|
Iterate
Iteration is the repetition of a process in order to generate a (possibly unbounded) sequence of outcomes. Each repetition of the process is a single iteration, and the outcome of each iteration is then the starting point of the next iteration. In mathematics and computer science, iteration (along with the related technique of recursion) is a standard element of algorithms. Mathematics In mathematics, iteration may refer to the process of iterating a function, i.e. applying a function repeatedly, using the output from one iteration as the input to the next. Iteration of apparently simple functions can produce complex behaviors and difficult problems – for examples, see the Collatz conjecture and juggler sequences. Another use of iteration in mathematics is in iterative methods which are used to produce approximate numerical solutions to certain mathematical problems. Newton's method is an example of an iterative method. Manual calculation of a number's square root is a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iteratees
In functional programming, an iteratee is a composable abstraction for incrementally processing sequentially presented chunks of input data in a purely functional fashion. With iteratees, it is possible to lazily transform how a resource will emit data, for example, by converting each chunk of the input to uppercase as they are retrieved or by limiting the data to only the five first chunks without loading the whole input data into memory. Iteratees are also responsible for opening and closing resources, providing predictable resource management. On each step, an iteratee is presented with one of three possible types of values: the next chunk of data, a value to indicate no data is available, or a value to indicate the iteration process has finished. It may return one of three possible types of values, to indicate to the caller what should be done next: one that means "stop" (and contains the final return value), one that means "continue" (and specifies how to continue), and one th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iterated Function
In mathematics, an iterated function is a function that is obtained by composing another function with itself two or several times. The process of repeatedly applying the same function is called iteration. In this process, starting from some initial object, the result of applying a given function is fed again into the function as input, and this process is repeated. For example, on the image on the right: : Iterated functions are studied in computer science, fractals, dynamical systems, mathematics and renormalization group physics. Definition The formal definition of an iterated function on a set ''X'' follows. Let be a set and be a function. Defining as the ''n''-th iterate of , where ''n'' is a non-negative integer, by: f^0 ~ \stackrel ~ \operatorname_X and f^ ~ \stackrel ~ f \circ f^, where is the identity function on and denotes function composition. This notation has been traced to and John Frederick William Herschel in 1813. Herschel credited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
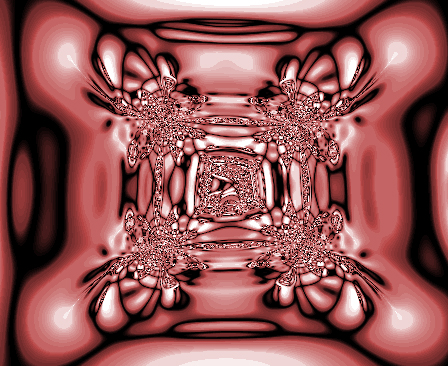
Fractals
In mathematics, a fractal is a Shape, geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine geometry, affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they Scaling (geometry), scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Infinite Compositions Of Analytic Functions
In mathematics, infinite Function composition, compositions of analytic functions (ICAF) offer alternative formulations of Generalized continued fraction, analytic continued fractions, series (mathematics), series, product (mathematics), products and other infinite expansions, and the theory evolving from such compositions may shed light on the convergence (mathematics), convergence/divergence of these expansions. Some functions can actually be expanded directly as infinite compositions. In addition, it is possible to use ICAF to evaluate solutions of fixed point (mathematics), fixed point equations involving infinite expansions. Complex dynamics offers another venue for iterated function system, iteration of systems of functions rather than a single function. For infinite compositions of a ''single function'' see Iterated function. For compositions of a finite number of functions, useful in fractal theory, see Iterated function system. Although the title of this article specifies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iterators
In computer programming, an iterator is an object (computing), object that progressively provides access to each item of a Collection (abstract data type), collection, in order. A collection may provide multiple iterators via its Interface (object-oriented programming), interface that provide items in different orders, such as forwards and backwards. An iterator is often implemented in terms of the structure underlying a collection implementation and is often tightly Coupling (computer programming), coupled to the collection to enable the operational semantics of the iterator. An iterator is behaviorally similar to a cursor (databases), database cursor. Iterators date to the CLU (programming language), CLU programming language in 1974. Pattern An iterator provides access to an element of a collection (''element access'') and can change its internal state to provide access to the next element (''element traversal''). It also provides for creation and initialization to a first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Recursion
Recursion occurs when the definition of a concept or process depends on a simpler or previous version of itself. Recursion is used in a variety of disciplines ranging from linguistics to logic. The most common application of recursion is in mathematics and computer science, where a function (mathematics), function being defined is applied within its own definition. While this apparently defines an infinite number of instances (function values), it is often done in such a way that no infinite loop or infinite chain of references can occur. A process that exhibits recursion is ''recursive''. Video feedback displays recursive images, as does an infinity mirror. Formal definitions In mathematics and computer science, a class of objects or methods exhibits recursive behavior when it can be defined by two properties: * A simple ''base case'' (or cases) — a terminating scenario that does not use recursion to produce an answer * A ''recursive step'' — a set of rules that reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, world trade. It is a forum (legal), forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. The majority of OECD members are generally regarded as developed country, developed countries, with High-income economy, high-income economies, and a very high Human Development Index. their collective population is 1.38 billion people with an average life expectancy of 80 years and a median age of 40, against a global average of 30. , OECD Member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of list of countries by GDP (nominal), global nom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Programming Idioms
In computer programming, a programming idiom, code idiom or simply idiom is a code fragment having a semantic role which recurs frequently across software projects. It often expresses a special feature of a recurring construct in one or more programming languages, frameworks or libraries. This definition is rooted in the linguistic definition of "idiom". The idiom can be seen by developers as an action on a programming concept underlying a pattern in code, which is represented in implementation by contiguous or scattered code snippets. Generally speaking, a programming idiom's semantic role is a natural language expression of a simple task, algorithm, or data structure that is not a built-in feature in the programming language being used, or, conversely, the use of an unusual or notable feature that ''is'' built into a programming language. Knowing the idioms associated with a programming language and how to use them is an important part of gaining fluency in that langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |