|
Antimalarial
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young children and pregnant women. As of 2018, modern treatments, including for severe malaria, continued to depend on therapies deriving historically from quinine and artesunate, both parenteral (injectable) drugs, expanding from there into the many classes of available modern drugs. Incidence and distribution of the disease ("malaria burden") is expected to remain high, globally, for many years to come; moreover, known antimalarial drugs have repeatedly been observed to elicit resistance in the malaria parasite—including for combination therapies featuring artemisinin, a drug of last resort, where resistance has now been observed in Southeast Asia. As such, the needs for new antimalarial agents and new strategies of treatment (e.g., new c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, Epileptic seizure, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected ''Anopheles'' mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial Immunity (medical), resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. The mosquitoes themselves are harmed by malaria, causing reduced lifespans in those infected by it. Malaria is caused by protozoa, single-celled microorganisms of the genus ''Plasmodium''. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Artemisinin
Artemisinin () and its semisynthetic derivatives are a group of drugs used in the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum''. It was discovered in 1972 by Tu Youyou, who shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for her discovery. Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are now standard treatment worldwide for ''P. falciparum'' malaria as well as malaria due to other species of ''Plasmodium''. Artemisinin can be extracted from the herb '' Artemisia annua'' (sweet wormwood), which is used in traditional Chinese medicine. Alternatively, it can be prepared by a semi-synthetic method from a precursor compound that can be produced using a genetically engineered yeast, which is much more efficient than extraction from the plant. Artemisinin and its derivatives are all sesquiterpene lactones containing an unusual peroxide bridge. This endoperoxide 1,2,4-trioxane ring is responsible for their antimalarial properties. Few other natural compounds wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chloroquine
Chloroquine is an antiparasitic medication that treats malaria. It works by increasing the levels of heme in the blood, a substance toxic to the malarial parasite. This kills the parasite and stops the infection from spreading. Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication. Chloroquine is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus. While it has not been formally studied in pregnancy, it appears safe. It is taken by mouth. It was studied to treat COVID-19 early in the COVID-19 pandemic, pandemic, but these studies were largely halted in the northern summer of 2020, and the National Institutes of Health, NIH does not recommend its use for this purpose. Common side effects include muscle problems, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and skin rash. Serious side effects include problems with vision, muscle damage, seizures, and aplas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
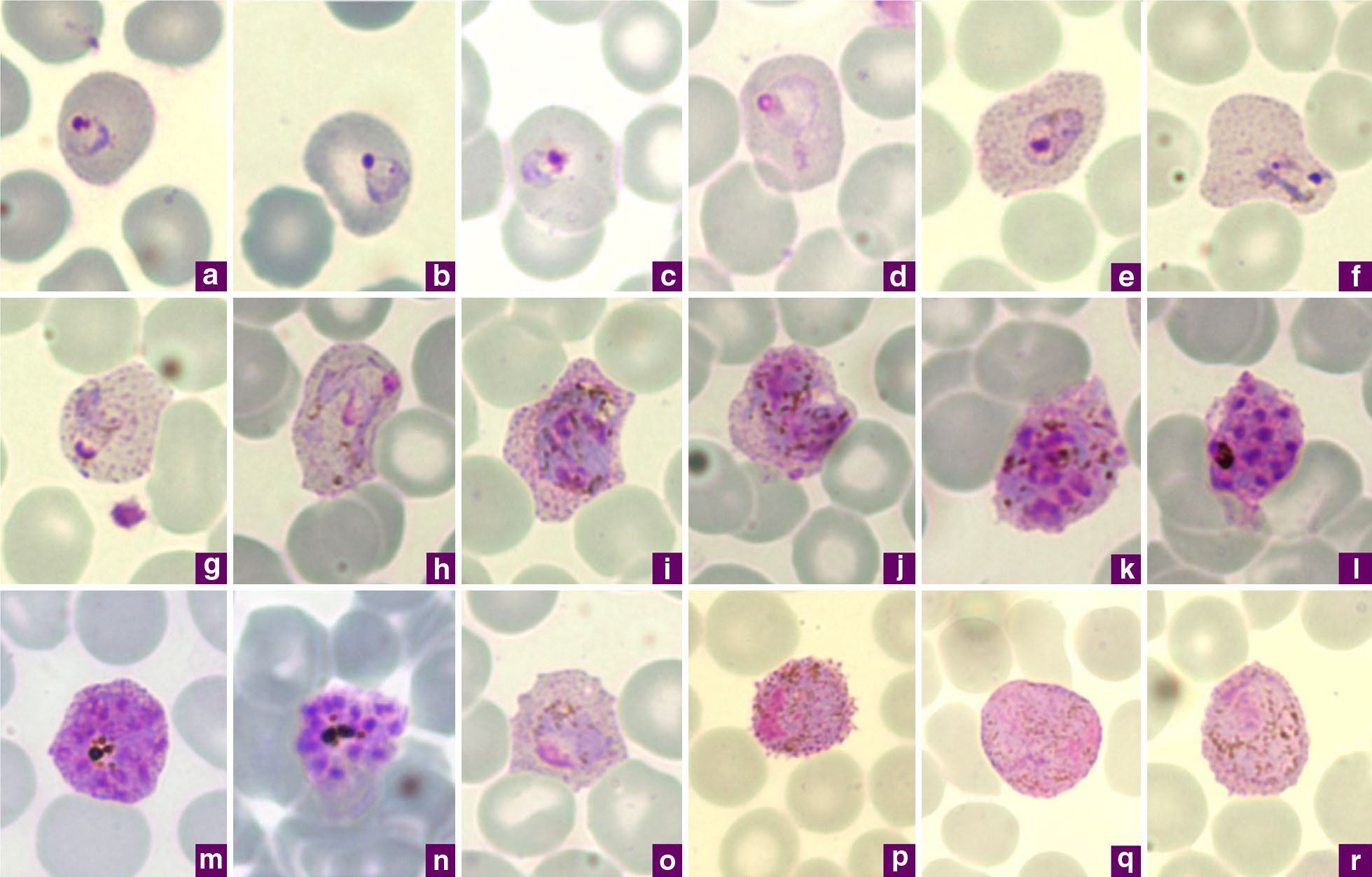
Plasmodium Falciparum
''Plasmodium falciparum'' is a Unicellular organism, unicellular protozoan parasite of humans and is the deadliest species of ''Plasmodium'' that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female ''Anopheles'' mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. ''P. falciparum'' is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer (Burkitt's lymphoma) and is classified as a List of IARC Group 2A carcinogens, Group 2A (probable) carcinogen. The species originated from the malarial parasite ''Laverania'' found in gorillas, around 10,000 years ago. Alphonse Laveran was the first to identify the parasite in 1880, and named it ''Oscillaria malariae''. Ronald Ross discovered its transmission by mosquito in 1897. Giovanni Battista Grassi elucidated the complete transmission from a female Anopheles, anopheline mosquito to humans in 1898. In 1897, William H. Welch create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intermittent Preventive Therapy
Intermittent preventive therapy or intermittent preventive treatment (IPT) is a public health intervention aimed at treating and preventing malaria Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ... episodes in infants (IPTi), children (IPTc), schoolchildren (IPTsc) and pregnant women (IPTp). The intervention builds on two tested malaria control strategies to clear existing parasites (treatment effect seen in mass drug administrations) and to prevent new infections ( prophylaxis). IPTi IPTi using the antimalarial drug sulfadoxine/ pyrimethamine (S/P) was pioneered in Ifakara, Tanzania in 1999. Infants received S/P at ages 3, 6, and 9 months in combination with their routine childhood (EPI) vaccinations. IPTi reduced clinical attacks of malaria by 59% (95% CI, 41%–72%) in Ifakara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hemozoin
Haemozoin is a disposal product formed from the digestion of blood by some blood-feeding parasites. These hematophagy, hematophagous organisms such as malaria parasites (''Plasmodium spp.''), ''Rhodnius'' and ''Schistosoma'' digest haemoglobin and release high quantities of free heme, which is the non-protein component of haemoglobin. Heme is a prosthetic group consisting of an iron atom contained in the center of a heterocyclic porphyrin ring. Free heme is toxic to cells, so the parasites convert it into an insoluble crystalline form called hemozoin. In malaria parasites, hemozoin is often called ''malaria pigment''. Since the formation of hemozoin is essential to the survival of these parasites, it is an attractive target for drug development, developing drugs and is much-studied in ''Plasmodium'' as a way to find drugs to treat malaria (malaria's Achilles' heel). Several currently used antimalarial drugs, such as chloroquine and mefloquine, are thought to kill malaria parasites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
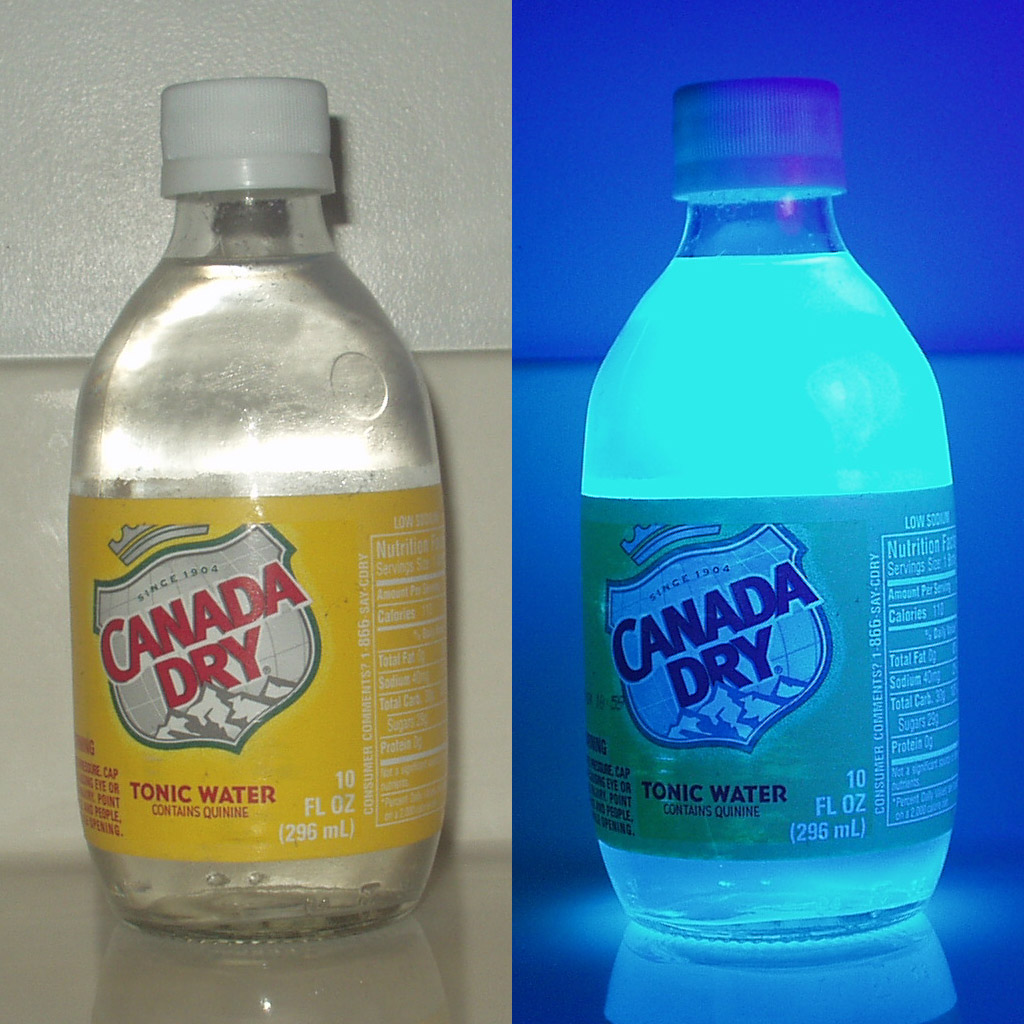
Quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg cramps, quinine is not recommended for this purpose due to the risk of serious side effects. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously. Malaria resistance to quinine occurs in certain areas of the world. Quinine is also used as an ingredient in tonic water and other beverages to impart a bitter taste. Common side effects include headache, tinnitus, ringing in the ears, vision issues, and sweating. More severe side effects include deafness, thrombocytopenia, low blood platelets, and an irregular heartbeat. Use can make one more prone to sunburn. While it is unclear if use during pregnancy carries potential for fetal harm, treating malaria during pregnancy with quinine when appropriate is still recommended. Quinine is an alkaloid, a natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine, sold under the brand name Plaquenil among others, is a medication used to prevent and treat malaria in areas where malaria remains sensitive to chloroquine. Other uses include treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and porphyria cutanea tarda. It is taken by mouth, often in the form of hydroxychloroquine sulfate. Common side effects may include vomiting, headache, blurred vision, and muscle weakness. Severe side effects may include allergic reactions, retinopathy, and irregular heart rate. Although all risk cannot be excluded, it remains a treatment for rheumatic disease during pregnancy. Hydroxychloroquine is in the antimalarial and 4-aminoquinoline families of medication. Hydroxychloroquine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1955. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2022, it was the 112th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. Hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plasmodium Vivax
''Plasmodium vivax'' is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than ''Plasmodium falciparum'', the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, ''P. vivax'' malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly (a pathologically enlarged spleen). ''P. vivax'' is carried by the female ''Anopheles'' mosquito; the males do not bite. Health Epidemiology ''Plasmodium vivax'' is found mainly in Asia, Latin America, and in some parts of Africa. ''P. vivax'' is believed to have originated in Asia, but recent studies have shown that wild chimpanzees and gorillas throughout central Africa are endemically infected with parasites that are closely related to human ''P. vivax.'' These findings indicate that human P. vivax is of African origin. ''Plasmodium vivax'' accounts for 65% of malaria cases in Asia and South America. Unlike ''Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a broad class of natural product, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including bacteria, fungus, fungi, Medicinal plant, plants, and animals. They can be purified from crude extracts of these organisms by acid-base extraction, or solvent extractions followed by silica-gel column chromatography. Alkaloids have a wide range of pharmacology, pharmacological activities including antimalarial medication, antimalarial (e.g. quinine), asthma, antiasthma (e.g. ephedrine), chemotherapy, anticancer (e.g. omacetaxine mepesuccinate, homoharringtonine), cholinomimetic (e.g. galantamine), vasodilation, vasodilatory (e.g. vincamine), Antiarrhythmic agent, antiarrhythmic (e.g. quinidine), analgesic (e.g. morphine), antibacterial (e.g. chelerythrine), and anti-diabetic, antihyperglycemic activities (e.g. berb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Malaria Prophylaxis
Malaria prophylaxis is the preventive treatment of malaria. Several malaria vaccines are under development. For pregnant women who are living in malaria endemic areas, routine malaria chemoprevention is recommended. It improves anemia and parasite level in the blood for the pregnant women and the birthweight in their infants. Strategies * Risk management * Bite prevention—clothes that cover as much skin as possible, insect repellent, insecticide-impregnated bed nets and indoor residual spraying * Chemoprophylaxis * Rapid diagnosis and treatment Recent improvements in malaria prevention strategies have further enhanced its effectiveness in combating areas highly infected with the malaria parasite. Additional bite prevention measures include mosquito and insect repellents that can be directly applied to skin. This form of mosquito repellent is slowly replacing indoor residual spraying, which is considered to have high levels of toxicity by World Health Organization (WHO). Furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |