|
Guaiacol
Guaiacol () is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OH)(OCH3). It is a phenolic compound containing a methoxy functional group. Guaiacol appears as a viscous colorless oil, although aged or impure samples are often yellowish. It occurs widely in nature and is a common product of the pyrolysis of wood. Occurrence Guaiacol is usually derived from guaiacum or wood creosote. There also appears to be a petrochemical route to it with great commercial use. It is produced by a variety of plants. It is also found in essential oils from celery seeds, tobacco leaves, orange leaves, and lemon peels. The pure substance is colorless, but samples become yellow upon exposure to air and light. The compound is present in wood smoke, resulting from the pyrolysis of lignin. The compound contributes to the flavor of many substances such as whiskey and roasted coffee. Preparation The compound was first isolated by Otto Unverdorben in 1826. Guaiacol is produced by methylation of ''o''-cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creosote
Creosote is a category of carbonaceous chemicals formed by the distillation of various tars and pyrolysis of plant-derived material, such as wood, or fossil fuel. They are typically used as preservatives or antiseptics. Some creosote types were used historically as a treatment for components of seagoing and outdoor wood structures to prevent rot (e.g., bridgework and railroad ties, see image). Samples may be found commonly inside chimney flues, where the coal or wood burns under variable conditions, producing soot and tarry smoke. Creosotes are the principal chemicals responsible for the stability, scent, and flavor characteristic of smoked meat; the name is derived . The two main kinds recognized in industry are coal-tar creosote and wood-tar creosote. The coal-tar variety, having stronger and more toxic properties, has chiefly been used as a preservative for wood; coal-tar creosote was also formerly used as an escharotic, to burn malignant skin tissue, and in dentistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methoxyphenol
Methoxyphenol or hydroxyanisole may refer to: * 2-Methoxyphenol (guaiacol, ''o''-methoxyphenol, methylcatechol, 2-hydroxyanisole) * 3-Methoxyphenol (''m''-methoxyphenol, ''m''-guaiacol, resorcinol monomethyl ether, 3-hydroxyanisole, ''m''-hydroxyanisole) * 4-Methoxyphenol (mequinol, para-guaiacol, 4-hydroxyanisole) {{Chemistry index Phenol ethers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
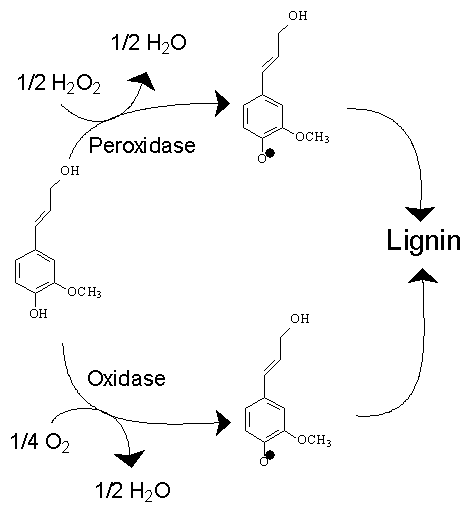
Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance "lignine", which is derived from the Latin word '' lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose and chitin. Lignin constitutes 30% of terrestrial non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 35% of the dry mass of wood. Lignin is present in red algae, which suggest that the common ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoke
Smoke is an aerosol (a suspension of airborne particulates and gases) emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires (including stoves, candles, internal combustion engines, oil lamps, and fireplaces), but may also be used for pest control ( fumigation), communication ( smoke signals), defensive and offensive capabilities in the military ( smoke screen), cooking, or smoking (tobacco, cannabis, etc.). It is used in rituals where incense, sage, or resin is burned to produce a smell for spiritual or magical purposes. It can also be a flavoring agent and preservative. Smoke inhalation is the primary cause of death in victims of indoor fires. The smoke kills by a combination of thermal damage, poisoning and pulmonary irritation caused by carbon monoxide, hydrogen cyanide and other combustion products. Smoke is an aerosol (or mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catechol
Catechol ( or ), also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is the ''ortho'' isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances. Small amounts of catechol occur in fruits and vegetables. Isolation and synthesis Catechol was first isolated in 1839 by Edgar Hugo Emil Reinsch (1809–1884) by distilling it from the solid tannic preparation catechin, which is the residuum of catechu, the boiled or concentrated juice of ''Mimosa catechu'' ('' Acacia catechu''). Upon heating catechin above its decomposition point, a substance that Reinsch first named ''Brenz-Katechusäure'' (burned catechu acid) sublimated as a white efflo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance "lignine", which is derived from the Latin word '' lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose and chitin. Lignin constitutes 30% of terrestrial non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 35% of the dry mass of wood. Lignin is present in red algae, which suggest that the common ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demethylation
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms. The counterpart of demethylation is methylation. In biochemistry : Demethylation is relevant to epigenetics. Demethylation of DNA is catalyst, catalyzed by demethylases. These enzymes oxidize N-methyl groups, which occur in histones, in lysine derivatives, and in some forms of DNA. :R2N-CH3 + O → R2N-H + CH2O One family of such oxidative enzymes is the cytochrome P450. Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases are also active for demethylation of DNA, operating by a similar stoichiometry. These reactions, which proceed via hydroxylation, exploit the slightly weakened Carbon–hydrogen bond, C-H bonds of methylamines and methyl ethers. Demethylation of some sterols are steps in the biosynthesis of testosterone and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazonium
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide. The parent, compound where R is hydrogen, is diazenylium. Structure and general properties Arene derivatives According to X-ray crystallography the linkage is linear in typical diazonium salts. The bond distance in benzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate is 1.083(3) Å, which is almost identical to that for dinitrogen molecule (N≡N). The linear free energy constants σm and σp indicate that the diazonium group is strongly electron-withdrawing. Thus, the diazonio-substituted phenols and benzoic acids have greatly reduced p''K''a values compared to their unsubstituted counterparts. The p''K''a of phenolic proton of 4-hydroxybenzenediazonium is 3.4, versus 9.9 for phenol itself. In other words, the diazonium group raises the ionization constant ''K''a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylation
Methylation, in the chemistry, chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate (chemistry), substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen#Compounds, hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and biology. In biological systems, methylation is Catalysis, catalyzed by enzymes; such methylation can be involved in modification of heavy metals, regulation of gene expression, regulation of Protein#Functions, protein function, and RNA processing. ''In vitro'' methylation of tissue samples is also a way to reduce some histology#Histological Artifacts, histological staining artifacts. The reverse of methylation is demethylation. In biology In biological systems, methylation is accomplished by enzymes. Methylation can modify heavy metals and can regulate gene expression, RNA processing, and protein function. It is a key pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-Anisidine
''o''-Anisidine (2-anisidine) is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4NH2. A colorless liquid, commercial samples can appear yellow owing to air oxidation. It is one of three isomers of the methoxy-containing aniline derivative. Production and use It is prepared via methanolysis of 2-chloronitrobenzene: :NaOCH3 + ClC6H4NO2 → CH3OC6H4NO2 + NaCl The resulting ''o''-nitroanisole is reduced to ''o''-anisidine. ''o''-Anisidine is used in the manufacture of dyes. It is nitrated to give 4-nitroanisidine. It is also a precursor to ''o''-dianisidine. One special use is as a heartwood indicator. An acid solution of ''o''-anisidine is diazotized by adding a sodium nitrite solution. This mixture is applied to the wood and by reaction with polyphenols in the heartwood a reddish brown azo dye is formed. : Safety and environmental aspects ''o''-Anisidine is a dangerous pollutant from the production of dyes. It is listed as RCRA hazardous waste Hazardous waste is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Sulfate
Dimethyl sulfate (DMS) is a chemical compound with formula (CH3O)2SO2. As the diester of methanol and sulfuric acid, its formula is often written as ( CH3)2 SO4 or Me2SO4, where CH3 or Me is methyl. Me2SO4 is mainly used as a methylating agent in organic synthesis. Me2SO4 is a colourless oily liquid with a slight onion-like odour. Like all strong alkylating agents, Me2SO4 is toxic. Its use as a laboratory reagent has been superseded to some extent by methyl triflate, CF3SO3CH3, the methyl ester of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. History Impure dimethyl sulfate was prepared in the early 19th century. J. P. Claesson later extensively studied its preparation. It was investigated for possible use in chemical warfare in World War I in 75% to 25% mixture with methyl chlorosulfonate (CH3ClO3S) called "C-stoff" in Germany, or with chlorosulfonic acid called "Rationite" in France. The esterification of sulfuric acid with methanol was described in 1835: : Production Dimethyl s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |