|
Hydrolyzed Corn Gluten
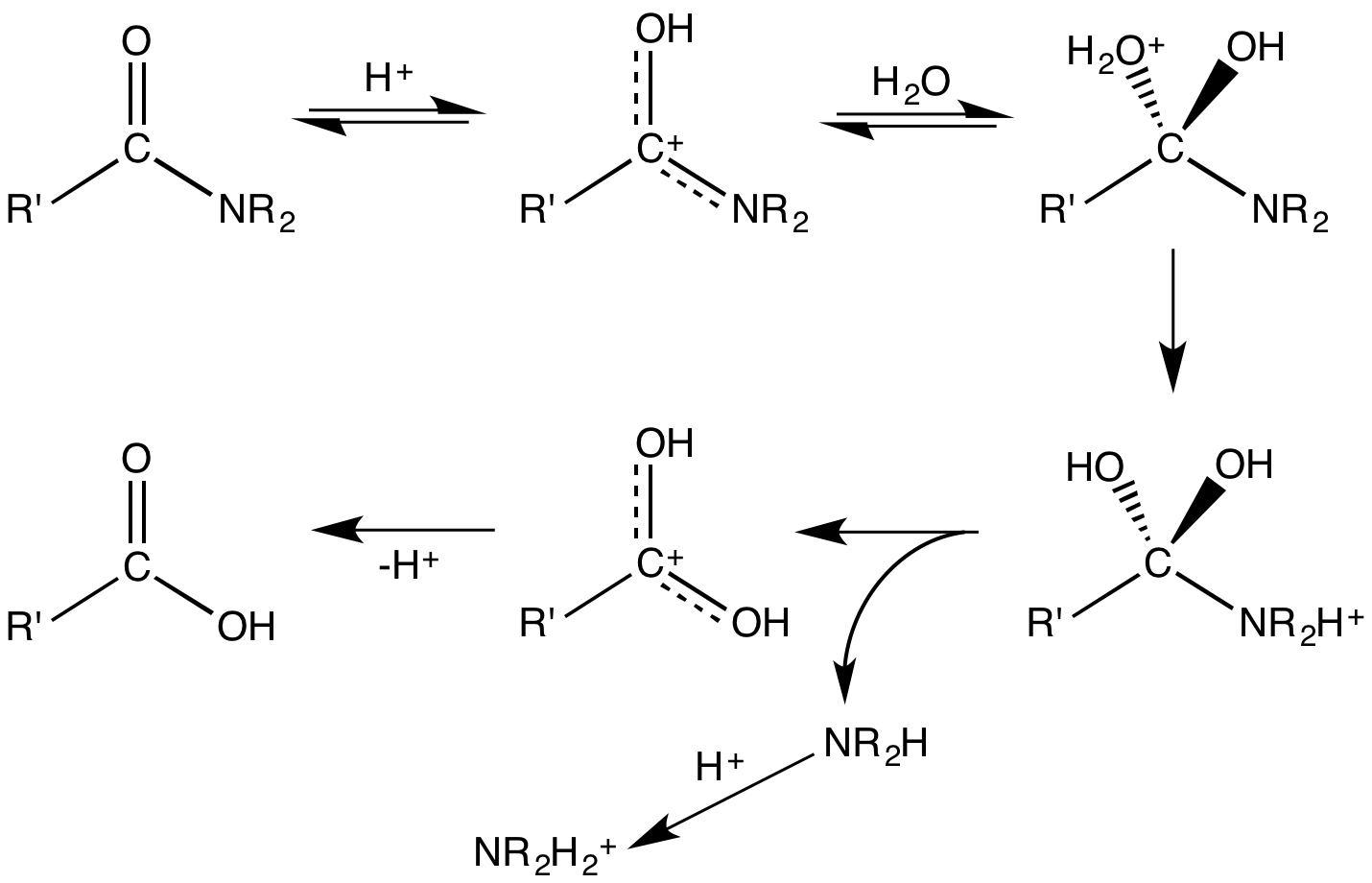
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. In su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Self-ionization Of Water
The self-ionization of water (also autoionization of water, autoprotolysis of water, autodissociation of water, or simply dissociation of water) is an ionization reaction in properties of water, pure water or in an aqueous solution, in which a water molecule, H2O, deprotonation, deprotonates (loses the nucleus of one of its hydrogen atoms) to become a hydroxide ion, OH−. The hydron (chemistry), hydrogen nucleus, H+, immediately protonation, protonates another water molecule to form a hydronium cation, H3O+. It is an example of autoprotolysis, and exemplifies the amphoterism, amphoteric nature of water. History and notation The self-ionization of water was first proposed in 1884 by Svante Arrhenius as part of the theory of ionic dissociation which he proposed to explain the Conductivity (electrolytic), conductivity of electrolytes including water. Arrhenius wrote the self-ionization as H2O H+ + OH-. At that time, nothing was yet known of atomic structure or subatomic particles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brønsted–Lowry Acid–base Theory
The Brønsted–Lowry theory (also called proton theory of acids and bases) is an acid–base reaction theory which was developed independently in 1923 by physical chemists Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted (in Denmark) and Thomas Martin Lowry (in the United Kingdom). The basic concept of this theory is that when an acid and a base react with each other, the acid forms its conjugate base, and the base forms its conjugate acid by exchange of a proton (the hydrogen cation, or H+). This theory generalises the Arrhenius theory. Definitions of acids and bases In the Arrhenius theory, acids are defined as substances that dissociate in aqueous solutions to give H+ ( hydrogen cations or protons), while bases are defined as substances that dissociate in aqueous solutions to give OH− (hydroxide ions). In 1923, physical chemists Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted in Denmark and Thomas Martin Lowry in England both independently proposed the theory named after them. In the Brønsted–Lowry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Conjugate Acid
A conjugate acid, within the Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, is a chemical compound formed when an acid gives a proton () to a base—in other words, it is a base with a hydrogen ion added to it, as it loses a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. On the other hand, a conjugate base is what remains after an acid has donated a proton during a chemical reaction. Hence, a conjugate base is a substance formed by the removal of a proton from an acid, as it can gain a hydrogen ion in the reverse reaction. Because some acids can give multiple protons, the conjugate base of an acid may itself be acidic. In summary, this can be represented as the following chemical reaction: \text + \text \; \ce \; \text + \text Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted and Martin Lowry introduced the Brønsted–Lowry theory, which said that any compound that can give a proton to another compound is an acid, and the compound that receives the proton is a base. A proton is a subatomic particle in the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bisulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a Polyatomic ion, polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salt (chemistry), salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid. Spelling "Sulfate" is the spelling recommended by International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, IUPAC, but "sulphate" was traditionally used in British English. Structure The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedron, tetrahedral arrangement. The symmetry of the isolated anion is the same as that of methane. The sulfur atom is in the +6 oxidation state while the four oxygen atoms are each in the −2 state. The sulfate ion carries an overall charge (physics), charge of −2 and it is the conjugate acid, conjugate base of the bisulfate (or hydrogensulfate) ion, , which is in turn the conjugate base of , sulfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydronium
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the cation , also written as , the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is dissolved in water, as Arrhenius acid molecules in solution give up a proton (a positive hydrogen ion, ) to the surrounding water molecules (). In fact, acids must be surrounded by more than a single water molecule in order to ionize, yielding aqueous and conjugate base. Three main structures for the aqueous proton have garnered experimental support: * the Eigen cation, which is a tetrahydrate, H3O+(H2O)3 * the Zundel cation, which is a symmetric dihydrate, H+(H2O)2 * and the Stoyanov cation, an expanded Zundel cation, which is a hexahydrate: H+(H2O)2(H2O)4 Spectroscopic evidence from well-defined IR spectra overwhelmingly supports the Stoyanov cation as the predominant form. For this reason, it has been suggested that wherever possible, the sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen, with the molecular formula . It is a colorless, odorless, and Viscosity, viscous liquid that is Miscibility, miscible with water. Pure sulfuric acid does not occur naturally due to its Dehydration reaction, strong affinity to water vapor; it is Hygroscopy, hygroscopic and readily absorbs water vapor from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. Concentrated sulfuric acid is a strong oxidant with powerful dehydrating properties, making it highly corrosive towards other materials, from rocks to metals. Phosphorus pentoxide is a notable exception in that it is not dehydrated by sulfuric acid but, to the contrary, dehydrates sulfuric acid to sulfur trioxide. Upon addition of sulfuric acid to water, a considerable amount of heat is releas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Strong Acids
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula , to dissociate into a hydron (chemistry), proton, , and an anion, . The Dissociation (chemistry), dissociation or ionization of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions. : Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (), perchloric acid (), nitric acid () and sulfuric acid (). A weak acid is only partially dissociated, or is partly ionized in water with both the undissociated acid and its dissociation products being present, in solution, in Equilibrium chemistry, equilibrium with each other. : Acetic acid () is an example of a weak acid. The strength of a weak acid is quantified by its acid dissociation constant, K_a value. The strength of a weak organic chemistry, organic acid may depend on substituent effects. The strength of an inorganic chemistry, inorganic acid is dependent on the oxidation state for the atom to which the proton may be atta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Solution (chemistry)
In chemistry, a solution is defined by IUPAC as "A liquid or solid phase containing more than one substance, when for convenience one (or more) substance, which is called the solvent, is treated differently from the other substances, which are called solutes. When, as is often but not necessarily the case, the sum of the mole fractions of solutes is small compared with unity, the solution is called a dilute solution. A superscript attached to the ∞ symbol for a property of a solution denotes the property in the limit of infinite dilution." One important parameter of a solution is the concentration, which is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solution or solvent. The term " aqueous solution" is used when one of the solvents is water. Types ''Homogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture form a single phase. ''Heterogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture are of different phase. The properties of the mixture (such as concentration, temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Historically, vinegar was produced from the third century BC and was likely the first acid to be produced in large quantities. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical across various fields, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is funda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Acetate
An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. alkaline, earthy, metallic, nonmetallic, or radical base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called an anion) typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula . The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a ''positive'' ion (called a cation) are also commonly called "acetates" (hence, ''acetate of lead'', ''acetate of aluminium'', etc.). The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate (called acetic acid) with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion , or . Most of the approximately 5 million tonnes of acetic acid produced annually in industry are used in the production of acetates, which usually take the form of polymers. In nature, acetate is the most common building block for biosynthesis. Nomenclature and common formula When part of a salt, the formula of the acetate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been Leaching (chemistry), leached by the action of water from the Earth, Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in Soap, soap manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |