Refractometer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an
product page of A.KRÜSS Optronic GmbH
(read March 13, 2013) In marine aquarium keeping, a refractometer is used to measure the
File:Bausch & Lomb Abbe Refractometer Serial No. 380 Prop147A-G 001.jpg , Bausch & Lomb Abbe Refractometer, ca. 1919-1926
Image:Gemref604.jpg, Gemology refractometer ER604 used to test light bending in gemstones; courtesy of A.KRÜSS Optronic GmbH
Image:2020 Refraktometr.jpg, Hand refractometer
Image:WinzerMitRefraktometer.jpg, A wine grape grower with refractometer
Image:FIP-Refraktometer.jpg, Density evaluation of abdominal fluid of a cat with feline infectious peritonitis by a refractometer.
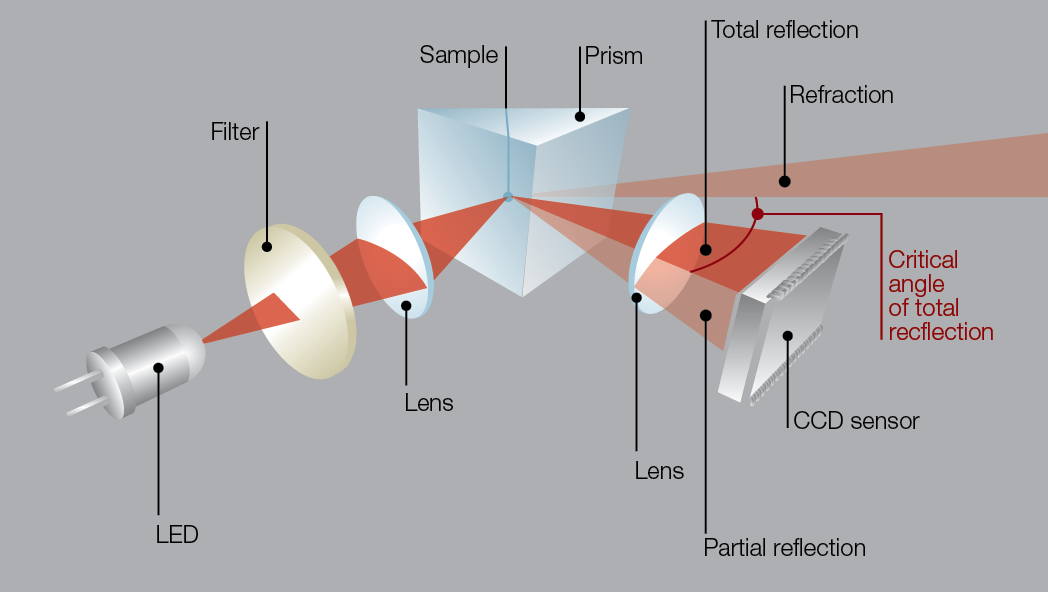 Automatic refractometers automatically measure the refractive index of a sample. The automatic measurement of the refractive index of the sample is based on the determination of the critical angle of total reflection.
A light source, usually a long-life LED, is focused onto a prism surface via a lens system. An interference filter guarantees the specified wavelength. Due to focusing light to a spot at the prism surface, a wide range of different angles is covered.
As shown in the figure ''"Schematic setup of an automatic refractometer"'' the measured sample is in direct contact with the measuring prism. Depending on its refractive index, the incoming light below the critical angle of total reflection is partly transmitted into the sample, whereas for higher angles of incidence the light is totally reflected. This dependence of the reflected light intensity from the incident angle is measured with a high-resolution sensor array. From the video signal taken with the CCD sensor the refractive index of the sample can be calculated.
This method of detecting the angle of total reflection is independent on the sample properties. It is even possible to measure the refractive index of optically dense strongly absorbing samples or samples containing air bubbles or solid particles . Furthermore, only a few microliters are required and the sample can be recovered. This determination of the refraction angle is independent of vibrations and other environmental disturbances.
Automatic refractometers automatically measure the refractive index of a sample. The automatic measurement of the refractive index of the sample is based on the determination of the critical angle of total reflection.
A light source, usually a long-life LED, is focused onto a prism surface via a lens system. An interference filter guarantees the specified wavelength. Due to focusing light to a spot at the prism surface, a wide range of different angles is covered.
As shown in the figure ''"Schematic setup of an automatic refractometer"'' the measured sample is in direct contact with the measuring prism. Depending on its refractive index, the incoming light below the critical angle of total reflection is partly transmitted into the sample, whereas for higher angles of incidence the light is totally reflected. This dependence of the reflected light intensity from the incident angle is measured with a high-resolution sensor array. From the video signal taken with the CCD sensor the refractive index of the sample can be calculated.
This method of detecting the angle of total reflection is independent on the sample properties. It is even possible to measure the refractive index of optically dense strongly absorbing samples or samples containing air bubbles or solid particles . Furthermore, only a few microliters are required and the sample can be recovered. This determination of the refraction angle is independent of vibrations and other environmental disturbances.

 Once an automatic refractometer is equipped with a flow cell, the sample can either be filled by means of a syringe or by using a peristaltic pump. Modern refractometers have the option of a built-in peristaltic pump. This is controlled via the instrument's software menu. A peristaltic pump opens the way to monitor batch processes in the laboratory or perform multiple measurements on one sample without any user interaction. This eliminates human error and assures a high sample throughput.
If an automated measurement of a large number of samples is required, modern automatic refractometers can be combined with an automatic sample changer. The sample changer is controlled by the refractometer and assures fully automated measurements of the samples placed in the vials of the sample changer for measurements.
Once an automatic refractometer is equipped with a flow cell, the sample can either be filled by means of a syringe or by using a peristaltic pump. Modern refractometers have the option of a built-in peristaltic pump. This is controlled via the instrument's software menu. A peristaltic pump opens the way to monitor batch processes in the laboratory or perform multiple measurements on one sample without any user interaction. This eliminates human error and assures a high sample throughput.
If an automated measurement of a large number of samples is required, modern automatic refractometers can be combined with an automatic sample changer. The sample changer is controlled by the refractometer and assures fully automated measurements of the samples placed in the vials of the sample changer for measurements.
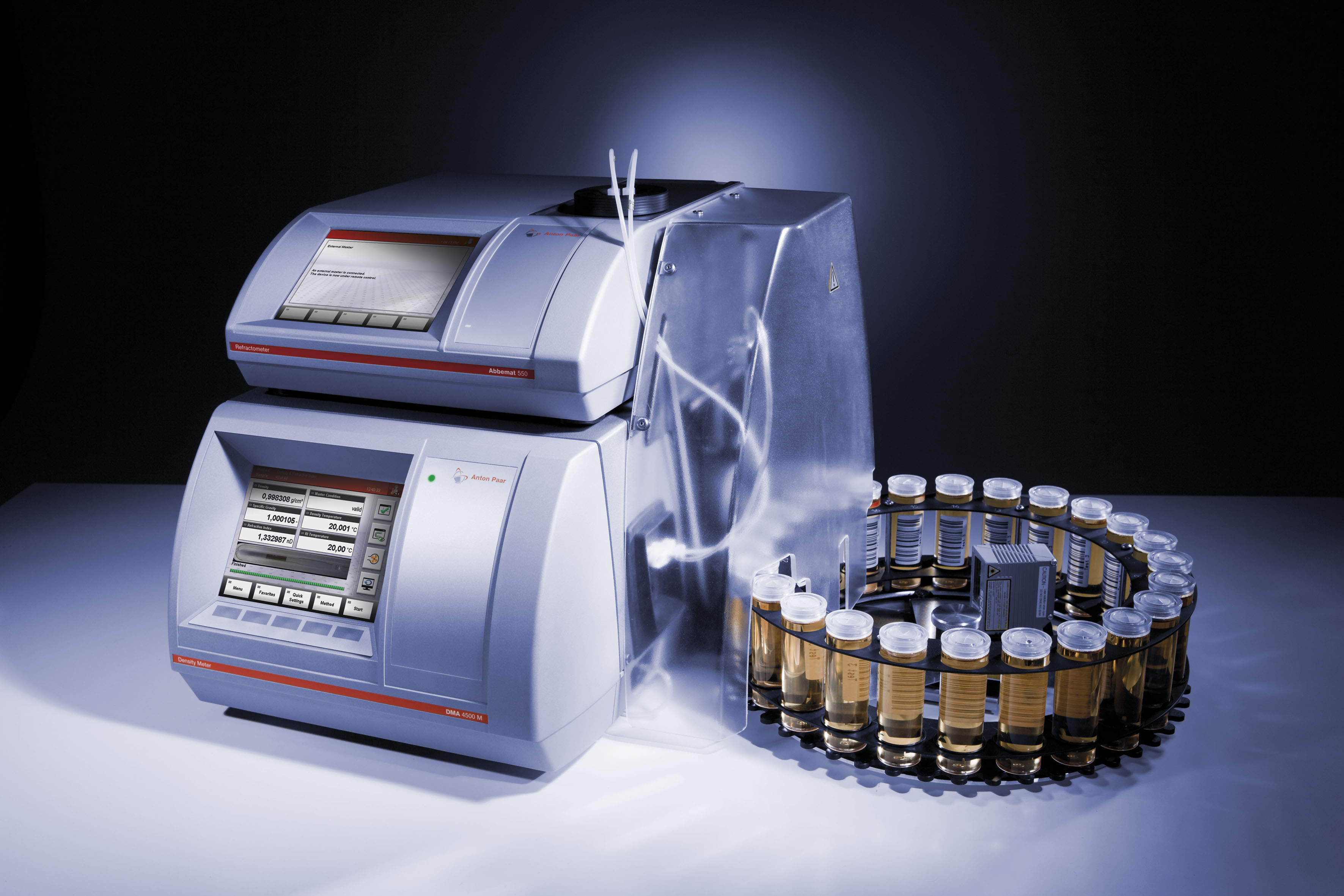 Today's laboratories do not only want to measure the refractive index of samples, but several additional parameters like density or viscosity to perform efficient quality control. Due to the microprocessor control and a number of interfaces, automatic refractometers are able to communicate with computers or other measuring devices, e.g. density meters, pH meters or viscosity meters, to store refractive index data and density data (and other parameters) into one database.
Today's laboratories do not only want to measure the refractive index of samples, but several additional parameters like density or viscosity to perform efficient quality control. Due to the microprocessor control and a number of interfaces, automatic refractometers are able to communicate with computers or other measuring devices, e.g. density meters, pH meters or viscosity meters, to store refractive index data and density data (and other parameters) into one database.
Refractometer – Gemstone Buzz
uses, procedure & limitations.
Refractometers and refractometry
explains how refractometers work. {{Authority control Measuring instruments Scales Beekeeping tools Food science
 A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an
A refractometer is a laboratory or field device for the measurement of an index of refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
( refractometry). The index of refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
is calculated from the observed refraction angle using Snell's law
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and ibn-Sahl law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing throug ...
. For mixtures, the index of refraction then allows to determine the concentration using mixing rules such as the Gladstone–Dale relation and Lorentz–Lorenz equation.
Refractometry
Standard refractometers measure the extent of light refraction (as part of a refractive index) of transparent substances in either a liquid or solid-state; this is then used in order to identify a liquid sample, analyze the sample's purity, and determine the amount or concentration of dissolved substances within the sample. As light passes through the liquid from the air it will slow down and create a ‘bending’ illusion, the severity of the ‘bend’ will depend on the amount of substance dissolved in the liquid. For example, the amount of sugar in a glass of water.Types
There are four main types of refractometers:traditional handheld refractometer
A traditional handheld refractometer is an analog instrument for measuring a liquid's refractive index. It works on the ''critical angle'' principle by which lenses and prisms project a shadow line onto a small glass reticle inside the instrume ...
s, digital handheld refractometer
A digital handheld refractometer is an instrument for measuring the refractive index of materials.
Principle of operation
Most operate on the same general ''critical angle'' principle as a traditional handheld refractometer. The difference is t ...
s, laboratory or Abbe refractometer
An Abbe refractometer is a bench-top device for the high-precision measurement of an Refractive index, index of refraction.
Details
Ernst Abbe (1840–1905), working for Carl Zeiss AG in Jena, Germany in the late 19th century, was the first ...
s (named for the instrument's inventor and based on Ernst Abbe's original design of the 'critical angle') and inline process refractometer
Inline process refractometers are a type of refractometer designed for the continuous measurement of a fluid flowing through a pipe or inside a tank. First patented by Carl A. Vossberg Jr.br>US2807976A- Refractometer US2549402A, these refractom ...
s. There is also the Rayleigh Refractometer used (typically) for measuring the refractive indices of gases.
In laboratory medicine
A medical laboratory or clinical laboratory is a laboratory where tests are conducted out on clinical specimens to obtain information about the health of a patient to aid in diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disease. Clinical Medical labor ...
, a refractometer is used to measure the total plasma protein
Blood-proteins, also termed plasma proteins, are proteins present in blood plasma. They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other bl ...
in a blood sample and urine specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its dens ...
in a urine sample.
In drug diagnostics, a refractometer is used to measure the specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its dens ...
of human urine.
In gemology
Gemology or gemmology is the science dealing with natural and artificial gemstone materials. It is a geoscience and a branch of mineralogy. Some jewelers (and many non-jewelers) are academically trained gemologists and are qualified to identif ...
, the gemstone refractometer is one of the fundamental pieces of equipment used in a gemological laboratory. Gemstones are transparent minerals and can therefore be examined using optical methods. Refractive index is a material constant, dependent on the chemical composition of a substance. The refractometer is used to help identify gem materials by measuring their refractive index, one of the principal properties used in determining the type of a gemstone. Due to the dependence of the refractive index on the wavelength of the light used ( ''i.e.'' dispersion), the measurement is normally taken at the wavelength of the sodium line D-line (NaD) of ~589 nm. This is either filtered out from daylight or generated with a monochromatic light-emitting diode ( LED). Certain stones such as rubies, sapphires, tourmalines and topaz are optically anisotropic. They demonstrate birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefri ...
based on the polarisation plane of the light. The two different refractive indexes are classified using a polarisation filter. Gemstone refractometers are available both as classic optical instruments and as electronic measurement devices with a digital display
A display device is an output device for presentation of information in visual or tactile form (the latter used for example in tactile electronic displays for blind people). When the input information that is supplied has an electrical signal ...
.(read March 13, 2013) In marine aquarium keeping, a refractometer is used to measure the
salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
and specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its dens ...
of the water.
In the automobile industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of companies and organizations involved in the design, development, manufacturing, marketing, and selling of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industries by revenue (from 16 % such ...
, a refractometer is used to measure the coolant concentration.
In the machine industry
The machine industry or machinery industry is a subsector of the industry, that produces and maintains machines for consumers, the industry, and most other companies in the economy.
This machine industry traditionally belongs to the heavy indust ...
, a refractometer is used to measure the amount of coolant concentrate that has been added to the water-based coolant for the machining process.
In homebrewing
Homebrewing is the brewing of beer or other alcoholic beverages on a small scale for personal, non-commercial purposes. Supplies, such as kits and fermentation tanks, can be purchased locally at specialty stores or online. Beer was brewed dom ...
, a brewing refractometer is used to measure the specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its dens ...
before fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food p ...
to determine the amount of fermentable sugars which will potentially be converted to alcohol.
Brix refractometers are often used by hobbyists for making preserves including jams, marmalades and honey. In beekeeping
Beekeeping (or apiculture) is the maintenance of bee colonies, commonly in man-made beehives. Honey bees in the genus ''Apis (insect), Apis'' are the most-commonly-kept species but other honey-producing bees such as ''Melipona'' stingless bees ar ...
, a brix refractometer is used to measure the amount of water in honey.
Automatic
 Automatic refractometers automatically measure the refractive index of a sample. The automatic measurement of the refractive index of the sample is based on the determination of the critical angle of total reflection.
A light source, usually a long-life LED, is focused onto a prism surface via a lens system. An interference filter guarantees the specified wavelength. Due to focusing light to a spot at the prism surface, a wide range of different angles is covered.
As shown in the figure ''"Schematic setup of an automatic refractometer"'' the measured sample is in direct contact with the measuring prism. Depending on its refractive index, the incoming light below the critical angle of total reflection is partly transmitted into the sample, whereas for higher angles of incidence the light is totally reflected. This dependence of the reflected light intensity from the incident angle is measured with a high-resolution sensor array. From the video signal taken with the CCD sensor the refractive index of the sample can be calculated.
This method of detecting the angle of total reflection is independent on the sample properties. It is even possible to measure the refractive index of optically dense strongly absorbing samples or samples containing air bubbles or solid particles . Furthermore, only a few microliters are required and the sample can be recovered. This determination of the refraction angle is independent of vibrations and other environmental disturbances.
Automatic refractometers automatically measure the refractive index of a sample. The automatic measurement of the refractive index of the sample is based on the determination of the critical angle of total reflection.
A light source, usually a long-life LED, is focused onto a prism surface via a lens system. An interference filter guarantees the specified wavelength. Due to focusing light to a spot at the prism surface, a wide range of different angles is covered.
As shown in the figure ''"Schematic setup of an automatic refractometer"'' the measured sample is in direct contact with the measuring prism. Depending on its refractive index, the incoming light below the critical angle of total reflection is partly transmitted into the sample, whereas for higher angles of incidence the light is totally reflected. This dependence of the reflected light intensity from the incident angle is measured with a high-resolution sensor array. From the video signal taken with the CCD sensor the refractive index of the sample can be calculated.
This method of detecting the angle of total reflection is independent on the sample properties. It is even possible to measure the refractive index of optically dense strongly absorbing samples or samples containing air bubbles or solid particles . Furthermore, only a few microliters are required and the sample can be recovered. This determination of the refraction angle is independent of vibrations and other environmental disturbances.
Influence of wavelength
The refractive index of a given sample varies with wavelength for all materials. This dispersion relation is nonlinear and is characteristic for every material. In the visible range, a decrease of the refractive index comes with increasing wavelength. In glass prisms very little absorption is observable. In the infrared wavelength range several absorption maxima and fluctuations in the refractive index appear. To guarantee a high quality measurement with an accuracy of up to 0.00002 in the refractive index the wavelength has to be determined correctly. Therefore, in modern refractometers the wavelength is tuned to a bandwidth of +/-0.2 nm to ensure correct results for samples with different dispersions.
Influence of temperature
Temperature has a very important influence on the refractive index measurement. Therefore, the temperature of the prism and the temperature of the sample have to be controlled with high precision. There are several subtly-different designs for controlling the temperature; but there are some key factors common to all, such as high-precision temperature sensors and Peltier devices to control the temperature of the sample and the prism. The temperature control of these devices should be designed so that the variation in sample temperature is small enough that it will not cause a detectable refractive-index change. External water baths were used in the past but are no longer needed.Extended possibilities of automatic refractometers
Automatic refractometers are microprocessor-controlled electronic devices. This means they can have a high degree of automation and also be combined with other measuring devicesFlow cells
There are different types of sample cells available, ranging from a flow cell for a few microliters to sample cells with a filling funnel for fast sample exchange without cleaning the measuring prism in between. The sample cells can also be used for the measurement of poisonous and toxic samples with minimum exposure to the sample. Micro cells require only a few microliters volume, assure good recovery of expensive samples and prevent evaporation of volatile samples or solvents. They can also be used in automated systems for automatic filling of the sample onto the refractometer prism. For convenient filling of the sample through a funnel, flow cells with a filling funnel are available. These are used for fast sample exchange in quality control applications.Automatic sample feeding
 Once an automatic refractometer is equipped with a flow cell, the sample can either be filled by means of a syringe or by using a peristaltic pump. Modern refractometers have the option of a built-in peristaltic pump. This is controlled via the instrument's software menu. A peristaltic pump opens the way to monitor batch processes in the laboratory or perform multiple measurements on one sample without any user interaction. This eliminates human error and assures a high sample throughput.
If an automated measurement of a large number of samples is required, modern automatic refractometers can be combined with an automatic sample changer. The sample changer is controlled by the refractometer and assures fully automated measurements of the samples placed in the vials of the sample changer for measurements.
Once an automatic refractometer is equipped with a flow cell, the sample can either be filled by means of a syringe or by using a peristaltic pump. Modern refractometers have the option of a built-in peristaltic pump. This is controlled via the instrument's software menu. A peristaltic pump opens the way to monitor batch processes in the laboratory or perform multiple measurements on one sample without any user interaction. This eliminates human error and assures a high sample throughput.
If an automated measurement of a large number of samples is required, modern automatic refractometers can be combined with an automatic sample changer. The sample changer is controlled by the refractometer and assures fully automated measurements of the samples placed in the vials of the sample changer for measurements.
Multiparameter measurements
 Today's laboratories do not only want to measure the refractive index of samples, but several additional parameters like density or viscosity to perform efficient quality control. Due to the microprocessor control and a number of interfaces, automatic refractometers are able to communicate with computers or other measuring devices, e.g. density meters, pH meters or viscosity meters, to store refractive index data and density data (and other parameters) into one database.
Today's laboratories do not only want to measure the refractive index of samples, but several additional parameters like density or viscosity to perform efficient quality control. Due to the microprocessor control and a number of interfaces, automatic refractometers are able to communicate with computers or other measuring devices, e.g. density meters, pH meters or viscosity meters, to store refractive index data and density data (and other parameters) into one database.
Software features
Automatic refractometers do not only measure the refractive index, but offer a lot of additional software features, like * Instrument settings and configuration via software menu * Automatic data recording into a database * User-configurable data output * Export of measuring data intoMicrosoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Microsoft Windows, Windows, macOS, Android (operating system), Android and iOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro (comp ...
data sheets
* Statistical functions
* Predefined methods for different kinds of applications
* Automatic checks and adjustments
* Check if sufficient amount of sample is on the prism
* Data recording only if the results are plausible
Pharma documentation and validation
Refractometers are often used in pharmaceutical applications for quality control of raw intermediate and final products. The manufacturers of pharmaceuticals have to follow several international regulations like FDA 21 CFR Part 11, GMP, Gamp 5, USP<1058>, which require a lot of documentation work. The manufacturers of automatic refractometers support these users providing instrument software fulfills the requirements of 21 CFR Part 11, with user levels, electronic signature and audit trail. Furthermore, Pharma Validation and Qualification Packages are available containing * Qualification Plan (QP) * Design Qualification (DQ) * Risk Analysis * Installation Qualification (IQ) * Operational Qualification (OQ) * Check List 21 CFR Part 11 / SOP * Performance Qualification (PQ)Scales typically used
*Brix
Degrees Brix (symbol °Bx) is a measure of the dissolved solids in a liquid, and is commonly used to measure dissolved sugar content of an aqueous solution. One degree Brix is 1 gram of sucrose in 100 grams of solution and represents the strength ...
* Oechsle scale
* Plato scale
* Baumé scale
The Baumé scale is a pair of hydrometer scales developed by French pharmacist Antoine Baumé in 1768 to measure density of various liquids. The unit of the Baumé scale has been notated variously as ''degrees Baumé'', ''B°'', ''Bé°'' and simp ...
See also
*Ernst Abbe
Ernst Karl Abbe HonFRMS (23 January 1840 – 14 January 1905) was a German physicist, optical scientist, entrepreneur, and social reformer. Together with Otto Schott and Carl Zeiss, he developed numerous optical instruments. He was also a c ...
* Refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, ...
* Gemology
Gemology or gemmology is the science dealing with natural and artificial gemstone materials. It is a geoscience and a branch of mineralogy. Some jewelers (and many non-jewelers) are academically trained gemologists and are qualified to identif ...
* Must weight
* Winemaking
Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. The science of wine and ...
* Harvest (wine)
The harvesting of wine grapes (Vintage) is one of the most crucial steps in the process of wine-making. The time of harvest is determined primarily by the ripeness of the grape as measured by sugar, acid and tannin levels with winemakers basing t ...
* Gravity (beer)
Gravity, in the context of fermenting alcoholic beverages, refers to the specific gravity (abbreviated SG), or relative density compared to water, of the wort or must at various stages in the fermentation. The concept is used in the brewing and ...
* High-fructose corn syrup
High-fructose corn syrup (HFCS), also known as glucose–fructose, isoglucose and glucose–fructose syrup, is a sweetener made from corn starch. As in the production of conventional corn syrup, the starch is broken down into glucose by enzy ...
* Cutting fluid
Cutting fluid is a type of coolant and lubricant designed specifically for metalworking processes, such as machining and stamping. There are various kinds of cutting fluids, which include oils, oil-water emulsions, pastes, gels, aerosols (mists) ...
* German inventors and discoverers
* High refractive index polymers
References
Further reading
*External links
Refractometer – Gemstone Buzz
uses, procedure & limitations.
Refractometers and refractometry
explains how refractometers work. {{Authority control Measuring instruments Scales Beekeeping tools Food science