|
Gerenuk
The gerenuk (''Litocranius walleri''), also known as the giraffe gazelle, is a long-necked, medium-sized antelope found in parts of East Africa. The sole member of the genus ''Litocranius'', the gerenuk was first described by the naturalist Victor Brooke in 1879. It is characterised by its long, slender neck and limbs. The antelope is tall, and weighs between . Two types of colouration are clearly visible on the smooth coat: the reddish brown back or the "saddle", and the lighter flanks, fawn to buff. The horns, present only on males, are lyre-shaped. Curving backward then slightly forward, these measure . Taxonomy and phylogeny The gerenuk was first described by Victor Brooke in 1879 on the basis of three male specimens procured on "the mainland of Africa, north of the island of Zanzibar". Brooke used the scientific name ''Gazella walleri'', on the request of Gerald Waller (who provided the specimens) to name it after his deceased brother. The type locality was later co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibatag
The dibatag (''Ammodorcas clarkei''), or Clarke's gazelle, is a medium-sized slender antelope native to Ethiopia and Somalia. Though not a true gazelle, it is similarly marked, with long legs and neck. It is often confused with the gerenuk due to their striking resemblance. The typical head-and-body length is about . They stand up to about . Male dibatag weigh between , whereas females range from . The length of the curved horns, present only on males, is typically between . The upper parts are gray to fawn, while the dorsal and lateral areas are cinnamon to rufous (reddish brown). The underparts, rump and the insides of the legs are all white. While markings are visible on the face, there are none on the flanks or the buttocks. Dibatag are alert and secretive, and their brown coat provides an excellent camouflage, making the dibatag one of the antelopes most difficult to hunt. They are diurnal animals, and navigate in very small herds. Both sexes attain sexual maturity at 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Diego Zoo
The San Diego Zoo is a zoo in San Diego, California, United States, located in Balboa Park (San Diego), Balboa Park. It began with a collection of animals left over from the 1915 Panama–California Exposition that were brought together by its founder, Dr. Harry M. Wegeforth. The zoo was a pioneer in the concept of open-air, cage-less exhibits that recreate natural animal habitats. The zoo sits on 100 acres (40 ha) of land leased from the City of San Diego. It houses over 12,000 animals of more than 680 species and subspecies. It is the most visited zoo in the United States; travelers have cited it as one of the best zoos in the world. Its parent organization, the San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance, is a private nonprofit conservation organization and has one of the largest zoological membership associations in the world. The San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance also operates the San Diego Zoo Safari Park. History The San Diego Zoo grew out of exotic animal exhibitions abandoned afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antelope
The term antelope refers to numerous extant or recently extinct species of the ruminant artiodactyl family Bovidae that are indigenous to most of Africa, India, the Middle East, Central Asia, and a small area of Eastern Europe. Antelopes do not form a monophyletic group, as some antelopes are more closely related to other bovid groups, such as bovines, goats, and sheep, than to other antelopes. A stricter grouping, known as the true antelopes, includes only the genera '' Gazella'', '' Nanger'', '' Eudorcas'', and '' Antilope''. One North American mammal, the pronghorn or "pronghorn antelope", is colloquially referred to as the "American antelope", despite the fact that it belongs to a completely different family ( Antilocapridae) than the true Old-World antelopes; pronghorn are the sole extant member of an extinct prehistoric lineage that once included many unique species. Although antelope are sometimes referred to, and easily misidentified as, "deer" ( cervids), true ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
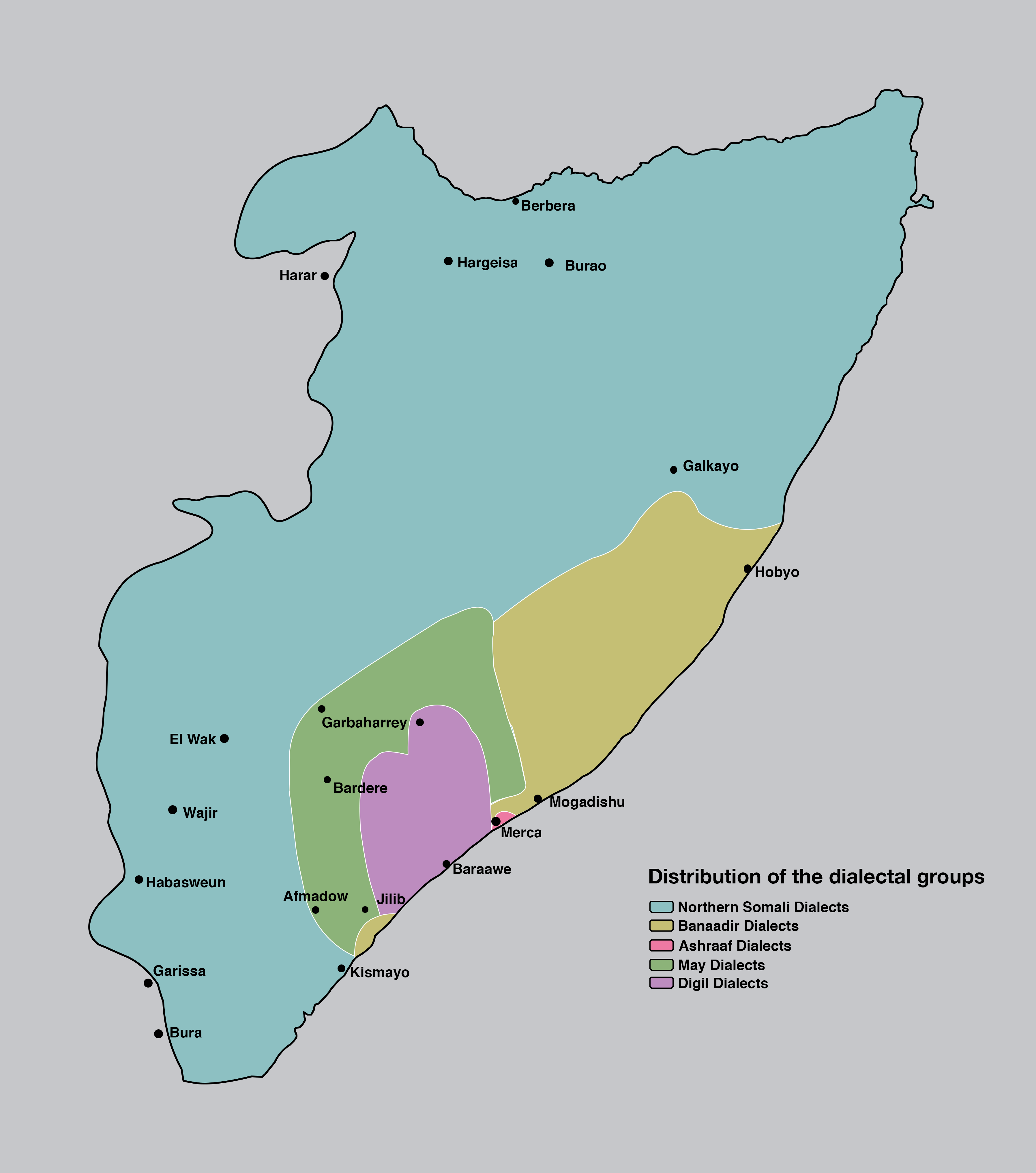
Somali Language
Somali is an Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch, primarily spoken by the Somalis, Somali people, native to Greater Somalia. It is an official language in Somalia, Somaliland, and Ethiopia; one of the two national languages in Djibouti; and a recognised minority language in Kenya. Somali is officially written in the Latin script (Somali Latin alphabet), with the Arabic script (Wadaad's writing) and several local scripts (Osmanya script, Osmanya, Kaddare script, Kaddare and Gadabuursi Somali Script, Borama scripts) being informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134–156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic languages, Lowland East Cushitic in addition to Afar language, Afar and Saho language, Saho. Somali is the bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe (biology)
In biology, a tribe is a taxonomic rank above genus, but below family and subfamily. It is sometimes subdivided into subtribes. By convention, all taxa ranked above species are capitalized, including both tribe and subtribe. In zoology, the standard ending for the name of a zoological tribe is "-ini". Examples include the tribes Caprini (goat-antelopes), Hominini (hominins), Bombini (bumblebees), and Thunnini (tunas). The tribe Hominini is divided into subtribes by some scientists; subtribe Hominina then comprises "humans". The standard ending for the name of a zoological subtribe is "-ina". In botany, the standard ending for the name of a botanical tribe is "-eae". Examples include the tribes Acalypheae and Hyacintheae. The tribe Hyacintheae is divided into subtribes, including the subtribe Massoniinae. The standard ending for the name of a botanical subtribe is "-inae". In bacteriology, the form of tribe names is as in botany, e.g., Pseudomonadeae, based on the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome C Oxidase Subunit III
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit III (COX3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MT-CO3'' gene. It is one of main transmembrane subunits of cytochrome c oxidase. It is also one of the three mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) encoded subunits (MT-CO1, MT-CO2, MT-CO3) of respiratory complex IV. Variants of it have been associated with isolated myopathy, severe encephalomyopathy, Leber hereditary optic neuropathy, mitochondrial complex IV deficiency, and recurrent myoglobinuria . Structure The ''MT-CO3'' gene produces a 30 kDa protein composed of 261 amino acids. COX3, the protein encoded by this gene, is a member of the cytochrome c oxidase subunit 3 family. This protein is located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. COX3 is a multi-pass transmembrane protein: in human, it contains 7 transmembrane domains at positions 15–35, 42–59, 81–101, 127–147, 159–179, 197–217, and 239–259. Function Cytochrome c oxidase () is the terminal enzyme of the respiratory chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome B
Cytochrome b is a protein found in the membranes of aerobic cells. In eukaryotic mitochondria (inner membrane) and in aerobic prokaryotes, cytochrome b is a component of respiratory chain complex III () — also known as the bc1 complex or ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase. In plant chloroplasts and cyanobacteria, there is a homologous protein, cytochrome b6, a component of the plastoquinone-plastocyanin reductase (), also known as the b6f complex. These complexes are involved in electron transport, the pumping of protons to create a proton-motive force ( PMF). This proton gradient is used for the generation of ATP. These complexes play a vital role in cells. Structure and function Cytochrome b/b6 is an integral membrane protein of approximately 400 amino acid residues that probably has 8 transmembrane segments. In plants and cyanobacteria, cytochrome b6 consists of two protein subunits encoded by the petB and petD genes. Cytochrome b/b6 non-covalently binds two heme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in question. In addition to their use for inferring phylogenetic pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin Groves
Colin Peter Groves (24 June 1942 – 30 November 2017) was a British-Australian biologist and anthropologist. Groves was professor of biological anthropology at the Australian National University in Canberra, Australia. Education Born in England, Groves completed a Bachelor of Science at University College London in 1963, and a Doctor of Philosophy at the Royal Free Hospital School of Medicine in 1966. From 1966 to 1973, he was a postdoctoral researcher and teaching fellow at the University of California, Berkeley, Queen Elizabeth College and the University of Cambridge. Career Groves emigrated to Australia in 1973 and joined the Australian National University, where he was promoted to full professor in 2000 and remained emeritus professor until his death. Along with the Czech biologist Professor Vratislav Mazák, Groves was the describer of ''Homo ergaster''. Groves also wrote ''Primate Taxonomy'' published by the Smithsonian Institution Press in 2001, and ''Ungulate Taxono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shebelle River
The Shebelle River ( Oromo: Laga Shabeellee, , , ) also known historically as the Nile of Mogadishu, begins in the highlands of Ethiopia, and then flows southeast into Somalia towards Mogadishu. Near Mogadishu, it turns sharply southwest, where it follows the coast. Below Mogadishu, the river becomes seasonal. During most years, the river dries up near the mouth of the Jubba River, while in seasons of heavy rainfall, the river actually reaches the Jubba and thus the ocean. During periods of heavy rainfall in Ethiopia, the Shebelle River and the Jubba River merge, and their combined waters ultimately reach the Indian Ocean. However, in drier years, the Shebelle River diminishes and transforms into a series of wetlands and sandy plains to the northeast of the confluence with the Jubba. The Shebelle River has a total length of 1,820 km. The area surrounding the Shebeli River is inhabited by Somali people in the Somali Region of Ethiopia and Somali people in Somalia. In the lower bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galcaio
Galkayo (, ,Dr Badal Kariye Ba Bsit Ma Mba & Phd, ''The Kaleidoscopic Lover: The Civil War in the Horn of Africa & My Itinerary for a Peaceful Lover'', (AuthorHouse: 2010), p.116. Italian: ''Gallacaio also known as Rocca Littorio'') is the third-largest city in Somalia which serves as the capital of the north-central Mudug region. Geographically, Galkayo is divided into four main quarters: Garsoor, Horumar, Israac, and Wadajir. Galkayo is divided between the regional states of Puntland and Galmudug. It serves as the capital of the Galkayo District and has grown considerably in recent times, becoming a commercial hub connecting southern Somalia with the northern parts of the country. History At its founding, the city was primarily inhabited by pastoralists, who sporadically fought in clan groups over resources like water and grazing land. In particular, the Darod, dominant in the north of the city, and the Hawiye, dominant in the south of the city, fought over the city due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |