|
Guineesine
Guineesine (or guineensine) is a compound isolated from long pepper (''Piper longum'') and black pepper (''Piper nigrum''). It was first isolated, studied and named from '' Piper guineense''. Research Guineensine inhibits the cellular reuptake of anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol in a mouse model ( EC50 = 290 nM). This causes an increase in the activity of the two neurotransmitters which are classified as endogenous cannabinoids. Guineesine can dose-dependently produce cannabimimetic effects in a mouse model which are indicated by potent catatonic, analgesic, hypo-locomotive and hypo-thermic effects. In addition, the analgesic and catatonic effects were reversed by the cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) inverse agonist rimonabant. Guineesine is also a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) ''in vitro ''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Pepper
Long pepper (''Piper longum''), sometimes called Indian long pepper or ''pippali'', is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit, which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. Long pepper has a taste similar to, but sweeter and more pungent than, that of its close relative '' Piper nigrum'' – from which black, green and white pepper are obtained. The fruit of the pepper consists of many minuscule fruits – each about the size of a poppy seed – embedded in the surface of a flower spike that closely resembles a hazel tree catkin. Like ''Piper nigrum'', the fruits contain the compound piperine, which contributes to their pungency. Another species of long pepper, '' Piper retrofractum'', is native to Java, Indonesia. The fruits of this plant are often confused with chili peppers, which belong to the genus ''Capsicum'', originally from the Americas. History Use of long pepper occurred in Greece in the sixth or fifth century BCE, thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypolocomotion
Locomotor activity is a measure of animal behavior which is employed in scientific research. Hyperlocomotion, also known as locomotor hyperactivity, hyperactivity, or increased locomotor activity, is an effect of certain drugs in animals in which locomotor activity (locomotion) is increased. It is induced by certain drugs like psychostimulants and NMDA receptor antagonists and is reversed by certain other drugs like antipsychotics and certain antidepressants. Stimulation of locomotor activity is thought to be mediated by increased signaling in the nucleus accumbens, a major brain area involved in behavioral activation and motivation, motivated behavior. Hypolocomotion, also known as locomotor hypoactivity, hypoactivity, and decreased locomotor activity, is an effect of certain drugs in animals in which locomotor activity is decreased. It is a characteristic effect of many sedative agents and general anesthetics. Antipsychotics, which are dopamine receptor antagonists, and many s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
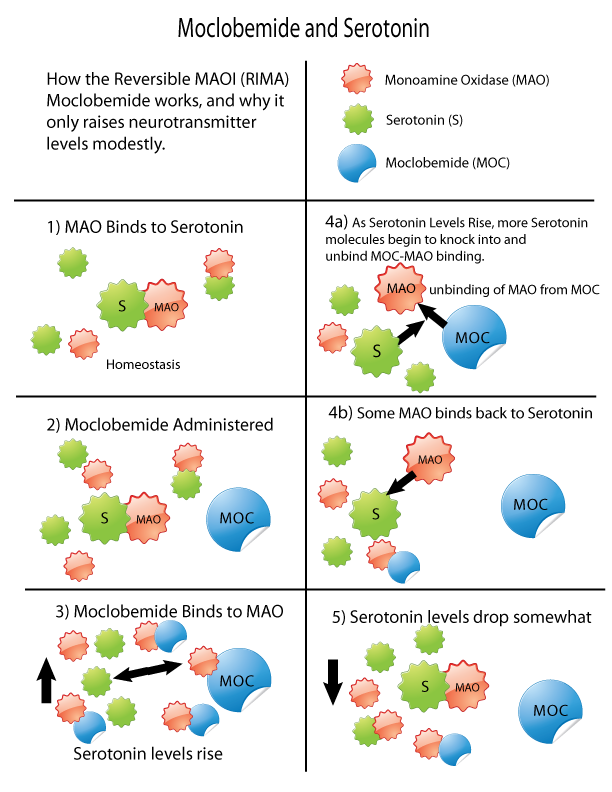
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with agoraphob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzodioxoles
The substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamines (abbreviated as MDxx) represent a diverse chemical class of compounds derived from phenethylamines. This category encompasses numerous Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substances with Empathogen, entactogenic, Psychedelic drug, psychedelic, and/or stimulant properties, in addition to entheogens. These compounds find application as research chemicals, designer drugs, and recreational substances. The base chemical compound, compound of the MDxx class is methylenedioxyphenethylamine, 3,4-methylenedioxyphenethylamine (MDPEA), and the prototypical agent of this class is MDMA, 3,4-methylenedioxy-''N''-methylamphetamine (MDMA; "ecstasy"). Other notable MDxx class substances include 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA), methylenedioxyethylamphetamine, 3,4-methylenedioxy-''N''-ethylamphetamine (MDEA; "Eve"), methylbenzodioxolylbutanamine, ''N''-methyl-1,3-benzodioxolylbutanamine (MBDB; "Eden"), and methylenedioxymethcathinone, 3,4-methylenedioxy- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloids Found In Plants
Alkaloids are a broad class of naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals. They can be purified from crude extracts of these organisms by acid-base extraction, or solvent extractions followed by silica-gel column chromatography. Alkaloids have a wide range of pharmacological activities including antimalarial (e.g. quinine), antiasthma (e.g. ephedrine), anticancer (e.g. homoharringtonine), cholinomimetic (e.g. galantamine), vasodilatory (e.g. vincamine), antiarrhythmic (e.g. quinidine), analgesic (e.g. morphine), antibacterial (e.g. chelerythrine), and antihyperglycemic activities (e.g. berberine). Many have found use in traditional or modern medicine, or as starting points for drug discovery. Other alkaloids possess psychotropic (e.g. psilocin) and stimulant activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IC50
Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is a measure of the potency of a substance in inhibiting a specific biological or biochemical function. IC50 is a quantitative measure that indicates how much of a particular inhibitory substance (e.g. drug) is needed to inhibit, ''in vitro'', a given biological process or biological component by 50%. The biological component could be an enzyme, cell, cell receptor or microbe. IC50 values are typically expressed as molar concentration. IC50 is commonly used as a measure of antagonist drug potency in pharmacological research. IC50 is comparable to other measures of potency, such as EC50 for excitatory drugs. EC50 represents the dose or plasma concentration required for obtaining 50% of a maximum effect ''in vivo''. IC50 can be determined with functional assays or with competition binding assays. Sometimes, IC50 values are converted to the pIC50 scale. :\ce = -\log_ \ce Due to the minus sign, higher values of pIC50 indicate ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, known as clinical trials, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' (Latin language, Latin for "in glass"; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a drug class, class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that binding selectivity, selectively and Enzyme inhibitor#Reversible inhibitors, reversibly enzyme inhibitor, inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the medication, treatment of major depressive disorder, depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rimonabant
Rimonabant (also known as SR141716; trade names Acomplia, Zimulti) is an anorectic antiobesity drug approved in Europe in 2006 but was withdrawn worldwide in 2008 due to serious psychiatric side effects; it was never approved in the United States. Rimonabant is an inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 and was first-in-class for clinical development. History Rimonabant is a selective CB1 receptor blocker and was discovered and developed by Sanofi-Aventis. On 21 June 2006, the European Commission approved the sale of rimonabant in the then-25-member European Union as a prescription drug for use in conjunction with diet and exercise for patients with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2, or patients with a BMI greater than 27 kg/m2 with associated risk factors, such as type 2 diabetes or dyslipidaemia. FroEMA index page It was first in its class to be approved anywhere in the world. Rimonabant was submitted to the Food and Drug Administration ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
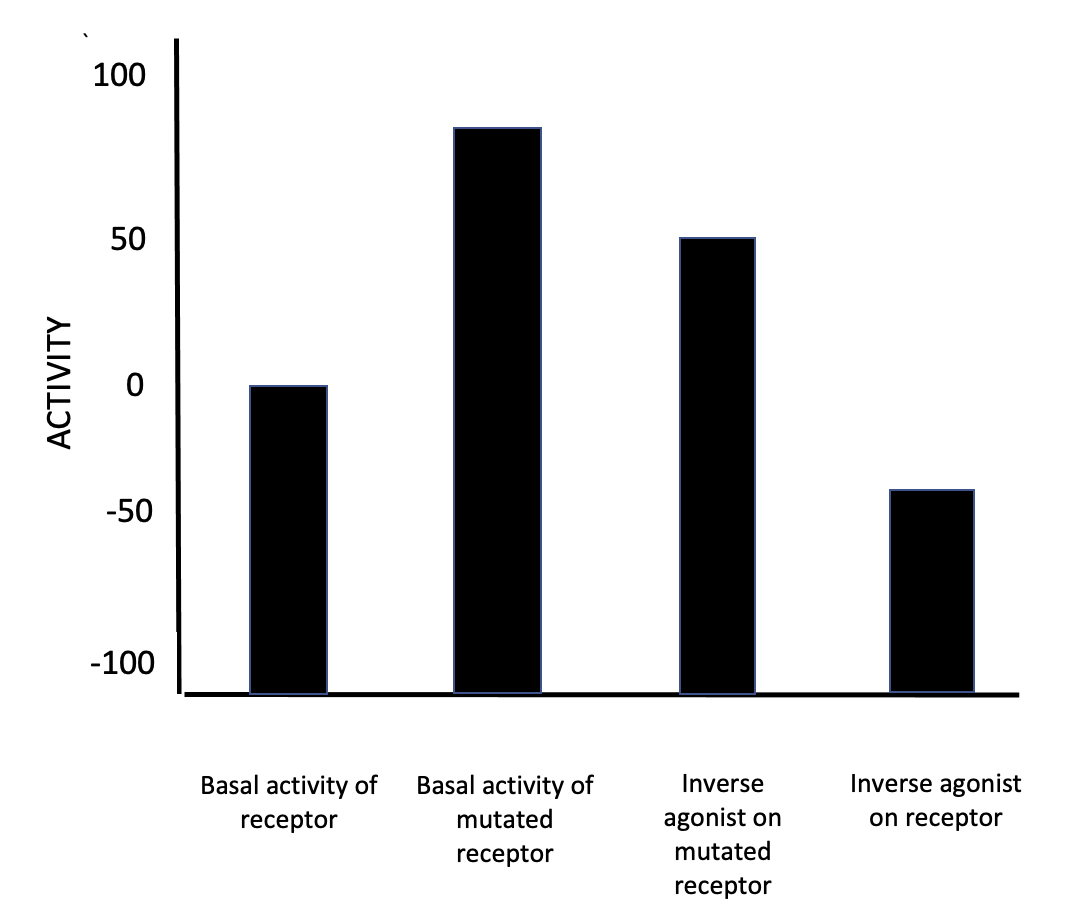
Inverse Agonist
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either; they are in fact sometimes called ''blockers'' (examples include alpha blockers, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers). Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1
Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1), is a G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''CNR1'' gene. And discovered, by determination and characterization in 1988, and cloned in 1990 for the first time. The human CB1 receptor is expressed in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. It is activated by endogenous cannabinoids called endocannabinoids, a group of retrograde neurotransmitters that include lipids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol; plant phytocannabinoids, such as docosatetraenoylethanolamide found in wild dagga, the compound tetrahydrocannabinol which is an active constituent of the psychoactive drug cannabis; and synthetic analogs of tetrahydrocannabinol. CB1 is antagonized by the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabivarin at low doses and at higher doses, it activates the CB1 receptor as an agonist, but with less potency than tetrahydrocannabinol. The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |