|
Fundus (eye)
The fundus of the eye is the interior surface of the eye opposite the lens and includes the retina, optic disc, macula, fovea, and posterior pole.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990. The fundus can be examined by ophthalmoscopy and/or fundus photography. Variation The color of the fundus varies both between and within species. In one study of primates the retina is blue, green, yellow, orange, and red; only the human fundus (from a lightly pigmented blond person) is red. The major differences noted among the "higher" primate species were size and regularity of the border of macular area, size and shape of the optic disc, apparent 'texturing' of retina, and pigmentation of retina. Clinical significance Medical signs that can be detected from observation of eye fundus (generally by funduscopy) include hemorrhages, exudates, cotton wool spots, blood vessel abnormalities ( tortuosity, puls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fundus Photographs
Fundus photography involves photographing the rear of an eye, also known as the fundus (eye), fundus. Specialized fundus cameras consisting of an intricate microscope attached to a flash (photography), flash enabled camera are used in fundus photography. The main structures that can be visualized on a fundus photo are the central and peripheral retina, optic disc and Macula of retina, macula. Fundus photography can be performed with colored filters, or with specialized dyes including Fluorescein angiography, fluorescein and indocyanine green. The models and technology of fundus photography have advanced and evolved rapidly over the last century. History The concept of fundus photography was first introduced in the mid 19th century, after the introduction of photography in 1839. In 1851, Hermann von Helmholtz introduced the Ophthalmoscopy, Ophthalmoscope, and James Clerk Maxwell presented a colour photography method in 1861. In the early 1860s, Henry Noyes and Abner Mulhollan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exudate
An exudate is a fluid released by an organism through pores or a wound, a process known as exuding or exudation. ''Exudate'' is derived from ''exude'' 'to ooze' from Latin language, Latin 'to (ooze out) sweat' (' 'out' and ' 'to sweat'). Medicine An exudate is any fluid that filters from the circulatory system into lesions or areas of inflammation. It can be a pus-like or clear fluid. When an injury occurs, leaving skin exposed, it leaks out of the blood vessels and into nearby tissues. The fluid is composed of serum (blood), serum, fibrin, and White blood cell, leukocytes. Exudate may ooze from cuts or from areas of infection or inflammation. Types * Purulent or suppurative exudate consists of plasma with both active and dead neutrophils, fibrinogen, and necrotic parenchymal cells. This kind of exudate is consistent with more severe infections, and is commonly referred to as pus. * Fibrinous exudate is composed mainly of fibrinogen and fibrin. It is characteristic of Rheuma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Red-eye Effect
The red-eye effect in photography is the common appearance of red pupils in color photographs of eyes. It occurs when using a photographic flash at low lighting or at night. When a flash passes through the eyes and rebounds at the back of the eye, it causes a red reflex in an image, turning the subject's eyes red. The hue is mostly caused by a high concentration of blood in the choroid. The effect can also be influenced by the near proximity of the flash and camera lens. In children, a different hue red reflex, such as white or yellow, may indicate an illness. In animals, a similar effect could cause their eyes to change colors in photographs. The effect can be avoided physically by instructing the subject to look away from the lens, increasing the brightness of the photographic location, or moving the flash further away from the lens, or digitally by using the red-eye correction option on digital cameras or by removing the effect in editing software. Scholars have developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Leukocoria
Leukocoria (also white pupillary reflex) is an abnormal white reflection from the retina of the eye. Leukocoria resembles eyeshine, but leukocoria can also occur in animals that lack eyeshine because their retina lacks a ''tapetum lucidum''. Leukocoria is a medical sign for a number of conditions, including Coats disease, congenital cataract, corneal scarring, melanoma of the ciliary body, Norrie disease, ocular toxocariasis, persistence of the tunica vasculosa lentis (PFV/PHPV), retinoblastoma, and retrolental fibroplasia. Because of the potentially life-threatening nature of retinoblastoma, a cancer, that condition is usually considered in the evaluation of leukocoria. In some rare cases (1%) the leukocoria is caused by Coats' disease (leaking retinal vessels). Diagnosis On photographs taken using a flash, instead of the familiar red-eye effect, leukocoria can cause a bright white reflection in an affected eye. Leukocoria may appear also in low indirect light, similar to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fundus Camera
Fundus photography involves photographing the rear of an eye, also known as the fundus. Specialized fundus cameras consisting of an intricate microscope attached to a flash enabled camera are used in fundus photography. The main structures that can be visualized on a fundus photo are the central and peripheral retina, optic disc and macula. Fundus photography can be performed with colored filters, or with specialized dyes including fluorescein and indocyanine green. The models and technology of fundus photography have advanced and evolved rapidly over the last century. History The concept of fundus photography was first introduced in the mid 19th century, after the introduction of photography in 1839. In 1851, Hermann von Helmholtz introduced the Ophthalmoscope, and James Clerk Maxwell presented a colour photography method in 1861. In the early 1860s, Henry Noyes and Abner Mulholland Rosebrugh both assembled fundus cameras and tried fundus photography on animals. Early fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dilated Fundus Examination
Dilated fundus examination (DFE) is a diagnostic procedure that uses mydriatic eye drops to dilate or enlarge the pupil in order to obtain a better view of the fundus of the eye. Once the pupil is dilated, examiners use ophthalmoscopy to view the eye's interior, which makes it easier to assess the retina, optic nerve head, blood vessels, and other important features. DFE has been found to be a more effective method for evaluating eye health when compared to non-dilated examination, and is the best method of evaluating structures behind the iris. It is frequently performed by ophthalmologists and optometrists as part of an eye examination. Examination The most common agents used to dilate the pupil are phenylephrine (2.5% in pediatrics or 10% in adults) and tropicamide (0.5% or 1%). While phenylephrine stimulates receptors that contract the dilator muscle of the pupil, tropicamide blocks stimulation of the pupillary sphincter muscle to allow for relaxation. As the insertio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
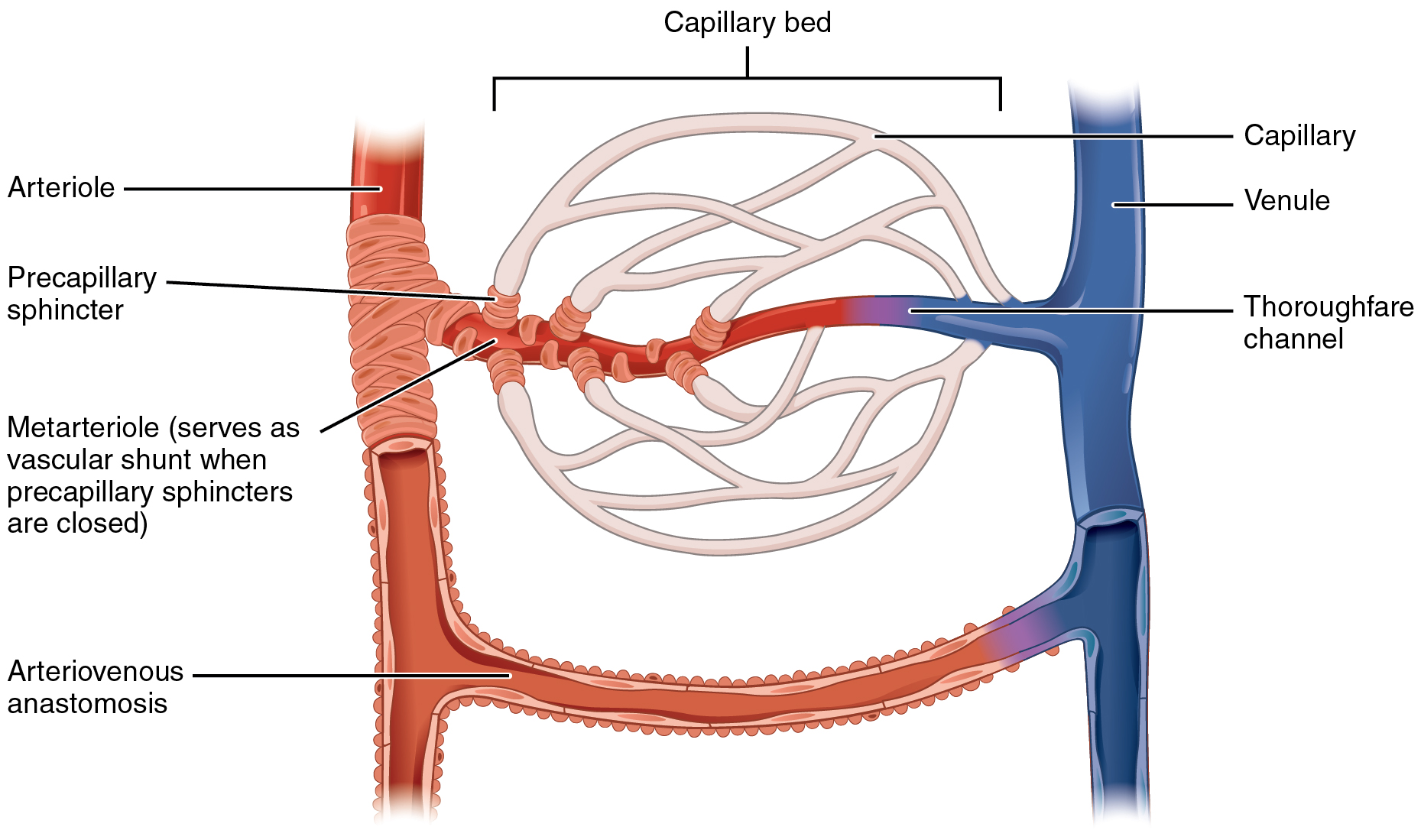
Microcirculation
The microcirculation is the circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ tissues. The microvessels include terminal arterioles, metarterioles, capillaries, and venules. Arterioles carry oxygenated blood to the capillaries, and blood flows out of the capillaries through venules into veins. In addition to these blood vessels, the microcirculation also includes lymphatic capillaries and collecting ducts. The main functions of the microcirculation are the delivery of oxygen and nutrients and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). It also serves to regulate blood flow and tissue perfusion, thereby affecting blood pressure and responses to inflammation which can include edema (swelling). Most vessels of the microcirculation are lined by flattened cells of the endothelium and many of them are surrounded by contractile cells called pericytes. The endothelium provides a smooth surface for the flow of blood and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hypertensive Retinopathy
Hypertensive retinopathy is damage to the retina and retinal circulation due to high blood pressure (i.e. hypertension). Signs and symptoms Most patients with hypertensive retinopathy have no symptoms. However, some may report decreased or blurred vision, and headaches. Signs Signs of damage to the retina caused by hypertension include: * Arteriolar changes, such as generalized arteriolar narrowing, focal arteriolar narrowing, arteriovenous nicking, changes in the arteriolar wall (arteriosclerosis) and abnormalities at points where arterioles and venules cross. Manifestations of these changes include ''Copper wire arterioles'' where the central light reflex occupies most of the width of the arteriole and ''Silver wire arterioles'' where the central light reflex occupies all of the width of the arteriole, and "arterio-venular (AV) nicking" or "AV nipping", due to venous constriction and banking. * Advanced retinopathy lesions, such as microaneurysms, blot hemorrhages and/or flam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pigmentation
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly insoluble and chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored substances which are soluble or go into solution at some stage in their use. Dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each year. Physical principles Like all materials, the color of pigments arises because they absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pulse
In medicine, the pulse refers to the rhythmic pulsations (expansion and contraction) of an artery in response to the cardiac cycle (heartbeat). The pulse may be felt ( palpated) in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body close to the skin, such as at the neck ( carotid artery), wrist (radial artery or ulnar artery), at the groin (femoral artery), behind the knee ( popliteal artery), near the ankle joint ( posterior tibial artery), and on foot (dorsalis pedis artery). The pulse is most commonly measured at the wrist or neck for adults and at the brachial artery (inner upper arm between the shoulder and elbow) for infants and very young children. A sphygmograph is an instrument for measuring the pulse. Physiology Claudius Galen was perhaps the first physiologist to describe the pulse. The pulse is an expedient tactile method of determination of systolic blood pressure to a trained observer. Diastolic blood pressure is non-palpable and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tortuosity
Tortuosity is widely used as a critical parameter to predict transport properties of porous media, such as rocks and soils. But unlike other standard microstructural properties, the concept of tortuosity is vague with multiple definitions and various evaluation methods introduced in different contexts. Hydraulic, electrical, diffusional, and thermal tortuosities are defined to describe different transport processes in porous media, while geometrical tortuosity is introduced to characterize the morphological property of porous microstructures. Tortuosity in 2-D Subjective estimation (sometimes aided by optometric grading scales) is often used. The simplest mathematical method to estimate tortuosity is the arc-chord ratio: the ratio of the length of the curve (''C'') to the distance between its ends (''L''): :\tau = \frac Arc-chord ratio equals 1 for a straight line and is infinite for a circle. Another method, proposed in 1999, is to estimate the tortuosity as the integral of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |