chloroquine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chloroquine is an antiparasitic medication that treats malaria. It works by increasing the levels of
 Chloroquine has been used in the treatment and prevention of
Chloroquine has been used in the treatment and prevention of

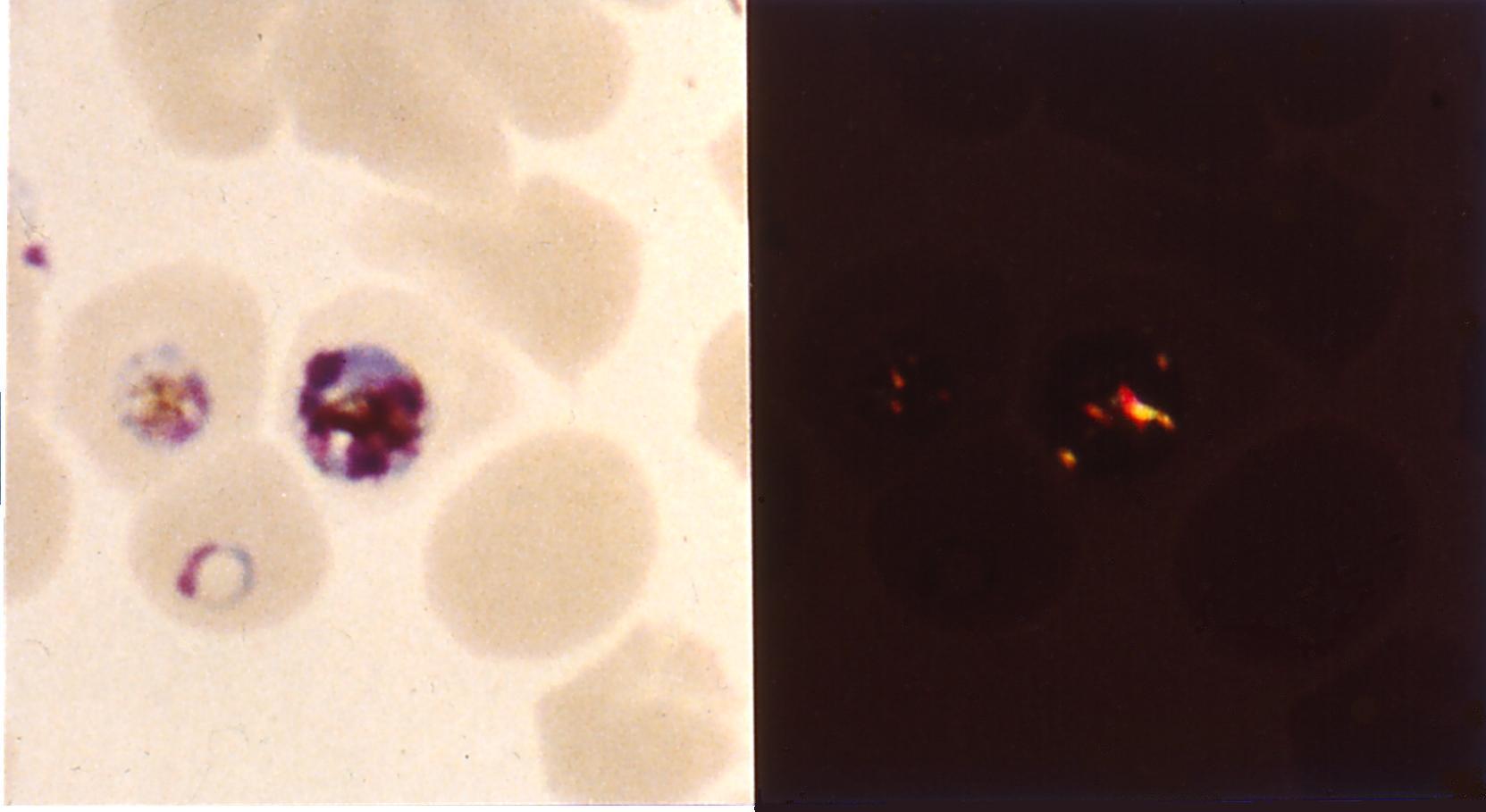 The lysosomotropic character of chloroquine is believed to account for much of its antimalarial activity; the drug concentrates in the acidic food vacuole of the parasite and interferes with essential processes. Its lysosomotropic properties further allow for its use for ''in vitro'' experiments pertaining to intracellular lipid related diseases, autophagy, and apoptosis.
Inside
The lysosomotropic character of chloroquine is believed to account for much of its antimalarial activity; the drug concentrates in the acidic food vacuole of the parasite and interferes with essential processes. Its lysosomotropic properties further allow for its use for ''in vitro'' experiments pertaining to intracellular lipid related diseases, autophagy, and apoptosis.
Inside
 In
In  After World War I, the German government sought alternatives to quinine. Chloroquine, a synthetic analogue with the same
After World War I, the German government sought alternatives to quinine. Chloroquine, a synthetic analogue with the same
 By 1949, chloroquine manufacturing processes had been established to allow its widespread use.
By 1949, chloroquine manufacturing processes had been established to allow its widespread use.
Chloroquine and its modified forms have also been evaluated as treatment options for inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prostheti ...
in the blood, a substance toxic to the malarial parasite. This kills the parasite and stops the infection from spreading. Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication. Chloroquine is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, and lupus erythematosus
is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, ...
. While it has not been formally studied in pregnancy, it appears safe. It is taken by mouth. It was studied to treat COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
early in the pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
, but these studies were largely halted in the northern summer of 2020, and the NIH does not recommend its use for this purpose.
Common side effects include muscle problems, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and skin rash. Serious side effects include problems with vision, muscle damage, seizures
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
, and low blood cell levels. Chloroquine is a member of the drug class 4-aminoquinoline. As an antimalarial, it works against the asexual form of the malaria parasite in the stage of its life cycle within the red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
. How it works in rheumatoid arthritis and lupus erythematosus is unclear.
Chloroquine was discovered in 1934 by Hans Andersag. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health s ...
. It is available as a generic medication
A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active ch ...
.
Medical uses
Malaria
 Chloroquine has been used in the treatment and prevention of
Chloroquine has been used in the treatment and prevention of malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
from ''Plasmodium vivax
''Plasmodium vivax'' is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than ''Plasmodium falciparum'', the deadliest of the five huma ...
'', '' P. ovale'', and '' P. malariae''. It is generally not used for ''Plasmodium falciparum
''Plasmodium falciparum'' is a Unicellular organism, unicellular protozoan parasite of humans and is the deadliest species of ''Plasmodium'' that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female ''Anopheles'' mos ...
'' as there is widespread resistance to it.
Chloroquine has been extensively used in mass drug administration
The administration of drugs to whole populations irrespective of disease status is referred to as mass drug administration (MDA) or mass dispensing.
This article describes the administration of antimalarial drugs to whole populations, an interven ...
s, which may have contributed to the emergence and spread of resistance. It is recommended to check if chloroquine is still effective in the region prior to using it. In areas where resistance is present, other antimalarials, such as mefloquine
Mefloquine, sold under the brand name Lariam among others, is a medication used to prevent or treat malaria. When used for prevention it is typically started before potential exposure and continued for several weeks after potential exposure. It ...
or atovaquone
Atovaquone, sold under the brand name Mepron, is an antimicrobial medication for the prevention and treatment of ''Pneumocystis jirovecii'' pneumonia (PCP).
Atovaquone is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of naphthoquinones. Atova ...
, may be used instead. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
recommend against treatment of malaria with chloroquine alone due to more effective combinations.
Amebiasis
In treatment of amoebic liver abscess, chloroquine may be used instead of or in addition to other medications in the event of failure of improvement withmetronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl and Metrogyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vagino ...
or another nitroimidazole
Nitroimidazoles are the group of organic compound, organic compounds consisting of an imidazole ring with at least one nitro group substituent. The term also refers to the class of antibiotics that have nitroimidazole in their structures. These an ...
within five days or intolerance to metronidazole or a nitroimidazole.
Rheumatic disease
As it mildly suppresses theimmune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
, chloroquine is used in some autoimmune disorder
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
s, such as rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
and has an off-label indication for lupus erythematosus
is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, ...
.
Side effects
Side effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect of the use of a medicinal drug or other treatment, usually adverse but sometimes beneficial, that is unintended. Herbal and traditional medicines also have side effects.
A drug or procedure usually used ...
include blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, headache, diarrhea, swelling legs/ankles, shortness of breath, pale lips/nails/skin, muscle weakness, easy bruising/bleeding, hearing and mental problems.
* Unwanted/uncontrolled movements (including tongue and face twitching, diskenesia, and dystonia
Dystonia is a neurology, neurological Hyperkinesia, hyperkinetic Movement disorders, movement disorder in which sustained or repetitive muscle contractions occur involuntarily, resulting in twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal fixed po ...
)
* Deafness or tinnitus
Tinnitus is a condition when a person hears a ringing sound or a different variety of sound when no corresponding external sound is present and other people cannot hear it. Nearly everyone experiences faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely ...
* Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps
* Headache
* Mental/mood changes (such as confusion, personality changes, unusual thoughts/behavior, depression, feeling being watched, hallucinating)
* Signs of serious infection (such as high fever, severe chills, persistent sore throat)
* Skin itch
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both ...
iness, skin color changes, hair loss, and skin rashes
** Chloroquine-induced itching is very common among black Africans (70%), but much less common in other races. It increases with age, and is so severe as to stop compliance with drug therapy. It is increased during malaria fever; its severity is correlated to the malaria parasite load in blood. Some evidence indicates it has a genetic basis and is related to chloroquine action with opiate receptors centrally or peripherally.
* Triggering of a severe psoriasis attack in those with psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete b ...
* Unpleasant metallic taste
** This could be avoided by "taste-masked and controlled release" formulations such as multiple emulsions.
* Chloroquine retinopathy (irreversible retinal damage)
* Electrocardiographic changes
** This manifests itself as either conduction disturbances (bundle-branch block, atrioventricular block) or cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of primary diseases of the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. A ...
— often with hypertrophy, restrictive physiology, and congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF ...
. The changes may be irreversible. Only two cases have been reported requiring heart transplantation, suggesting this particular risk is very low. Electron microscopy of cardiac biopsies show pathognomonic cytoplasmic inclusion bodies.
* Pancytopenia
Pancytopenia is a medical condition in which there is significant reduction in the number of almost all blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, monocytes, lymphocytes, etc.).
If only two parameters from the complete blood cou ...
, aplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia (AA) is a severe hematologic condition in which the body fails to make blood cells in sufficient numbers.
Normally, blood cells are produced in the bone marrow by stem cells that reside there, but patients with aplastic anemia ...
, reversible agranulocytosis
Agranulocytosis, also known as agranulosis or granulopenia, is an acute condition involving a severe and dangerous lowered white blood cell count (leukopenia, most commonly of neutrophils) and thus causing neutropenia in the circulating blood. I ...
, low blood platelets, neutropenia
Neutropenia is an abnormally low concentration of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. Neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells and serve as the primary defense against infections by destroying bacteria ...
* Worsening of the condition for those with porphyria
Porphyria ( or ) is a group of disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, adversely affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as Porphyria#Acute porphyrias, acute p ...
*Delayed hypersensitivity syndrome has been described.Pregnancy
Chloroquine has not been shown to have any harmful effects on the fetus when used in the recommended doses for malarial prophylaxis. Small amounts of chloroquine are excreted in the breast milk of lactating women. However, this drug can be safely prescribed to infants, the effects are not harmful. Studies with mice show that radioactively tagged chloroquine passed through theplacenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
rapidly and accumulated in the fetal eyes which remained present five months after the drug was cleared from the rest of the body. Women who are pregnant or planning on getting pregnant are still advised against traveling to malaria-risk regions.
Elderly
There is not enough evidence to determine whether chloroquine is safe to be given to people aged 65 and older. Since it is cleared by the kidneys, toxicity should be monitored carefully in people with poor kidney functions, as is more likely to be the case in the elderly.Drug interactions
Chloroquine has a number of drug–drug interactions that might be of clinical concern: *Ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic belonging to the aminopenicillin class of the penicillin family. The drug is used to prevent and treat several bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, s ...
levels may be reduced by chloroquine;
* Antacids may reduce absorption of chloroquine;
* Cimetidine
Cimetidine, sold under the brand name Tagamet among others, is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production. It is mainly used in the treatment of heartburn and peptic ulcers.
With the development of proton pump ...
may inhibit metabolism of chloroquine; increasing levels of chloroquine in the body;
* Cyclosporine
Ciclosporin, also spelled cyclosporine and cyclosporin, is a calcineurin inhibitor, used as an immunosuppressant medication. It is taken orally or intravenously for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease, nephrotic syndrome, ecz ...
levels may be increased by chloroquine; and
* Mefloquine
Mefloquine, sold under the brand name Lariam among others, is a medication used to prevent or treat malaria. When used for prevention it is typically started before potential exposure and continued for several weeks after potential exposure. It ...
may increase risk of convulsions.
Overdose
Chloroquine, in overdose, has a risk of death of about 20%. It is rapidly absorbed from the gut with an onset of symptoms generally within an hour. Symptoms of overdose may include sleepiness, vision changes,seizures
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
, stopping of breathing, and heart problems such as ventricular fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the Ventricle (heart), ventricles of the heart Fibrillation, quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical conduction system of the heart, electrical activity. Ventricula ...
and low blood pressure. Low blood potassium may also occur.
While the usual dose of chloroquine used in treatment is 10 mg/kg, toxicity begins to occur at 20 mg/kg, and death may occur at 30 mg/kg. In children as little as a single tablet can be fatal.
Treatment recommendations include early mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, wit ...
, cardiac monitoring, and activated charcoal
"Activated" is a song by English singer Cher Lloyd. It was released on 22 July 2016 through Vixen Records. The song was made available to stream exclusively on ''Rolling Stone'' a day before to release (on 21 July 2016).
Background
In an inter ...
. Intravenous fluids
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
and vasopressors may be required with epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
being the vasopressor of choice. Seizures may be treated with benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat co ...
. Intravenous potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a sa ...
may be required, however this may result in high blood potassium later in the course of the disease. Dialysis has not been found to be useful.
Pharmacology
Absorption of chloroquine is rapid and primarily happens in the gastrointestinal tract. It is widely distributed in body tissues. Protein binding in plasma ranges from 46% to 79%. Its metabolism is partially hepatic, giving rise to its main metabolite, desethylchloroquine. Its excretion is ≥50% as unchanged drug in urine, where acidification of urine increases its elimination. It has a very high volume of distribution, as it diffuses into the body'sadipose tissue
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
.
Accumulation of the drug may result in deposits that can lead to blurred vision and blindness
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficul ...
. It and related quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
s have been associated with cases of retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
l toxicity, particularly when provided at higher doses for longer times. With long-term doses, routine visits to an ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a ...
are recommended.
Chloroquine is also a lysosomotropic agent, meaning it accumulates preferentially in the lysosomes
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
of cells in the body. The pKa for the quinoline nitrogen of chloroquine is 8.5, meaning it is about 10% deprotonated at physiological pH (per the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation). This decreases to about 0.2% at a lysosomal pH of 4.6. Because the deprotonated form is more membrane-permeable than the protonated form, a quantitative "trapping" of the compound in lysosomes results.
Mechanism of action

Malaria
 The lysosomotropic character of chloroquine is believed to account for much of its antimalarial activity; the drug concentrates in the acidic food vacuole of the parasite and interferes with essential processes. Its lysosomotropic properties further allow for its use for ''in vitro'' experiments pertaining to intracellular lipid related diseases, autophagy, and apoptosis.
Inside
The lysosomotropic character of chloroquine is believed to account for much of its antimalarial activity; the drug concentrates in the acidic food vacuole of the parasite and interferes with essential processes. Its lysosomotropic properties further allow for its use for ''in vitro'' experiments pertaining to intracellular lipid related diseases, autophagy, and apoptosis.
Inside red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
s, the malarial parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
, which is then in its asexual lifecycle stage, must degrade hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
to acquire essential amino acids, which the parasite requires to construct its own protein and for energy metabolism. Digestion is carried out in a vacuole of the parasitic cell.
Hemoglobin is composed of a protein unit (digested by the parasite) and a heme unit (not used by the parasite). During this process, the parasite releases the toxic and soluble molecule heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prostheti ...
. The heme moiety consists of a porphyrin ring called Fe(II)-protoporphyrin IX (FP). To avoid destruction by this molecule, the parasite biocrystallizes heme to form hemozoin
Haemozoin is a disposal product formed from the digestion of blood by some blood-feeding parasites. These hematophagy, hematophagous organisms such as malaria parasites (''Plasmodium spp.''), ''Rhodnius'' and ''Schistosoma'' digest haemoglobin an ...
, a nontoxic molecule. Hemozoin collects in the digestive vacuole as insoluble crystals.
Chloroquine enters the red blood cell by simple diffusion, inhibiting the parasite cell and digestive vacuole. Chloroquine (CQ) then becomes protonated (to CQ2+), as the digestive vacuole is known to be acidic (pH 4.7); chloroquine then cannot leave by diffusion. Chloroquine caps hemozoin molecules to prevent further biocrystallization
Biocrystallization is the formation of crystals from organic macromolecules by living organisms. This may be a stress response, a normal part of metabolism such as processes that dispose of waste compounds, or a pathology. Template mediated crysta ...
of heme, thus leading to heme buildup. Chloroquine binds to heme (or FP) to form the FP-chloroquine complex; this complex is highly toxic to the cell and disrupts membrane function. Action of the toxic FP-chloroquine and FP results in cell lysis and ultimately parasite cell autodigestion. Parasites that do not form hemozoin are therefore resistant to chloroquine.
Resistance in malaria
Since the first documentation of ''P. falciparum'' chloroquine resistance in the 1950s, resistant strains have appeared throughout East and West Africa, Southeast Asia, and South America. The effectiveness of chloroquine against ''P. falciparum'' has declined as resistant strains of the parasite evolved. Resistant parasites are able to rapidly remove chloroquine from the digestive vacuole using a transmembrane pump. Chloroquine-resistant parasites pump chloroquine out at 40 times the rate of chloroquine-sensitive parasites; the pump is coded by the ''P. falciparum'' chloroquine resistance transporter (''PfCRT'') gene. The natural function of the chloroquine pump is to transport peptides: mutations to the pump that allow it to pump chloroquine out impairs its function as a peptide pump and comes at a cost to the parasite, making it less fit. Resistant parasites also frequently have mutation in the ABC transporter ''P. falciparum'' multidrug resistance (''PfMDR1'') gene, although these mutations are thought to be of secondary importance compared to ''PfCRT''. An altered chloroquine-transporter protein, ''CG2'' has been associated with chloroquine resistance, but other mechanisms of resistance also appear to be involved.Verapamil
Verapamil, sold under various trade names, is a calcium channel blocker medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure, angina (chest pain from not enough blood flow to the heart), and supraventricular tachycardia. It may also be use ...
, a Ca2+ channel blocker, has been found to restore both the chloroquine concentration ability and sensitivity to this drug. Other agents which have been shown to reverse chloroquine resistance in malaria are chlorpheniramine
Chlorphenamine (CP, CPM), also known as chlorpheniramine, is an antihistamine used to treat the symptoms of allergic conditions such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever). It is taken orally (by mouth). The medication takes effect within two hour ...
, gefitinib
Gefitinib, sold under the brand name Iressa, is a medication used for certain breast, lung and other cancers. Gefitinib is an EGFR inhibitor, like erlotinib, which interrupts signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in targe ...
, imatinib
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral targeted therapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple tyrosine kinases ...
, tariquidar and zosuquidar.
chloroquine is still effective against poultry malaria in Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
. Sohsuebngarm et al. 2014 test '' P. gallinaceum'' at Chulalongkorn University
Chulalongkorn University (CU; ; , ) is a public university, public Autonomous university, autonomous research university in Bangkok, Thailand. The university was originally founded during King Chulalongkorn's reign as a school for training ro ...
and find the parasite is not resistant. Sertraline
Sertraline, sold under the brand name Zoloft among others, is an Antidepressant, antidepressant medication of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, socia ...
, fluoxetine
Fluoxetine, sold under the brand name Prozac, among others, is an Antidepressant, antidepressant medication of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class used for the treatment of major depressive disorder, Anxiety disorder, anx ...
and paroxetine
Paroxetine ( ), sold under the brand name Paxil among others, is an Antidepressant, antidepressant medication of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class used to treat major depressive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, o ...
reverse chloroquine resistance, making resistant biotypes susceptible if used in a cotreatment.
Antiviral
Chloroquine has antiviral effects against some viruses. It increases late endosomal and lysosomal pH, resulting in impaired release of the virus from the endosome or lysosome — release of the virus requires a low pH. The virus is therefore unable to release its genetic material into the cell and replicate. Chloroquine also seems to act as a zincionophore
In chemistry, an ionophore () is a chemical species that reversibly binds ions. Many ionophores are lipid-soluble entities that transport ions across the cell membrane. Ionophores catalyze ion transport across hydrophobic membranes, such as l ...
that allows extracellular zinc to enter the cell and inhibit viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions that synthesize RNA from a DNA template.
Using the e ...
.
Other
Chloroquine inhibitsthiamine
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin – an Nutrient#Micronutrients, essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosp ...
uptake. It acts specifically on the transporter SLC19A3.
Against rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, it operates by inhibiting lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), an ...
proliferation, phospholipase A2
The enzyme phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4, PLA2, systematic name phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase) catalyses the cleavage of fatty acids in position 2 of phospholipids, hydrolyzing the bond between the second fatty acid "tail" and the glycero ...
, antigen presentation in dendritic cells, release of enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s from lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
s, release of reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
from macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s, and production of IL-1.
History
Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
, the indigenous people extracted the bark of the ''Cinchona
''Cinchona'' (pronounced or ) is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae containing at least 23 species of trees and shrubs. All are native to the Tropical Andes, tropical Andean forests of western South America. A few species are ...
'' tree (''Cinchona officinalis
''Cinchona officinalis'' is a South American tree in the family Rubiaceae. It is native to wet montane forests in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Bolivia, between 1600–2700 meters above sea level.
Description
''Cinchona officinalis'' is a shrub ...
'') and used the extract to fight chills and fever in the seventeenth century. In 1633, this herbal medicine was introduced in Europe, where it was given the same use and also began to be used against malaria. The quinoline antimalarial drug quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
was isolated from the extract in 1820.
mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical Drug interaction, interaction through which a Medication, drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention o ...
was discovered in 1934, by Hans Andersag and coworkers at the Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer' ...
laboratories, who named it ''resochin''. It was ignored for a decade, because it was considered too toxic for human use. Instead, in World War II, the German Africa Corps used the chloroquine analogue 3-methyl-chloroquine, known as ''sontochin''. After Allied forces arrived in Tunis, sontochin fell into the hands of Americans, who sent the material back to the United States for analysis, leading to renewed interest in chloroquine. United States government-sponsored clinical trials for antimalarial drug development
Drug development is the process of bringing a new pharmaceutical drug to the market once a lead compound has been identified through the process of drug discovery. It includes preclinical research on microorganisms and animals, filing for regu ...
showed unequivocally that chloroquine has a significant therapeutic value as an antimalarial drug. It was introduced into clinical practice in 1947 for the prophylactic treatment of malaria.
Chemical synthesis
The first synthesis of chloroquine was disclosed in a patent filed byIG Farben
I. G. Farbenindustrie AG, commonly known as IG Farben, was a German Chemical industry, chemical and Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical conglomerate (company), conglomerate. It was formed on December 2, 1925 from a merger of six chemical co ...
in 1937. In the final step, 4,7-dichloroquinoline was reacted with 1-diethylamino-4-aminopentane.
: Society and culture
Formulations
Chloroquine comes in tablet form as the phosphate, sulfate, and hydrochloride salts. Chloroquine is usually dispensed as the phosphate.Names
Brand names include Chloroquine FNA, Resochin, Dawaquin, and Lariago.Other animals
Chloroquine, in various chemical forms, is used to treat and control surface growth of anemones and algae, and many protozoan infections in aquariums, e.g. the fish parasite '' Amyloodinium ocellatum''. It is also used in poultry malaria.Research
In biomedicinal science, chloroquine is used for ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
'' experiments to inhibit lysosomal degradation of protein products.
SARS-CoV
Chloroquine was proposed as a treatment forSARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the virus SARS-CoV-1, the first identified strain of the SARS-related coronavirus. The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the ...
, with ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
'' tests inhibiting the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus ( SARS-CoV). In October 2004, a published report stated that chloroquine acts as an effective inhibitor of the replication of SARS-CoV in vitro. In August 2005, a peer-reviewed study confirmed and expanded upon the results.
COVID-19
Other
Chloroquine was being considered in 2003, in pre-clinical models as a potential agent againstchikungunya
Chikungunya is an infection caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV). The disease was first identified in 1952 in Tanzania and named based on the Kimakonde words for "to become contorted". Chikungunya has become a global health concern due to ...
fever.
The radiosensitizing and chemosensitizing properties of chloroquine are being evaluated for anticancer strategies in humans.Chloroquine and its modified forms have also been evaluated as treatment options for inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
References
External links
* * {{Authority control 1934 introductions Antimalarial agents Chloroarenes CYP2D6 inhibitors Drugs developed by AstraZeneca Diethylamino compounds HERG blocker Quinolines World Health Organization essential medicines Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate German inventions of the Nazi period Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs