|
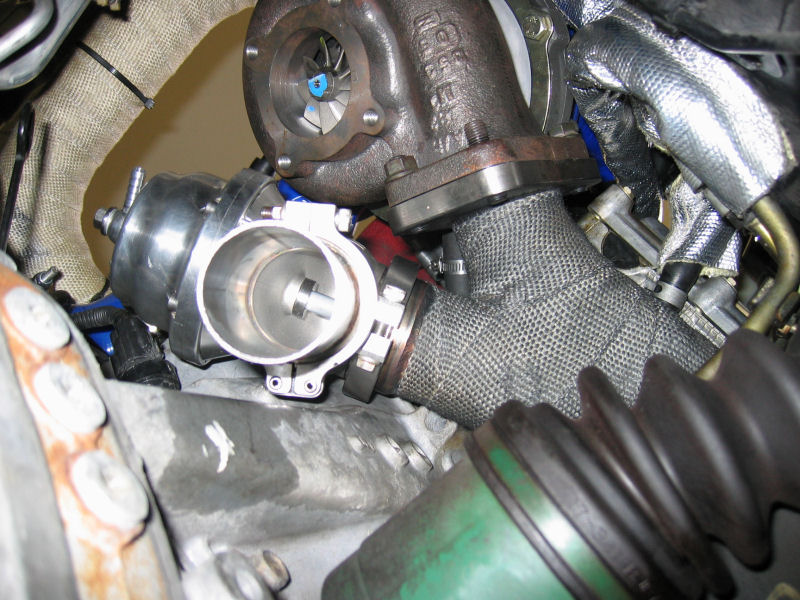
Blowoff Valve
A blowoff valve (also called dump valve or compressor bypass valve) is a pressure release system present in most petrol turbocharged engines. Blowoff valves are used to reduce pressure in the intake system as the throttle is closed, thus preventing compressor surge. Design A key function of blowoff valves is to prevent compressor surge, a phenomenon that would otherwise occur as the throttle is closed in a turbocharged engine. If the turbocharger's compressor wheel is spinning at high speed when the throttle is suddenly closed (such as during a gear change), the flow reduces beyond the surge line of the compressor. At this point the change in pressure across the compressor reduces, leading to a collapse in flow and possibly even flow reversal and a collapse in plenum pressure. As the compressor is still spinning at high speed, once the flow has reduced sufficiently, the change in pressure across the compressor begins to rise and flow is re-established into the plenum. This ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
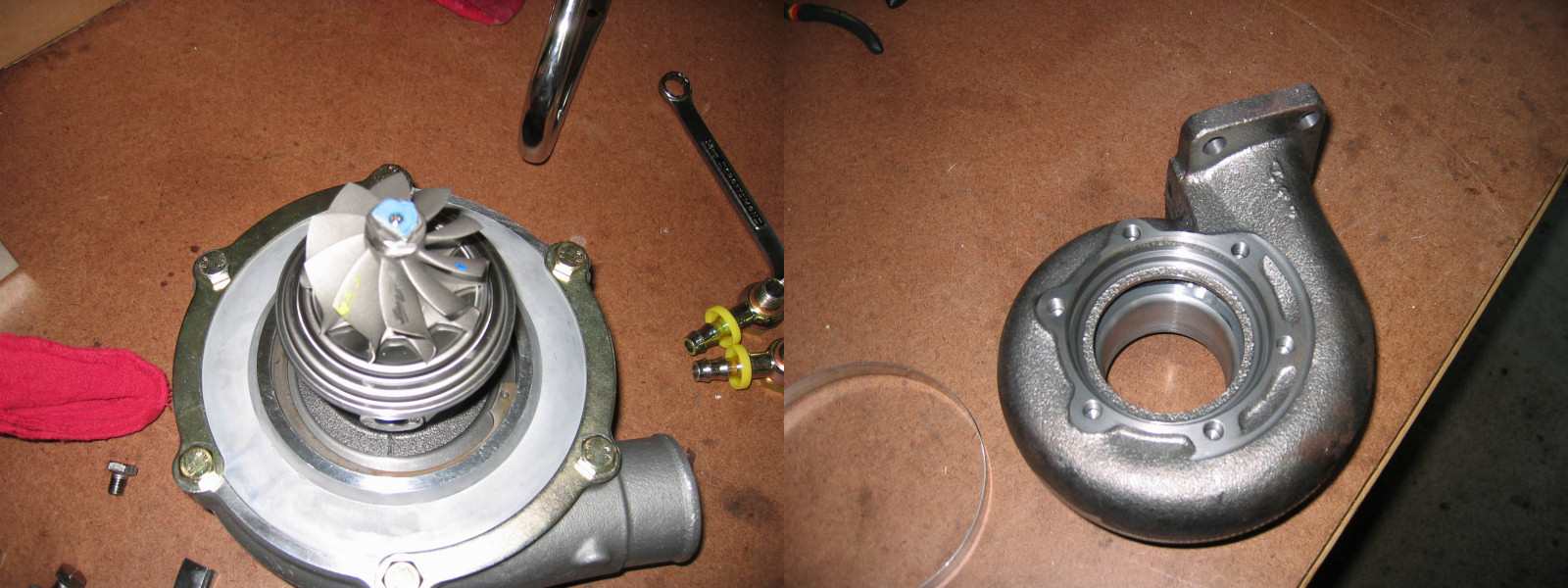
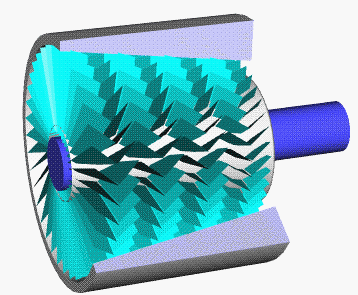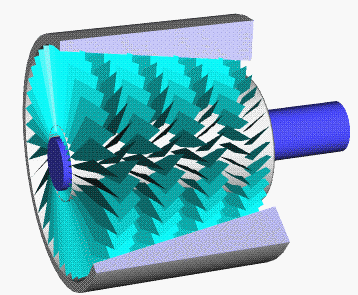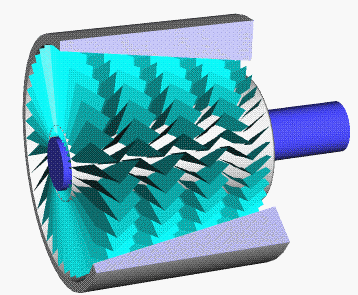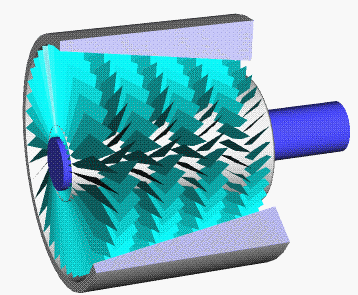
Turbocharger
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses, whereas a is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the invention of the turbocharger, |
Compressor Stall
A compressor stall is a local disruption of the airflow in the compressor of a gas turbine or turbocharger. A stall that results in the complete disruption of the airflow through the compressor is referred to as a compressor surge. The severity of the phenomenon ranges from a momentary power drop barely registered by the engine instruments to a complete loss of compression in case of a surge, requiring adjustments in the fuel flow to recover normal operation. Compressor stall was a common problem on early jet engines with simple aerodynamics and manual or mechanical fuel control units, but has been virtually eliminated by better design and the use of hydromechanical and electronic control systems such as Full Authority Digital Engine Control. Modern compressors are carefully designed and controlled to avoid or limit stall within an engine's operating range. Types There are two types of compressor stall: Rotating stall Rotating stall is a local disruption of airflow within the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dahlbäck Valve
Dahlbäck may refer to: * Björn Dahlbäck (born 1949), Swedish physician and medical researcher * Jesper Dahlbäck (born 1974), Swedish music producer and DJ * John Dahlbäck (born 1985), Swedish music producer and DJ * Helena Dahlbäck (1960–2000), Swedish children's book author * Herman Dahlbäck (1891–1968), Swedish Olympic rower {{DEFAULTSORT:Dahlback ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction. An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' has come to refer, informally, to any mechanism by which the power or speed of an engine is regulated, such as a car's accelerator pedal. What is often termed a ''throttle'' (in an aviation context) is also called a thrust lever, particularly for jet engine powered aircraft. For a steam locomotive, the valve which controls the steam is known as the regulator. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the throttle is a means of controlling an engine's power by regulating the amount of fuel or air entering the engine. In a motor vehicle the control used by the driver to regulate power is sometimes called the throttle, accelerator, or gas pedal. For a gasoline engine, the throttle most commonly regulates the amount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbo Flutter
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a turbocharger is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses, whereas a supercharger is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft). However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. History Prior to the invention of the turbocharger, |
Intake Manifold
In automotive engineering, an inlet manifold or intake manifold (in American English) is the part of an engine that supplies the fuel/ air mixture to the cylinders. The word ''manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the Anglo-Saxon ''manig'' anyand ''feald'' epeatedly and refers to the multiplying of one (pipe) into many.manifold, (adv.) "in the proportion of many to one, by many times". AD1526 ''Oxford English Dictionary'', In contrast, an exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from multiple cylinders into a smaller number of pipes – often down to one pipe. The primary function of the intake manifold is to ''evenly'' distribute the combustion mixture (or just air in a direct injection engine) to each intake port in the cylinder head(s). Even distribution is important to optimize the efficiency and performance of the engine. It may also serve as a mount for the carburetor, throttle body, fuel injectors and other components of the engine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Flow Sensor
A mass (air) flow sensor (MAF) is a sensor used to determine the mass flow rate of air entering a fuel-injected internal combustion engine. The air mass information is necessary for the engine control unit (ECU) to balance and deliver the correct fuel mass to the engine. Air changes its density with temperature and pressure. In automotive applications, air density varies with the ambient temperature, altitude and the use of forced induction, which means that mass flow sensors are more appropriate than volumetric flow sensors for determining the quantity of intake air in each cylinder. There are two common types of mass airflow sensors in use on automotive engines. These are the vane meter and the hot wire. Neither design employs technology that measures air mass directly. However, with additional sensors and inputs, an engine's ECU can determine the mass flow rate of intake air. Both approaches are used almost exclusively on electronic fuel injection (EFI) engines. Both s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spark Plug
A spark plug (sometimes, in British English, a sparking plug, and, colloquially, a plug) is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air mixture by an electric spark, while containing combustion pressure within the engine. A spark plug has a metal threaded shell, electrically isolated from a central electrode by a ceramic insulator. The central electrode, which may contain a resistor, is connected by a heavily insulated wire to the output terminal of an ignition coil or magneto. The spark plug's metal shell is screwed into the engine's cylinder head and thus electrically grounded. The central electrode protrudes through the porcelain insulator into the combustion chamber, forming one or more spark gaps between the inner end of the central electrode and usually one or more protuberances or structures attached to the inner end of the threaded shell and designated the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is an vehicle emissions control, exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis, catalyzing a redox chemical reaction, reaction. Catalytic converters are usually used with internal combustion engines fueled by gasoline or diesel fuel, diesel, including lean-burn engines, and sometimes on kerosene heaters and stoves. The first widespread introduction of catalytic converters was in the United States automobile market. To comply with the United States Environmental Protection Agency, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's stricter regulation of exhaust emissions, most gasoline-powered vehicles starting with the 1975 model year are equipped with catalytic converters. These "two-way" converters combine oxygen with carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Although two-way converters on gaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manifold Absolute Pressure
The manifold absolute pressure sensor (MAP sensor) is one of the sensors used in an internal combustion engine's electronic control system. Engines that use a MAP sensor are typically fuel injected. The manifold absolute pressure sensor provides instantaneous manifold pressure information to the engine's electronic control unit (ECU). The data is used to calculate air density and determine the engine's air mass flow rate, which in turn determines the required fuel metering for optimum combustion (see stoichiometry) and influence the advance or retard of ignition timing. A fuel-injected engine may alternatively use a mass airflow sensor (MAF sensor) to detect the intake airflow. A typical naturally aspirated engine configuration employs one or the other, whereas forced induction engines typically use both; a MAF sensor on the Cold Air Intake leading to the turbo and a MAP sensor on the intake tract post-turbo before the throttle body on the intake manifold. MAP sensor data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wastegate
A wastegate is a valve that controls the flow of exhaust gases to the turbine wheel in a turbocharged engine system.Robson, D. (2018). Aircraft General Knowledge. Aviation Theory Centre Pty Ltd. . Diversion of exhaust gases regulates the turbine speed, which in turn regulates the rotating speed of the compressor. The primary function of the wastegate is to regulate the maximum boost pressure in turbocharger systems, to protect the engine and the turbocharger. One advantage of installing a remote mount wastegate to a free-float (or non-WG) turbo includes allowance for a smaller A/R turbine housing, resulting in less lag time before the turbo begins to spool and create boost. Wastegate types External An external wastegate is a separate self-contained mechanism typically used with turbochargers that do not have internal wastegates. An external wastegate requires a specially constructed turbo manifold with a dedicated runner going to the wastegate. The external wastegate may be pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relief Valve
A relief valve or pressure relief valve (PRV) is a type of safety valve used to control or limit the pressure in a system; pressure might otherwise build up and create a process upset, instrument or equipment failure, or fire. The pressure is relieved by allowing the pressurized fluid to flow from an auxiliary passage out of the system. The relief valve is designed or set to open at a predetermined set pressure to protect pressure vessels and other equipment from being subjected to pressures that exceed their design limits. When the set pressure is exceeded, the relief valve becomes the " path of least resistance" as the valve is forced open and a portion of the fluid is diverted through the auxiliary route. In systems containing flammable fluids, the diverted fluid (liquid, gas or liquid-gas mixture) is either recaptured by a low pressure, high-flow vapor recovery system or is routed through a piping system known as a ''flare header'' or ''relief header'' to a central, elevated g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |