|
Harakeke
''Phormium tenax'' (called flax in New Zealand English; in Māori; New Zealand flax outside New Zealand; and New Zealand hemp in historical nautical contexts) is an evergreen perennial plant native to New Zealand and Norfolk Island that is an important fibre plant and a popular ornamental plant.Roger Holmes and Lance Walheim. 2005. ''California Home Landscaping'', Creative Homeowner Press The plant grows as a clump of long, straplike leaves, up to two metres long, from which arises a much taller flowering shoot, with dramatic yellow or red flowers. Despite being commonly known as 'flax', harakeke is of the genus ''Phormium'', a monocot, and is a leaf fibre, whereas flax (linen) is of the genus ''Linum'', a rosid, and is a bast fibre (which comes from the stem of the plant). The two plants have an evolutionary extremely distant relationship with each other. The fibre has been widely used since the arrival of Māori to New Zealand, originally in Māori traditional textiles an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tāniko
Tāniko (or taaniko) is a traditional weaving technique of the Māori of New Zealand related to "twining". It may also refer to the resulting bands of weaving, or to the traditional designs. The tāniko technique does not require a loom, although one can be used. Traditionally free hanging warps were suspended between two weaving pegs and the process involved twining downward. The traditional weaving material is muka, fibre prepared from the New Zealand flax (''Phormium tenax'') by scraping, pounding and washing. The muka fibre was dyed using natural dyes. There has been a resurgence of tāniko and other Māori cultural practices starting in the 1950s and as part of the broader Māori Renaissance. This has led to tāniko practitioners Diggeress Te Kanawa and her mother Dame Rangimārie Hetet receiving honorary doctorates from the University of Waikato. The award-winning designer, Adrienne Whitewood ( Rongowhaakata), demonstrates a new wave of Māori designers connecting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Piha
Piha is a coastal settlement in West Auckland, on the western coast of the Auckland Region in New Zealand. It is one of the most popular beaches in the area and a major day-trip destination for Aucklanders throughout the year, and especially in summer. Piha is 39 kilometres west of Auckland city centre, on the Tasman Sea coast to the north of the Manukau Harbour, on the western edge of the Waitākere Ranges. Immediately to the north of Piha is Whites Beach, and immediately to the south is Te Unuhanga-a-Rangitoto / Mercer Bay; land access to both is only by foot. The nearest beaches accessible by road are Karekare to the south, and Anawhata to the north. History The area is traditionally a part of rohe of the Tāmaki Māori tribe Te Kawerau ā Maki. The area is named for Te Piha, the traditional name of Lion Rock which was later applied to the wider area, and refers to the pattern made when waves hit against the rock. The area was the location of many pā and villages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pandanus
''Pandanus'' is a genus of monocots with about 578 accepted species. They are palm-like, dioecious trees and shrubs native to the Old World tropics and subtropics. Common names include pandan, screw palm and screw pine. The genus is classified in the order Pandanales, family Pandanaceae, and is the largest in the family. Description The species vary in size from small shrubs less than tall, to medium-sized trees tall, typically with a broad canopy, heavy fruit, and moderate growth rate. The trunk is stout, wide-branching, and ringed with many leaf scars. Mature plants can have branches. Depending on the species, the trunk can be smooth, rough, or warty. The roots form a pyramidal tract to hold the trunk. They commonly have many thick stilt roots near the base, which provide support as the tree grows top-heavy with leaves, fruit, and branches. These roots are adventitious and often branched. The top of the plant has one or more crowns of strap-shaped leaves that may be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tukutuku
Tukutuku panelling is a distinctive art form of the Māori people of New Zealand, a traditional latticework used to decorate meeting houses (wharenui). Other names are Tuitui and Arapaki. Tukutuku flank the posts around the edge of the wharenui; the posts are usually carved and represent ancestors. The patterns of tukutuku have symbolic meanings. Tukutuku are made with various materials. One description is vertical rods of toetoe stalks, with wooden slats across. These slats are held in place with knotting or weaving that forms a decorative pattern. The materials for this weaving are narrow strips of kiekie or harakeke, some died black and the coastal plant pingao as yellow colour. The traditional skills of tukutuku are held mostly within the Māori women weaving community alongside other Māori traditional weaving techniques as the skills of whakaīro (carving) are mostly held within the Māori men carving community. Tukutuku for a wharenui are designed alongside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
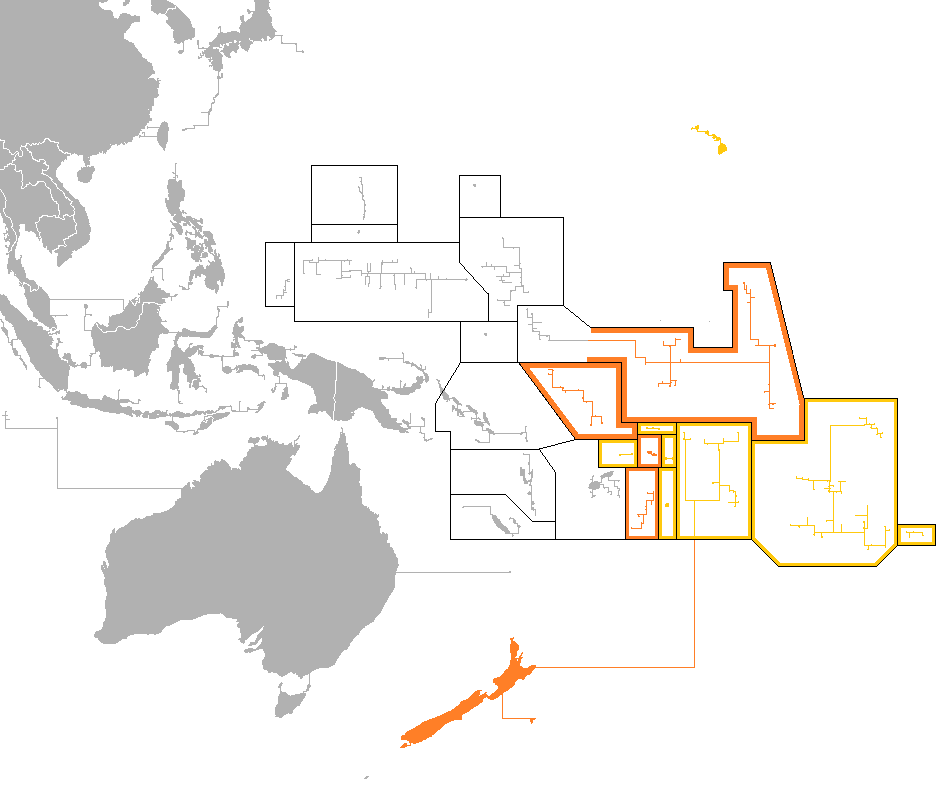
Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including Polynesian languages, linguistic relations, Polynesian culture, cultural practices, and Tradition, traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and Polynesian navigation, using stars to navigate at night. The term was first used in 1756 by the French writer Charles de Brosses, who originally applied it to all the list of islands in the Pacific Ocean, islands of the Pacific. In 1831, Jules Dumont d'Urville proposed a narrower definition during a lecture at the Société de Géographie of Paris. By tradition, the islands located in the South Seas, southern Pacific have also often been called the South Sea Islands, and their inhabitants have been called South Sea Islanders. The Hawai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paper Mulberry
The paper mulberry (''Broussonetia papyrifera'', syn. ''Morus papyrifera'' L.) is a species of flowering plant in the family Moraceae. It is native to Asia,''Broussonetia papyrifera''. Flora of North America. where its range includes mainland China, Taiwan, Japan, Korea, Southeast Asia, , and India. It is widely cultivated elsewhere and it grows as an in New Zealand, parts of Europe, the United States, and Africa. Other common names include tapa cloth tree.
|