|
Axial Parallelism
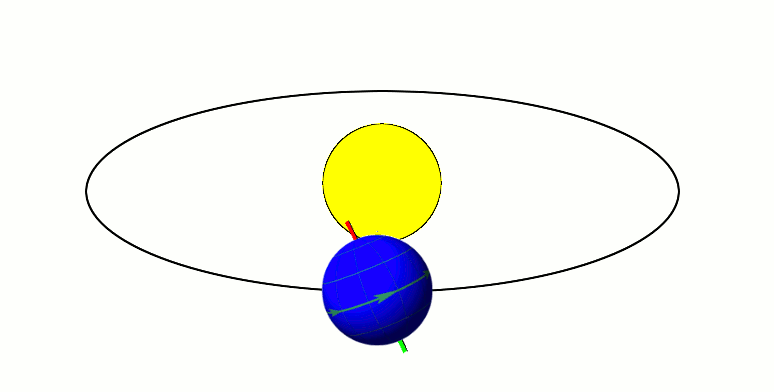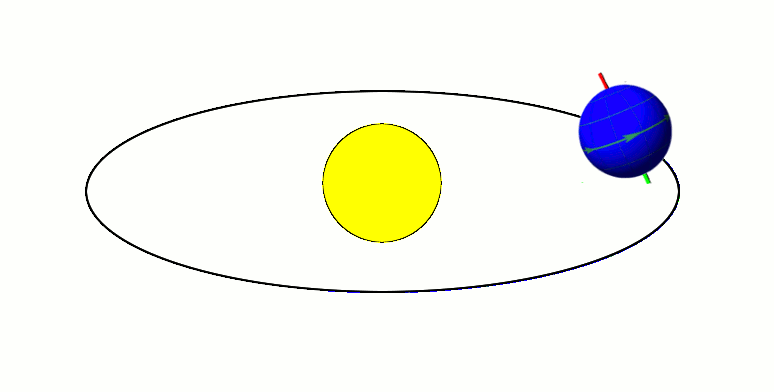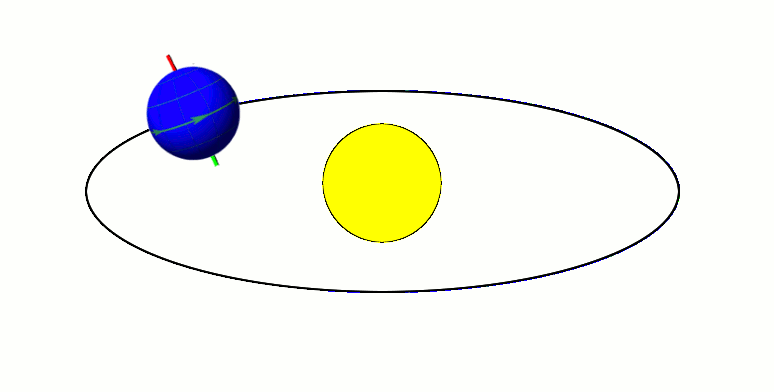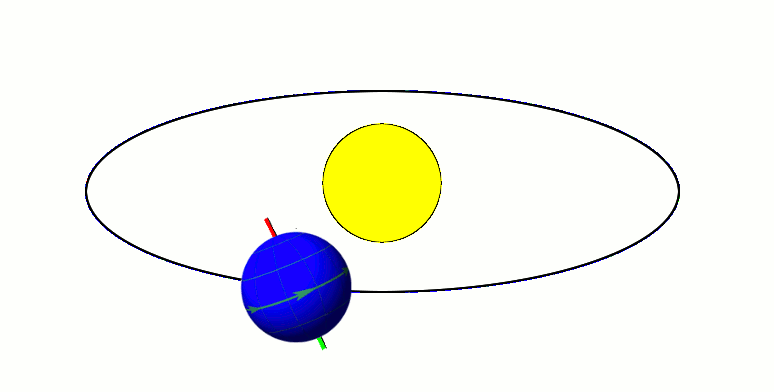
Axial parallelism (also known as gyroscopic stiffness, inertia or rigidity, or "rigidity in space") is the characteristic of a spinning body in which the direction of the axis of rotation remains fixed as the object moves through space. In astronomy, this characteristic is found in astronomical bodies in orbit. It is the same effect that causes a gyroscope's axis of rotation to remain constant as the Earth rotates, allowing the devices to measure Earth's rotation. Examples Earth's axial parallelism The Earth's orbit, with its Axial tilt, axis tilted at 23.5 degrees, exhibits approximate axial parallelism, maintaining its direction towards Polaris (the "North Star") year-round. Together with the Earth's axial tilt, this is one of the primary reasons for the Earth's seasons, as illustrated by the diagram to the right. Minor variation in the direction of the axis, known as axial precession, takes place over the course of 26,000 years. As a result, over the next 11,000 years the Eart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Tilt Animation
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large list of largest lakes and seas in the Solar System, volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only water distribution on Earth, Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving plate tectonics, tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, Volcano, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. Atmosphere of Earth, The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the Solar irradiance, energy from the Sun c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |