|
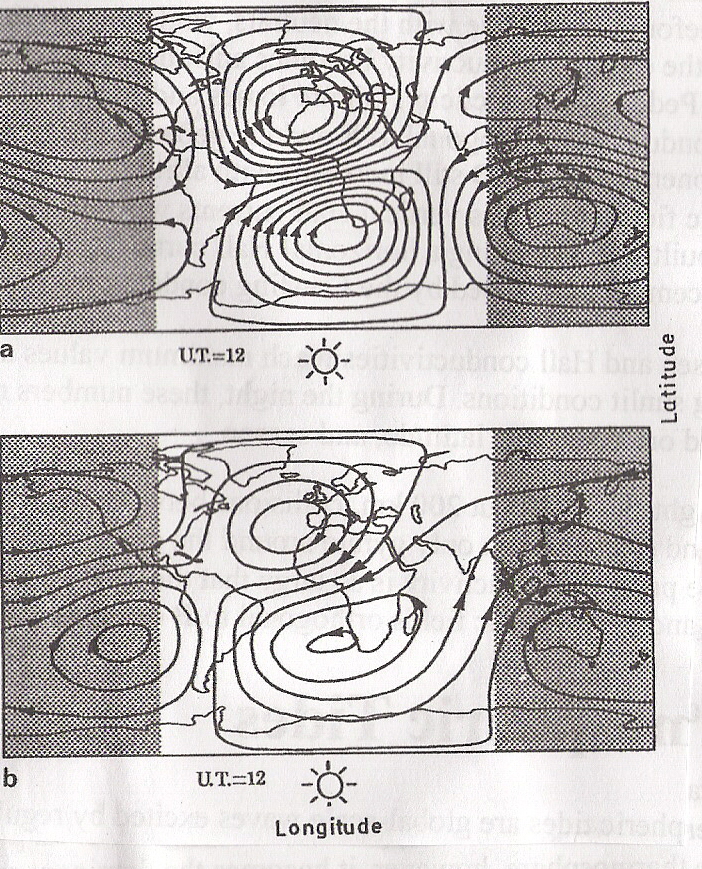
Ionospheric Dynamo Region
In the height region between about 85 and 200 km altitude on Earth, the ionospheric plasma is electrically conducting. Atmospheric tidal winds due to differential solar heating or due to gravitational lunar forcing move the ionospheric plasma against the geomagnetic field lines thus generating electric fields and currents just like a dynamo coil moving against magnetic field lines. That region is therefore called ionospheric dynamo region.Chapman, S.J. and J. Bartels, „Geomagnetism“, Clarendon Press, 1951 The magnetic manifestation of these electric currents on the ground can be observed during magnetospheric quiet conditions. They are called Sq-variations (S=solar; q=quiet) and L-variations (L=lunar) of the geomagnetic field. Additional electric currents are generated by the varying magnetospheric electric convection field. These are the DP1-currents (the auroral electrojets) and the polar DP2-currents. Akasofu, S.I., "Physics of Magnetospheric Substorms", Reidel, Dord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geomagnetic Field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from . As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11° with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were an enormous bar magnet placed at that angle through the center of Earth. The North geomagnetic pole (Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada) actually represents the South pole of Earth's magnetic field, and conversely the South geomagnetic pole correspon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spherical Harmonics
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields. The table of spherical harmonics contains a list of common spherical harmonics. Since the spherical harmonics form a complete set of orthogonal functions and thus an orthonormal basis, every function defined on the surface of a sphere can be written as a sum of these spherical harmonics. This is similar to periodic functions defined on a circle that can be expressed as a sum of circular functions (sines and cosines) via Fourier series. Like the sines and cosines in Fourier series, the spherical harmonics may be organized by (spatial) angular frequency, as seen in the rows of functions in the illustration on the right. Further, spherical harmonics are basis functions for irreducible representations of SO(3), the group of rotations in three dimensions, and thus play a cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vortex
In fluid dynamics, a vortex (: vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil. Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis. In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex carries s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, Geodesy, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observatory and professor of astronomy from 1807 until his death in 1855. While studying at the University of Göttingen, he propounded several mathematical theorems. As an independent scholar, he wrote the masterpieces ''Disquisitiones Arithmeticae'' and ''Theoria motus corporum coelestium''. Gauss produced the second and third complete proofs of the fundamental theorem of algebra. In number theory, he made numerous contributions, such as the Gauss composition law, composition law, the Quadratic reciprocity, law of quadratic reciprocity and the Fermat polygonal number theorem. He also contributed to the theory of binary and ternary quadratic forms, the construction of the heptadecagon, and the theory of Hypergeometric function, hypergeometric ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |