|
Max Pooling
In neural networks, a pooling layer is a kind of network layer that downsamples and aggregates information that is dispersed among many vectors into fewer vectors. It has several uses. It removes redundant information, reducing the amount of computation and memory required, makes the model more robust to small variations in the input, and increases the receptive field of neurons in later layers in the network. Convolutional neural network pooling Pooling is most commonly used in convolutional neural networks (CNN). Below is a description of pooling in 2-dimensional CNNs. The generalization to n-dimensions is immediate. As notation, we consider a tensor x \in \R^, where H is height, W is width, and C is the number of channels. A pooling layer outputs a tensor y \in \R^. We define two variables f, s called "filter size" (aka "kernel size") and "stride". Sometimes, it is necessary to use a different filter size and stride for horizontal and vertical directions. In such cases, we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
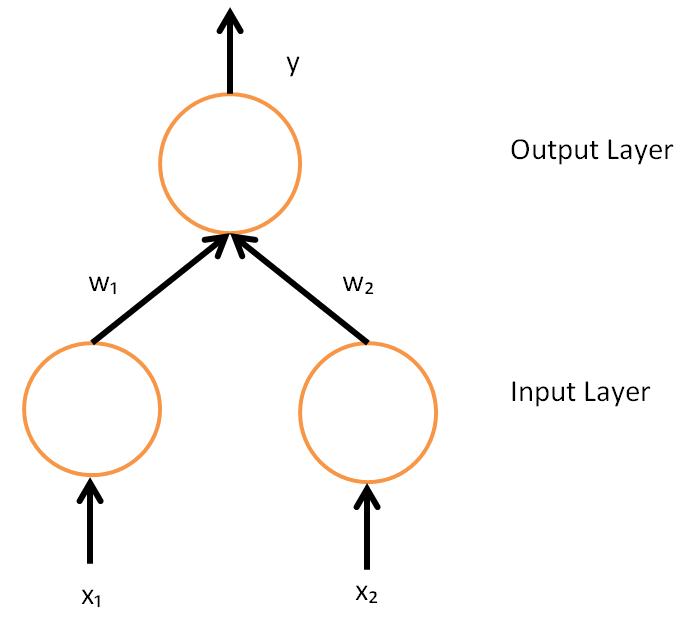
Neural Network (machine Learning)
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called ''artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the ''activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BERT (language Model)
Bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) is a language model introduced in October 2018 by researchers at Google. It learns to represent text as a sequence of vectors using self-supervised learning. It uses the Transformer (machine learning model), encoder-only transformer architecture. BERT dramatically improved the State of the art, state-of-the-art for large language model, large language models. , BERT is a ubiquitous baseline in natural language processing (NLP) experiments. BERT is trained by masked token prediction and next sentence prediction. As a result of this training process, BERT learns contextual, Latent space, latent representations of tokens in their context, similar to ELMo and GPT-2. It found applications for many natural language processing tasks, such as coreference resolution and polysemy resolution. It is an evolutionary step over ELMo, and spawned the study of "BERTology", which attempts to interpret what is learned by BERT. BERT wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Convolutional Neural Network
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a type of feedforward neural network that learns features via filter (or kernel) optimization. This type of deep learning network has been applied to process and make predictions from many different types of data including text, images and audio. Convolution-based networks are the de-facto standard in deep learning-based approaches to computer vision and image processing, and have only recently been replaced—in some cases—by newer deep learning architectures such as the transformer. Vanishing gradients and exploding gradients, seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks, are prevented by the regularization that comes from using shared weights over fewer connections. For example, for ''each'' neuron in the fully-connected layer, 10,000 weights would be required for processing an image sized 100 × 100 pixels. However, applying cascaded ''convolution'' (or cross-correlation) kernels, only 25 weights for each convolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Béla Julesz
Béla Julesz (also Bela Julesz in English; February 19, 1928 – December 31, 2003) was a Hungarian-born American visual neuroscientist and experimental psychologist in the fields of visual and auditory perception. Julesz was the originator of random dot stereograms which led to the creation of autostereograms. He also was the first to study texture discrimination by constraining second-order statistics. Biography Béla Julesz was born in Budapest, Hungary, on February 19, 1928. He graduated from Budapest University of Technology and Economics in 1950. He started his electrical engineering career at the Telecommunications Research Institute. He immigrated to the United States with his wife Margit after receiving his Ph.D. from the Hungarian Academy of Sciences in 1956. The topic of his doctoral thesis was the theory of microwave systems and television signals. In 1956, Julesz joined the renowned Bell Telephone Laboratories, Incorporated, where he headed the Sensory and Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Torsten Wiesel
Torsten Nils Wiesel (born 3 June 1924) is a Swedish Neurophysiology, neurophysiologist. With David H. Hubel, he received the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, for their discoveries concerning information processing in the visual system; the prize was shared with Roger W. Sperry for his independent research on the cerebral hemispheres. Career Wiesel was born in Uppsala, Sweden, in 1924, the youngest of five children. In 1947, he began his scientific career in Carl Gustaf Bernhard's laboratory at the Karolinska Institute, where he received his medical degree in 1954. He went on to teach in the institute's department of physiology and worked in the child psychiatry unit of the Karolinska Hospital. In 1955 he moved to the United States to work at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine under Stephen Kuffler. Wiesel began a fellowship in ophthalmology, and in 1958 he became an assistant professor. That same year, he met David Hubel, beginning a collaboration that would last over tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
David H
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the Kings of Israel and Judah, third king of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as "Davidic line, House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the ''Seder Olam Rabbah'', ''Seder Olam Zutta'', and ''Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, Historicity of the Bible, the historicit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Backpropagation
In machine learning, backpropagation is a gradient computation method commonly used for training a neural network to compute its parameter updates. It is an efficient application of the chain rule to neural networks. Backpropagation computes the gradient of a loss function with respect to the weights of the network for a single input–output example, and does so efficiently, computing the gradient one layer at a time, iterating backward from the last layer to avoid redundant calculations of intermediate terms in the chain rule; this can be derived through dynamic programming. Strictly speaking, the term ''backpropagation'' refers only to an algorithm for efficiently computing the gradient, not how the gradient is used; but the term is often used loosely to refer to the entire learning algorithm – including how the gradient is used, such as by stochastic gradient descent, or as an intermediate step in a more complicated optimizer, such as Adaptive Moment Estimation. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sigmoid Function
A sigmoid function is any mathematical function whose graph of a function, graph has a characteristic S-shaped or sigmoid curve. A common example of a sigmoid function is the logistic function, which is defined by the formula :\sigma(x) = \frac = \frac = 1 - \sigma(-x). Other sigmoid functions are given in the #Examples, Examples section. In some fields, most notably in the context of artificial neural networks, the term "sigmoid function" is used as a synonym for "logistic function". Special cases of the sigmoid function include the Gompertz curve (used in modeling systems that saturate at large values of ''x'') and the ogee curve (used in the spillway of some dams). Sigmoid functions have domain of all real numbers, with return (response) value commonly monotonically increasing but could be decreasing. Sigmoid functions most often show a return value (''y'' axis) in the range 0 to 1. Another commonly used range is from −1 to 1. A wide variety of sigmoid functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Matrix Multiplication
In mathematics, specifically in linear algebra, matrix multiplication is a binary operation that produces a matrix (mathematics), matrix from two matrices. For matrix multiplication, the number of columns in the first matrix must be equal to the number of rows in the second matrix. The resulting matrix, known as the matrix product, has the number of rows of the first and the number of columns of the second matrix. The product of matrices and is denoted as . Matrix multiplication was first described by the French mathematician Jacques Philippe Marie Binet in 1812, to represent the composition of functions, composition of linear maps that are represented by matrices. Matrix multiplication is thus a basic tool of linear algebra, and as such has numerous applications in many areas of mathematics, as well as in applied mathematics, statistics, physics, economics, and engineering. Computing matrix products is a central operation in all computational applications of linear algebra. Not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Projection (mathematics)
In mathematics, a projection is an idempotent mapping of a set (or other mathematical structure) into a subset (or sub-structure). In this case, idempotent means that projecting twice is the same as projecting once. The restriction to a subspace of a projection is also called a ''projection'', even if the idempotence property is lost. An everyday example of a projection is the casting of shadows onto a plane (sheet of paper): the projection of a point is its shadow on the sheet of paper, and the projection (shadow) of a point on the sheet of paper is that point itself (idempotency). The shadow of a three-dimensional sphere is a disk. Originally, the notion of projection was introduced in Euclidean geometry to denote the projection of the three-dimensional Euclidean space onto a plane in it, like the shadow example. The two main projections of this kind are: * The projection from a point onto a plane or central projection: If is a point, called the center of projection, then t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nearest Neighbor Graph
The nearest neighbor graph (NNG) is a directed graph defined for a set of points in a metric space, such as the Euclidean distance in the plane. The NNG has a vertex for each point, and a directed edge from ''p'' to ''q'' whenever ''q'' is a nearest neighbor of ''p'', a point whose distance from ''p'' is minimum among all the given points other than ''p'' itself. In many uses of these graphs, the directions of the edges are ignored and the NNG is defined instead as an undirected graph. However, the nearest neighbor relation is not a symmetric one, i.e., ''p'' from the definition is not necessarily a nearest neighbor for ''q''. In theoretical discussions of algorithms a kind of general position is often assumed, namely, the nearest (k-nearest) neighbor is unique for each object. In implementations of the algorithms it is necessary to bear in mind that this is not always the case. For situations in which it is necessary to make the nearest neighbor for each object unique, the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
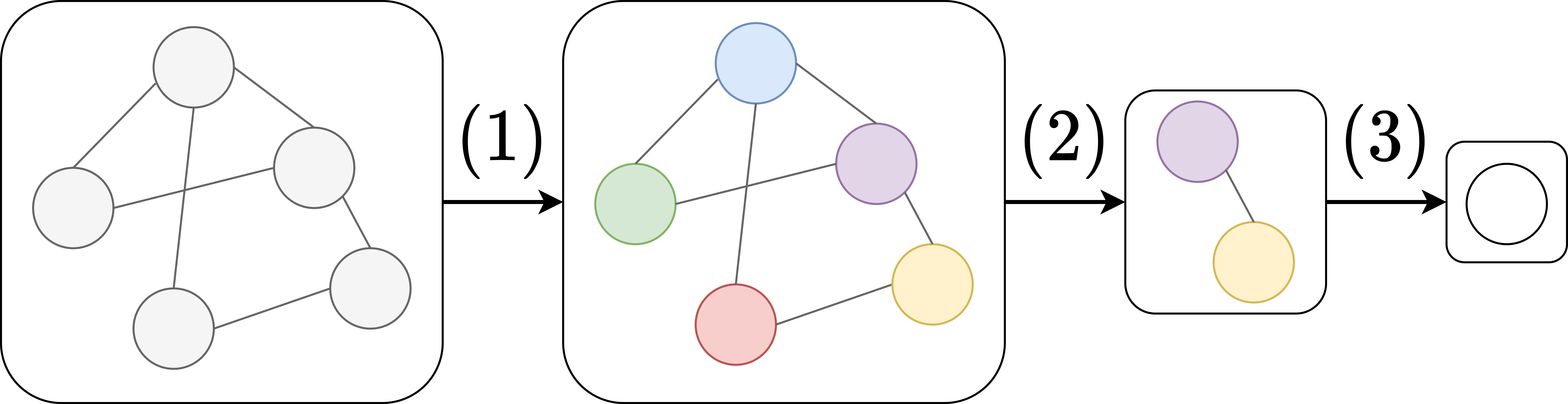
Graph Neural Network
Graph neural networks (GNN) are specialized artificial neural networks that are designed for tasks whose inputs are graphs. One prominent example is molecular drug design. Each input sample is a graph representation of a molecule, where atoms form the nodes and chemical bonds between atoms form the edges. In addition to the graph representation, the input also includes known chemical properties for each of the atoms. Dataset samples may thus differ in length, reflecting the varying numbers of atoms in molecules, and the varying number of bonds between them. The task is to predict the efficacy of a given molecule for a specific medical application, like eliminating ''E. coli'' bacteria. The key design element of GNNs is the use of ''pairwise message passing'', such that graph nodes iteratively update their representations by exchanging information with their neighbors. Several GNN architectures have been proposed, which implement different flavors of message passing, started ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |