|
Microcirculation
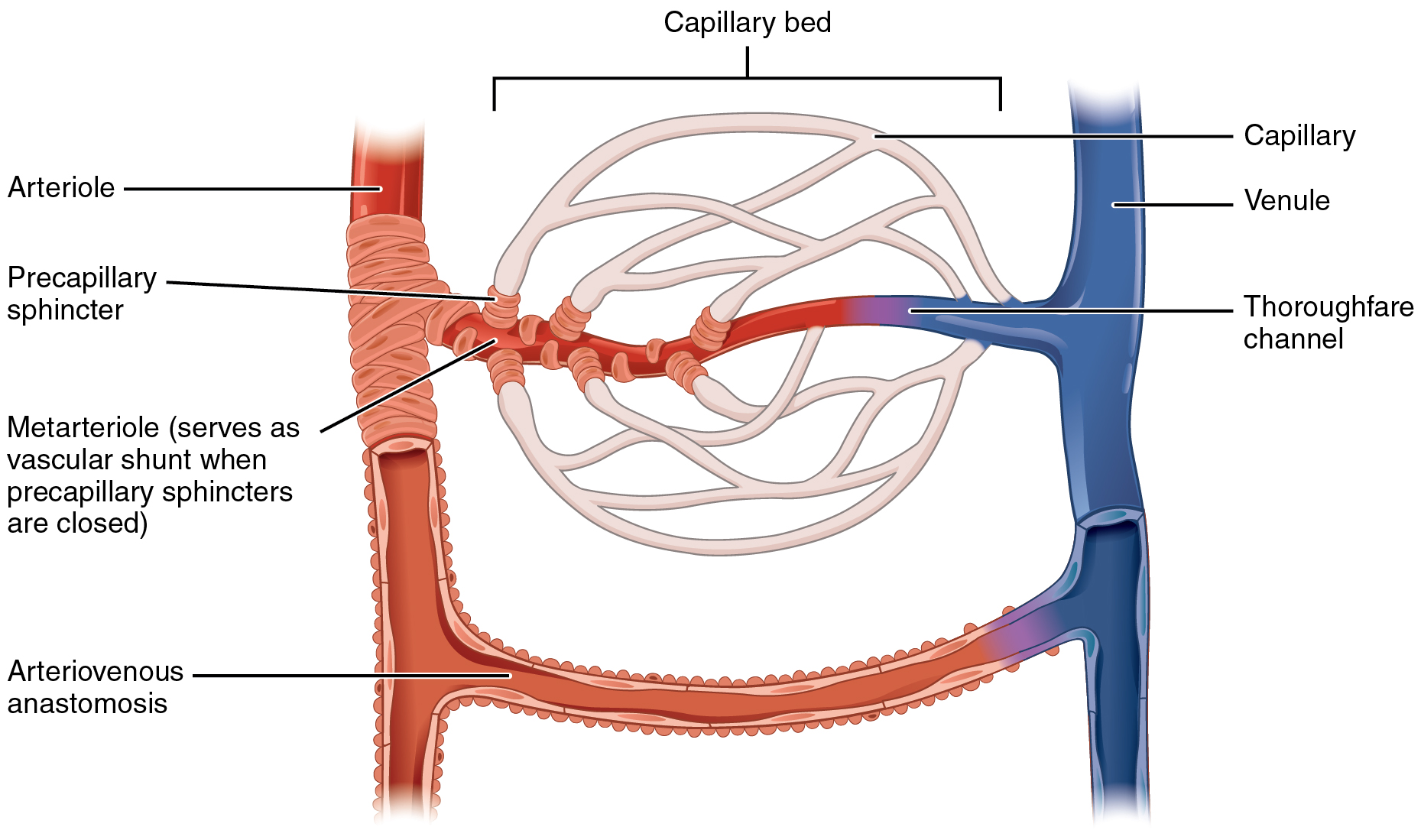
The microcirculation is the circulation of the blood in the smallest blood vessels, the microvessels of the microvasculature present within organ tissues. The microvessels include terminal arterioles, metarterioles, capillaries, and venules. Arterioles carry oxygenated blood to the capillaries, and blood flows out of the capillaries through venules into veins. In addition to these blood vessels, the microcirculation also includes lymphatic capillaries and collecting ducts. The main functions of the microcirculation are the delivery of oxygen and nutrients and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2). It also serves to regulate blood flow and tissue perfusion thereby affecting blood pressure and responses to inflammation which can include edema (swelling). Most vessels of the microcirculation are lined by flattened cells of the endothelium and many of them are surrounded by contractile cells called pericytes. The endothelium provides a smooth surface for the flow of blood and reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary
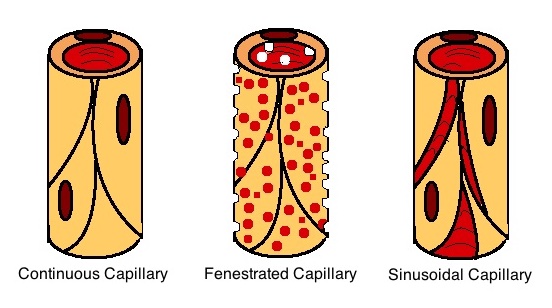
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: they convey blood between the arterioles and venules. These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them. Substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in the microcirculation. During early embryonic development, new capillaries are formed through vasculogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation that occurs through a '' de novo'' production of endothelial cells that then form vascular tubes. The term '' angiogenesis'' denotes the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels and already pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: they convey blood between the arterioles and venules. These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them. Substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in the microcirculation. During early embryonic development, new capillaries are formed through vasculogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation that occurs through a '' de novo'' production of endothelial cells that then form vascular tubes. The term '' angiogenesis'' denotes the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels and already p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arterioles
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the primary site of vascular resistance. The greatest change in blood pressure and velocity of blood flow occurs at the transition of arterioles to capillaries.This function is extremely important because it prevents the thin, one-layer capillaries from exploding upon pressure. The arterioles achieve this decrease in pressure, as they are the site with the highest resistance (a large contributor to total peripheral resistance) which translates to a large decrease in the pressure. Structure Microanatomy In a healthy vascular system the endothelium lines all blood-contacting surfaces, including arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, capillaries, and heart chambers. This healthy condition is promoted by the ample production of nitric oxide by the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriole
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the primary site of vascular resistance. The greatest change in blood pressure and velocity of blood flow occurs at the transition of arterioles to capillaries.This function is extremely important because it prevents the thin, one-layer capillaries from exploding upon pressure. The arterioles achieve this decrease in pressure, as they are the site with the highest resistance (a large contributor to total peripheral resistance) which translates to a large decrease in the pressure. Structure Microanatomy In a healthy vascular system the endothelium lines all blood-contacting surfaces, including arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, capillaries, and heart chambers. This healthy condition is promoted by the ample production of nitric oxide by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venule
A venule is a very small blood vessel in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the larger blood vessels, the veins. Venules range from 7μm to 1mm in diameter. Veins contain approximately 70% of total blood volume, while about 25% is contained in the venules. Many venules unite to form a vein. Structure Venule walls have three layers: An inner endothelium composed of squamous endothelial cells that act as a membrane, a middle layer of muscle and elastic tissue and an outer layer of fibrous connective tissue. The middle layer is poorly developed so that venules have thinner walls than arterioles. They are porous so that fluid and blood cells can move easily from the bloodstream through their walls. Short portal venules between the neural and anterior pituitary lobes provide an avenue for rapid hormonal exchange via the blood. Specifically within and between the pituitary lobes is anatomical evidence for confluent interlobe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriole
An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the primary site of vascular resistance. The greatest change in blood pressure and velocity of blood flow occurs at the transition of arterioles to capillaries.This function is extremely important because it prevents the thin, one-layer capillaries from exploding upon pressure. The arterioles achieve this decrease in pressure, as they are the site with the highest resistance (a large contributor to total peripheral resistance) which translates to a large decrease in the pressure. Structure Microanatomy In a healthy vascular system the endothelium lines all blood-contacting surfaces, including arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, capillaries, and heart chambers. This healthy condition is promoted by the ample production of nitric oxide by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venules
A venule is a very small blood vessel in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the larger blood vessels, the veins. Venules range from 7μm to 1mm in diameter. Veins contain approximately 70% of total blood volume, while about 25% is contained in the venules. Many venules unite to form a vein. Structure Venule walls have three layers: An inner endothelium composed of squamous endothelial cells that act as a membrane, a middle layer of muscle and elastic tissue and an outer layer of fibrous connective tissue. The middle layer is poorly developed so that venules have thinner walls than arterioles. They are porous so that fluid and blood cells can move easily from the bloodstream through their walls. Short portal venules between the neural and anterior pituitary lobes provide an avenue for rapid hormonal exchange via the blood. Specifically within and between the pituitary lobes is anatomical evidence for confluent interlobe ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venule
A venule is a very small blood vessel in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the larger blood vessels, the veins. Venules range from 7μm to 1mm in diameter. Veins contain approximately 70% of total blood volume, while about 25% is contained in the venules. Many venules unite to form a vein. Structure Venule walls have three layers: An inner endothelium composed of squamous endothelial cells that act as a membrane, a middle layer of muscle and elastic tissue and an outer layer of fibrous connective tissue. The middle layer is poorly developed so that venules have thinner walls than arterioles. They are porous so that fluid and blood cells can move easily from the bloodstream through their walls. Short portal venules between the neural and anterior pituitary lobes provide an avenue for rapid hormonal exchange via the blood. Specifically within and between the pituitary lobes is anatomical evidence for confluent interlobe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area may feel heavy, and joint stiffness. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause. Causes may include venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, infections, angioedema, certain medications, and lymphedema. It may also occur after prolonged sitting or standing and during menstruation or pregnancy. The condition is more concerning if it starts suddenly, or pain or shortness of breath is present. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying mechanism involves sodium retention, decreased salt intake and a diuretic may be used. Elevating the legs and support stockings may be useful for edema of the legs. Older people are more commonly affected. The wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metarteriole
A metarteriole is a short microvessel in the microcirculation that links arterioles and capillaries. Instead of a continuous tunica media, they have individual smooth muscle cells placed a short distance apart, each forming a precapillary sphincter that encircles the entrance to that capillary bed. Constriction of these sphincters reduces or shuts off blood flow through their respective capillary beds. This allows the blood to be diverted to elsewhere in the body. Metarterioles exist in the '' mesenteric microcirculation'', and the name was originally conceived only to define the "''thoroughfare channels ''" between arterioles An arteriole is a small-diameter blood vessel in the microcirculation that extends and branches out from an artery and leads to capillaries. Arterioles have muscular walls (usually only one to two layers of smooth muscle cells) and are the prima ... and venules. In recent times the term has often been used instead to describe the smallest arterioles di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |