|
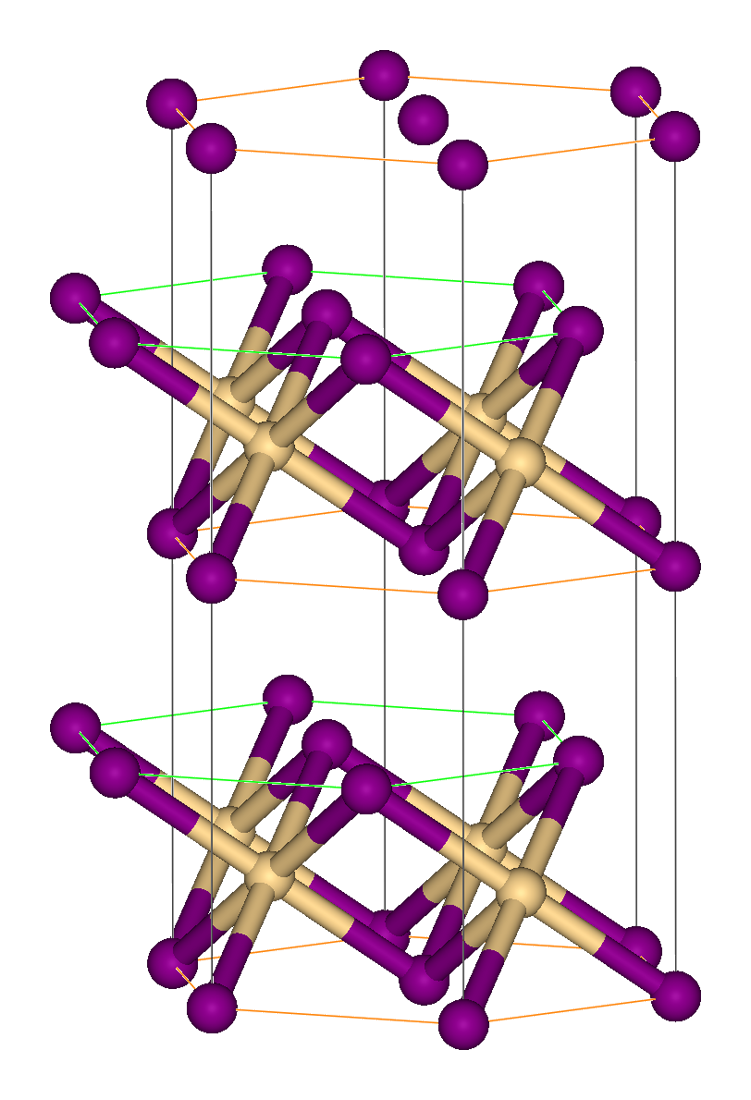
Iron(II) Iodide
Iron(II) iodide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula FeI2. It is used as a catalyst in organic reactions. Preparation Iron(II) iodide can be synthesised by the reaction of iron with iodine at 500 °C: : This is in contrast to the other iron(II) halides, which are best prepared by reaction of heated iron with the appropriate hydrohalic acid. : Alternatively, the synthesis can be carried out by treating freshly reduced iron with concentrated hydriodic acid under a nitrogen atmosphere in methanol. The initially obtained hexamethanol solvate is then thermally decomposed to anhydrous iodide: : :: Extremely finely divided iron(II) iodide is obtained by thermal decomposition of tetracarbonyldiiodidoiron(II) (Fe(CO)4I2). In contrast to the ferrous fluoride, chloride and bromide, which form known hydrates, the diiodide is speculated to form a stable tetrahydrate but it not been characterized directly. Chemical properties Iron(II) iodide is a hygroscopic red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iron(II) Fluoride
Iron(II) fluoride or ferrous fluoride is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula FeF2. It forms a tetrahydrate FeF2·4H2O that is often referred to by the same names. The anhydrous and hydrated forms are white crystalline solids.Dale L. Perry (1995),Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, page 167. CRC Press. Structure and bonding Anhydrous FeF2 adopts the TiO2 rutile structure. As such, the iron cations are octahedral and fluoride anions are trigonal planar. The tetrahydrate can exist in two structures, or polymorphs. One form is rhombohedral and the other is hexagonal, the former having a disorder. Like most fluoride compounds, the anhydrous and hydrated forms of iron(II) fluoride feature high spin metal center. Low temperature neutron diffraction studies show that the FeF2 is antiferromagnetic. Heat capacity measurements reveal an event at 78.3 K corresponding to ordering of antiferromagnetic state. Selected physical properties FeF2 sublimes between 958 and 1178 K. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often abbreviated as MeOH). It is a light, Volatility (chemistry), volatile, colorless and flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odor similar to that of ethanol (potable alcohol), but is more acutely toxic than the latter. Methanol acquired the name wood alcohol because it was once produced through destructive distillation of wood. Today, methanol is mainly produced industrially by hydrogenation of carbon monoxide. Methanol consists of a methyl group linked to a polar hydroxyl group. With more than 20 million tons produced annually, it is used as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to other commodity chemicals, including formaldehyde, acetic acid, methyl tert-butyl ether, methyl ''tert''-butyl ether, methyl benzoate, anisole, peroxyacids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Iron(II) Compounds
In chemistry, iron(II) refers to the element iron in its +2 oxidation state. The adjective ''ferrous'' or the prefix ''ferro-'' is often used to specify such compounds, as in ''ferrous chloride'' for iron(II) chloride (). The adjective ''ferric'' is used instead for iron(III) salts, containing the cation Fe3+. The word ''ferrous'' is derived from the Latin word , meaning "iron". In ionic compounds (salts), such an atom may occur as a separate cation (positive ion) abbreviated as Fe2+, although more precise descriptions include other ligands such as water and halides. Iron(II) centres occur in coordination complexes, such as in the anion ferrocyanide, , where six cyanide ligands are bound the metal centre; or, in organometallic compounds, such as the ferrocene , where two cyclopentadienyl anions are bound to the FeII centre. Ferrous ions in biology All known forms of life require iron. Many proteins in living beings contain iron(II) centers. Examples of such metalloproteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Homeopathic
Homeopathy or homoeopathy is a pseudoscientific system of alternative medicine. It was conceived in 1796 by the German physician Samuel Hahnemann. Its practitioners, called homeopaths or homeopathic physicians, believe that a substance that causes symptoms of a disease in healthy people can cure similar symptoms in sick people; this doctrine is called '' similia similibus curentur'', or "like cures like". Homeopathic preparations are termed ''remedies'' and are made using homeopathic dilution. In this process, the selected substance is repeatedly diluted until the final product is chemically indistinguishable from the diluent. Often not even a single molecule of the original substance can be expected to remain in the product. Between each dilution homeopaths may hit and/or shake the product, claiming this makes the diluent "remember" the original substance after its removal. Practitioners claim that such preparations, upon oral intake, can treat or cure disease. All relevan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lattice Constant
A lattice constant or lattice parameter is one of the physical dimensions and angles that determine the geometry of the unit cells in a crystal lattice, and is proportional to the distance between atoms in the crystal. A simple cubic crystal has only one lattice constant, the distance between atoms, but, in general, lattices in three dimensions have six lattice constants: the lengths ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' of the three cell edges meeting at a vertex, and the angles ''α'', ''β'', and ''γ'' between those edges. The crystal lattice parameters ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' have the dimension of length. The three numbers represent the size of the unit cell, that is, the distance from a given atom to an identical atom in the same position and orientation in a neighboring cell (except for very simple crystal structures, this will not necessarily be distance to the nearest neighbor). Their SI unit is the meter, and they are traditionally specified in angstroms (Å); an angstrom being 0.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Space Group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cadmium Hydroxide
Cadmium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(OH)2. It is a white crystalline ionic compound that is a key component of nickel–cadmium battery.Karl-Heinz Schulte-Schrepping, Magnus Piscator "Cadmium and Cadmium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2007 Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Structure Cadmium hydroxide adopts the same structure as Mg(OH)2, consisting of slabs of metal centers, each bonded by six hydroxide ligands.Hemmingsen, L.; Bauer, R.; Bjerrum, M. J.; Schwarz, K.; Blaha, P.; Andersen, P., "Structure, Chemical Bonding, and Nuclear Quadrupole Interactions of β-Cd(OH)2: Experiment and First Principles Calculations", Inorganic Chemistry 1999, volume 38, 2860-2867. The Cd(OH)2 structure is a recurring motif in inorganic chemistry. For example it is adopted by vanadium ditelluride. Preparation, and reactions Cadmium hydroxide is produced by treating an aqueous solution containing Cd2+ (say cadmium nitrate) with sodium hydroxide: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trigonal Crystal System
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal system and the rhombohedral lattice system are not equivalent (see section crystal systems below). In particular, there are crystals that have trigonal symmetry but belong to the hexagonal lattice (such as α-quartz). The hexagonal crystal family consists of the 12 point groups such that at least one of their space groups has the hexagonal lattice as underlying lattice, and is the union of the hexagonal crystal system and the trigonal crystal system. There are 52 space groups associated with it, which are exactly those whose Bravais lattice is either hexagonal or rhombohedral. __TOC__ Lattice systems The hexagonal crystal family consists of two lattice systems: hexagonal and rhombohedral. Each lattice system consists of one Bravais lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cadmium Iodide
Cadmium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects. Preparation Cadmium iodide is prepared by the addition of cadmium metal, or its oxide, hydroxide or carbonate to hydroiodic acid. Also, the compound can be made by heating cadmium with iodine. Applications Historically, cadmium iodide was used as a catalyst for the Henkel process, a high-temperature isomerisation of dipotassium phthalate to yield the terephthalate. The salt was then treated with acetic acid to yield potassium acetate and commercially valuable terephthalic acid. While uneconomical compared to the production of terephthalic acid from ''p''-xylene, the Henkel method has been proposed as a potential route to produce terephthalic acid from furfural. As existing B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature of constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in a material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of principal axes/edges, of the unit cell and angles between them are lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of a crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of particles in three-dimensional space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydroiodic Acid
Hydroiodic acid (or hydriodic acid) is a colorless liquid. It is an aqueous solution of hydrogen iodide with the chemical formula . It is a strong acid, in which hydrogen iodide is ionized completely in an aqueous solution. Concentrated aqueous solutions of hydrogen iodide are usually 48% to 57% HI by mass. Preparation Reactions Hydroiodic acid reacts with oxygen in air to give iodine: : Like hydrogen halides, hydroiodic acid adds to alkenes to give alkyl iodides. It can also be used as a reducing agent, for example in the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to anilines. Cativa process The Cativa process is a major end use of hydroiodic acid, which serves as a co-catalyst for the production of acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol. Illicit uses Hydroiodic acid is listed as a U.S. Federal DEA List I Chemical, owing to its use as a reducing agent related to the production of methamphetamine from ephedrine or pseudoephedrine Pseudoephedrine, sold under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diethyl Ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound with the chemical formula , sometimes abbreviated as . It is a colourless, highly Volatility (chemistry), volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liquid. It belongs to the ether class of organic compounds. It is a common solvent and was formerly used as a general anesthetic. Production Most diethyl ether is produced as a byproduct of the vapor-phase Hydration reaction, hydration of ethylene to make ethanol. This process uses solid-supported phosphoric acid Catalysis, catalysts and can be adjusted to make more ether if the need arises: Vapor-phase Dehydration reaction, dehydration of ethanol over some Aluminium oxide, alumina catalysts can give diethyl ether yields of up to 95%. : Diethyl ether can be prepared both in laboratories and on an industrial scale by the acid ether synthesis. Uses The dominant use of diethyl ether is as a solvent. One particular application is in the production of cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |