid-14th century witnessed the emergence of Middle French, the lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scientific Name
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammar, Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (often shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name, or a scientific name; more informally, it is also called a Latin name. In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), the system is also called nomenclature, with an "n" before the "al" in "binominal", which is a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system". The first part of the name – the ''generic name (biology), generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously thought of by the Europeans as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marmaduke Tunstall
Marmaduke Tunstall (1743 – 11 October 1790) was an England, English ornithologist and collector. He was the author of ''Ornithologia Britannica'' (1771), probably the first British work to use binomial nomenclature. Tunstall was born at Burton Constable in Yorkshire. In 1760, he succeeded to the family estates of Scargill, County Durham, Scargill, Hutton, Long Villers and Wycliffe, County Durham, Wycliffe. Being a Catholic, he was educated at Douai in France. On completing his studies, he took up residence in Welbeck Street, London, where he formed an extensive museum, as well as a large collection of living birds and animals. He is known for formally describing the Peregrine falcon. After his marriage in 1776, the museum was moved to Wycliffe, and at the time, was one of the finest in England. Tunstall became a fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London at the age of twenty-one, and in 1771, was elected a fellow of the Royal Society. Tunstall died at Wycliffe, and his es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sickle
A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting or reaping grain crops, or cutting Succulent plant, succulent forage chiefly for feeding livestock. Falx was a synonym, but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge. Since the beginning of the Iron Age hundreds of region-specific variants of the sickle have evolved, initially of iron and later steel. This great diversity of sickle types across many cultures can be divided into smooth or serrated blades, both of which can be used for cutting either green grass or mature cereals using slightly different techniques. The serrated blade that originated in prehistoric sickles still dominates in the reaping of grain and is even found in modern grain-harvesting machines and in some kitchen knives. History Pre-Neolithic The development of the sickle in Mesopota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |