|
Gastornithiforms
Gastornithiformes are an extinct order of giant flightless fowl with fossils found in North America, Eurasia, possibly Australia. Members of Gastornithidae were long considered to be a part of the order Gruiformes. However, the traditional concept of Gruiformes has since been shown to be polyphyletic. Beginning in the late 1980s and the first phylogenetic analysis of gastornithid relationships, consensus began to grow that they were close relatives of the lineage that includes waterfowl and screamers, the Anseriformes. Recognizing the apparent close relationship between ''Gastornis'' and waterfowl, some researchers even classify them within the anseriform group itself. Others restrict the name Anseriformes only to the crown group formed by all modern species, and label the larger group including extinct relatives of anseriformes in the clade Anserimorphae (which this article and related pages have adopted). While the order is generally considered to be monotypic, a 2017 paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anserimorphae
The Odontoanserae is a proposed clade that includes the family Pelagornithidae (pseudo-toothed birds) and the clade Anserimorphae (the order Anseriformes and their stem-relatives). The placement of the pseudo-toothed birds in the evolutionary tree of birds has been problematic, with some supporting the placement of them near the orders Procellariformes and Pelecaniformes based on features in the sternum. In 2005 a cladistic analysis had found support in placing pseudo-toothed birds as the sister group to waterfowl. Evidence for this comes from shared characteristics in the skull such as lack of a crest on the underside of the palatine bone and two condyles on the mandibular process of the quadrate bone, with the middle condyle beakwards of the side condyle. In addition to that, both groups have similar features in their pelvic and pectoral regions. Furthermore, a 2013 study on the growth pattern and structure of the pseudoteeth in ''Pelagornis mauretanicus'' shows more support of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dromornithidae
Dromornithidae, known as mihirungs (after Tjapwuring ''Mihirung paringmal'', "giant bird") and informally as thunder birds or demon ducks, were a clade of large, flightless Australian birds of the Oligocene through Pleistocene epochs. All are now extinct. They were long classified in Struthioniformes (the ratites), but are now usually classified as galloanseres. Dromornithids were part of the Australian megafauna. One species, '' Dromornis stirtoni'', was tall. Only a single species, ''Genyornis newtoni'' survived into the Late Pleistocene. They are thought to have been herbivorous.McInerney, P. L.; Blokland, J. C.; Worthy, T. H. (2024). "Skull morphology of the enigmatic Genyornis newtoni Stirling and Zeitz, 1896 (Aves, Dromornithidae), with implications for functional morphology, ecology, and evolution in the context of Galloanserae". Historical Biology: An International Journal of Paleobiology. 36 (6): 1093–1165. doi:10.1080/08912963.2024.2308212. Classification The scient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
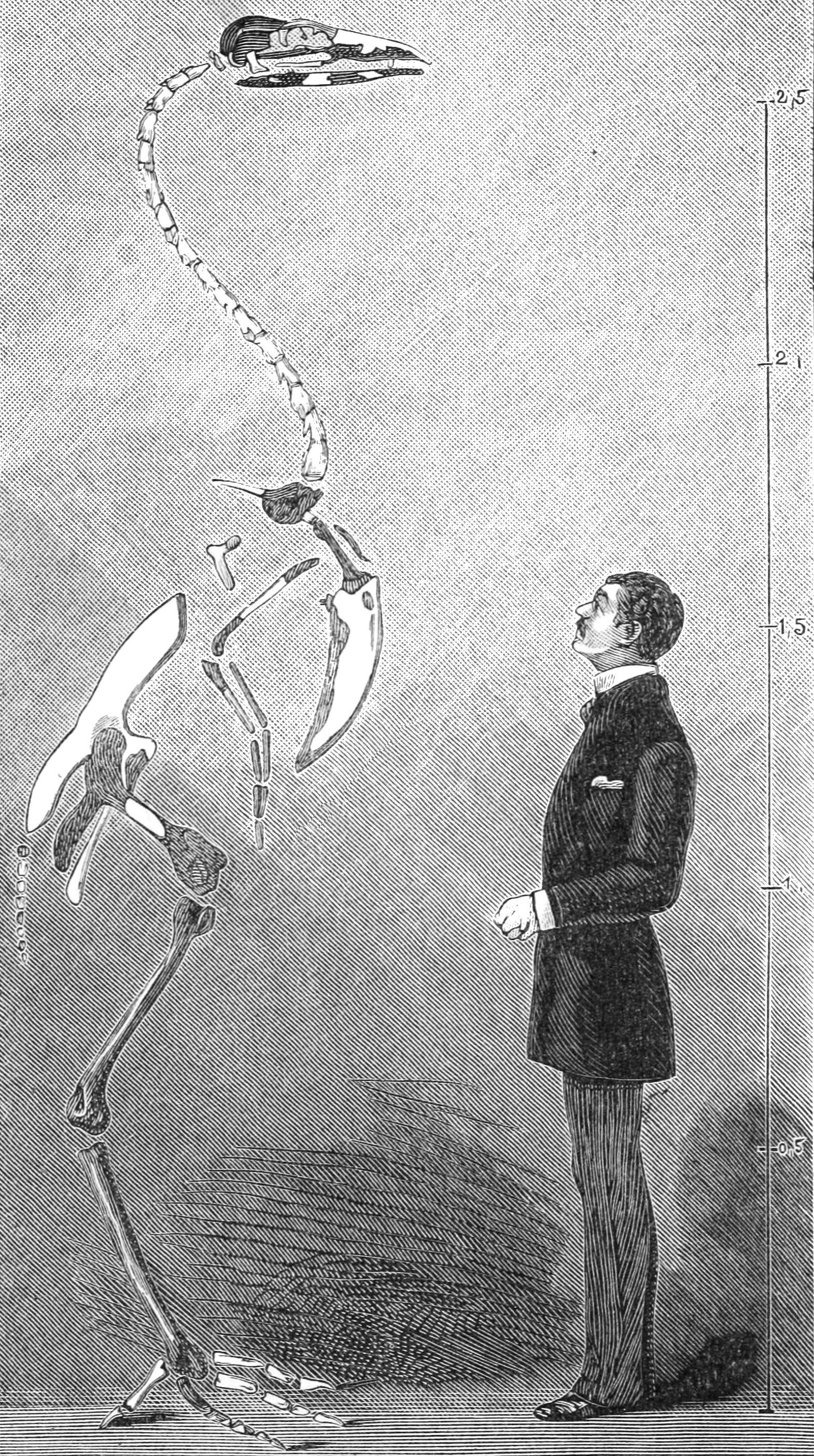
Gastornis Giganteus
''Gastornis'' is an extinct genus of large, flightless birds that lived during the mid-Paleocene to mid-Eocene epochs of the Paleogene period. Most fossils have been found in Europe, and some species typically referred to the genus are known from North America and Asia. Several genera, including the well-studied genus ''Diatryma'', have historically been considered junior synonyms of ''Gastornis''. However, this interpretation has been challenged recently, and some researchers currently consider ''Diatryma'' to be a valid genus. ''Gastornis'' species were very large birds that were traditionally thought to have been predators of various smaller mammals, such as ancient, diminutive equids. However, several lines of evidence, including the lack of hooked claws (in known ''Gastornis'' footprints), studies of their beak structure and isotopic signatures of their bones, have caused scientists to now consider that these birds were probably herbivorous, feeding on tough plant material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |