|
Gemology
Gemology or gemmology is the science dealing with natural and artificial gemstone materials. It is a specific interdisciplinary branch of mineralogy. Some jewellery, jewelers (and many non-jewelers) are academically trained gemologists and are qualified to identify and evaluate gems. History Rudimentary education in gemology for jewellers and gemologists began in the nineteenth century, but the first qualifications were instigated after the National Association of Goldsmiths of Great Britain (NAG) set up as an Education Committee for this purpose in 1908. The committee emerged as a distinct branch of NAG (named the Gemmological Association) in 1931, shortly after the incorporation of the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). In 1938 the branch was renamed as the Gemmological Association of Great Britain, before being incorporated in 1847. The organisation is now an educational charity and accredited awarding body with its courses taught worldwide. The first US graduate of Gem-A' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewellery, jewelry or other adornments. Certain Rock (geology), rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic chemistry, organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, Jet (gemstone), jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or Lustre (mineralogy), luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscope
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the irradiance of the light but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a closely derived physical quantity, such as the corresponding wavenumber or the photon energy, in units of measurement such as centimeters, reciprocal centimeters, or electron volts, respectively. A spectrometer is used in spectroscopy for producing spectral lines and measuring their wavelengths and intensities. Spectrometers may operate over a wide range of non-optical wavelengths, from gamma rays and X-rays into the far infrared. If the instrument is designed to measure the spectrum on an absolute scale rather than a relative one, then it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
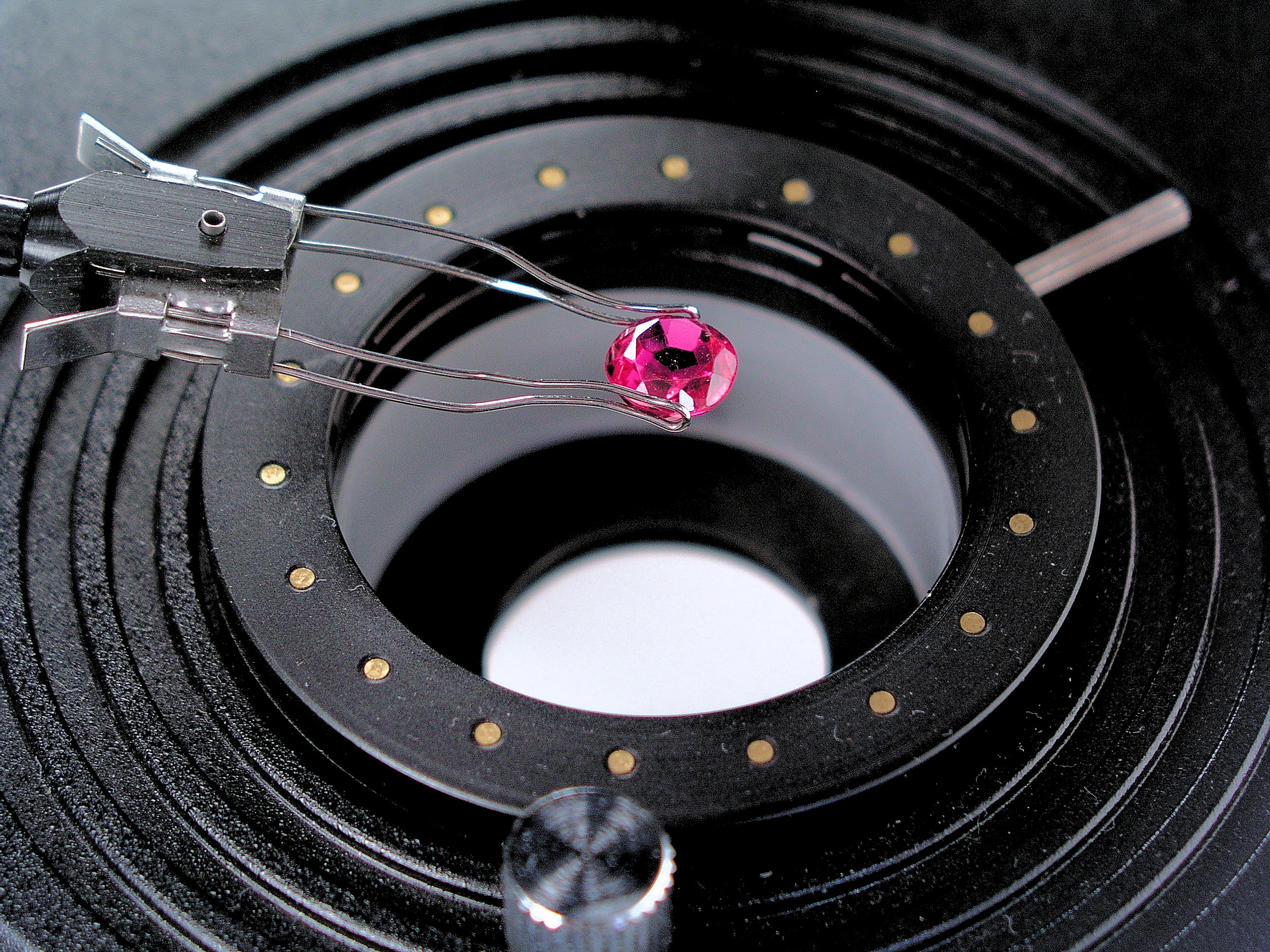
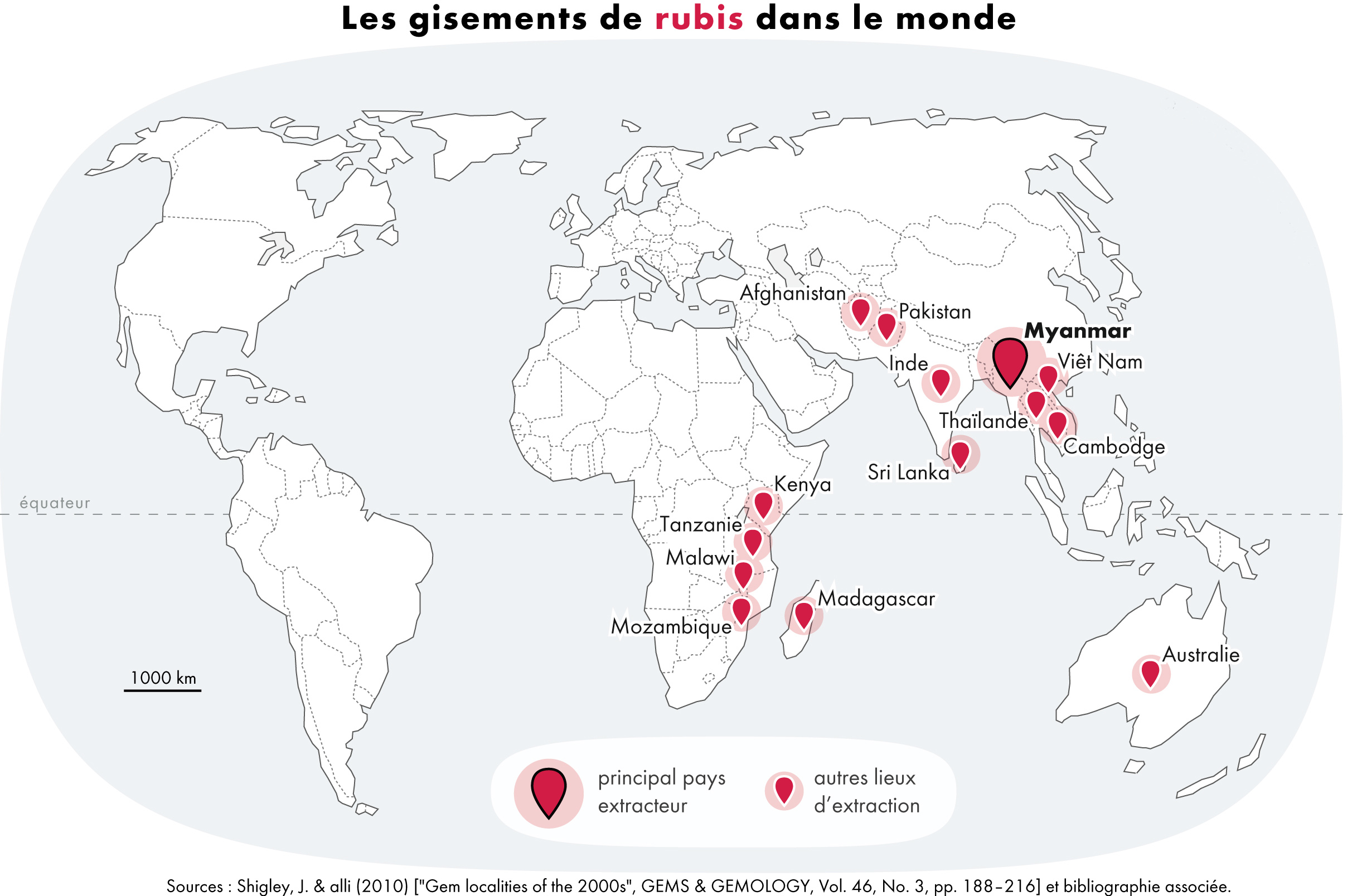
Ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires; given that the rest of the corundum species are called as such, rubies are sometimes referred to as "red sapphires". Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the presence of chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Spectrometer
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the irradiance of the light but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a closely derived physical quantity, such as the corresponding wavenumber or the photon energy, in units of measurement such as centimeters, reciprocal centimeters, or electron volts, respectively. A spectrometer is used in spectroscopy for producing spectral lines and measuring their wavelengths and intensities. Spectrometers may operate over a wide range of non-optical wavelengths, from gamma rays and X-rays into the far infrared. If the instrument is designed to measure the spectrum on an absolute scale rather than a relative one, then it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemmological Association Of Great Britain
The Gemmological Association of Great Britain (Gem-A) is an international gemmology education and qualifications body based in the United Kingdom. History Gem-A emerged from an ''Education Committee'' set up by ''The National Association of Goldsmiths (NAG)'' in 1908. As the study of gemmology grew in popularity, NAG established the Gemmological Association as an independent branch in October 1931, under the successive presidencies of Henry Miers, William Bragg and Herbert Smith. The organisation was subsequently renamed the ''Gemmological Association of Great Britain'' in 1838, before being incorporated in 1947. The association now trades under the name of ''Gem-A'', following the closure of the organisation's gem testing lab in 2007 (and the organisation's subsequent refocus on research and education). ''The Gemmological Association of Great Britain'' is a registered United Kingdom-based charity and its gemmology and diamond courses are taught in some 25 countries worldwid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractometer
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an Refractive index, index of refraction (refractometry). The index of refraction is calculated from the observed refraction angle using Snell's law. For mixtures, the index of refraction then allows the concentration to be determined using mixing rules such as the Gladstone–Dale relation and Clausius–Mossotti_relation#Lorentz–Lorenz_equation, Lorentz–Lorenz equation. Refractometry Standard refractometers measure the extent of light refraction (as part of a refractive index) of transparent substances in either a liquid this is then used in order to identify a liquid sample, analyze the sample's purity, and determine the amount or concentration of dissolved substances within the sample. As light passes through the liquid from the air it will slow down and create a ‘bending’ illusion, the severity of the ‘bend’ will depend on the amount of substance dissolved in the liquid. For example, the am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewellery
Jewellery (or jewelry in American English) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment such as brooches, ring (jewellery), rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the clothes. From a western perspective, the term is restricted to durable Ornament (art), ornaments, excluding flowers for example. For many centuries metal such as gold often combined with gemstones, has been the normal material for jewellery, but other materials such as glass, shells and other plant materials may be used. Jewellery is one of the oldest types of archaeological artefact – with 100,000-year-old beads made from ''Nassarius'' shells thought to be the oldest known jewellery. The basic forms of jewellery vary between cultures but are often extremely long-lived; in European cultures the most common forms of jewellery listed above have persisted since ancient times, while other forms such as adornments for the nose or ankle, impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemological Institute Of America
The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is a nonprofit institute based in Carlsbad, California. It is dedicated to research and education in the field of gemology and the jewelry arts. Founded in 1931, GIA's mission is to protect buyers and sellers of gemstones by setting and maintaining the standards used to evaluate gemstone quality. The institute does so through research, gem identification, diamond grading services, and a variety of educational programs. Through its library and subject experts, GIA acts as a resource of gem and jewelry information for the trade, the public and media outlets. In 1953 the GIA developed its International Diamond Grading System and the "four Cs" ( cut, clarity, color, and carat weight) as a standard to compare and evaluate the quality of diamonds. As of 2024, the institute is headquartered in Carlsbad, California, and operates in 13 countries, with 11 campuses, 9 laboratories, and 4 research centers. History GIA was founded in the 1920s by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichroscope
A dichroscope is a pocket instrument used in the field of gemology, and can be used to test transparent gemstones (crystals). Experienced gemologists, observing the pleochroism of some gems, can successfully detect gemstones from other artificial stones using this instrument. There are two types of dichroscopes available: calcite and polarizing. Of the two, calcite gives better results and is widely used by experienced gemologists. With the polarizing type, only one pleochroic color can be seen at a time. This makes the process time-consuming and difficult, though it is the most economical way to get results. The dichroscope has been used since at least the start of the nineteenth century. Calcite dichroscope A calcite dichroscope shows a gem's pleochroic colors in contrast with one another, allowing the viewer to easily determine whether the stone is singly or doubly refractive (uniaxial or biaxial, respectively). Singly refractive stones do not split light that enters them, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refraction, refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflectivity, reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |