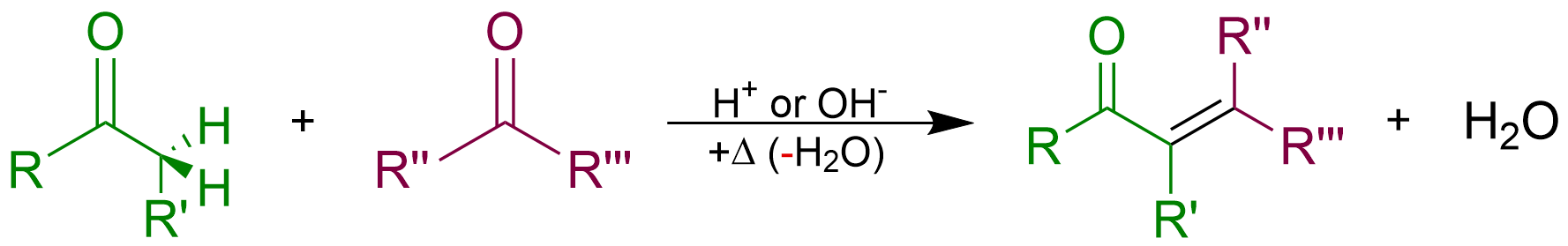|
Aldol Condensation
An aldol condensation is a condensation reaction in organic chemistry in which two carbonyl moieties (of aldehydes or ketones) react to form a β-hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone (an aldol reaction), and this is then followed by dehydration to give a conjugated enone. The overall reaction equation is as follows (where the Rs can be H) Aldol condensations are important in organic synthesis and biochemistry as ways to form carbon–carbon bonds. In its usual form, it involves the nucleophilic addition of a ketone enolate to an aldehyde to form a β-hydroxy ketone, or aldol (aldehyde + alcohol), a structural unit found in many naturally occurring molecules and pharmaceuticals. The term ''aldol condensation'' is also commonly used, especially in biochemistry, to refer to just the first (addition) stage of the process—the aldol reaction itself—as catalyzed by aldolases. However, the first step is formally an addition reaction rather than a condensation reaction bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' are methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, ''e.g.'', testosterone, and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considered retained IUPAC names, although some introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carbon–carbon Bond
A carbon–carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms. The most common form is the single bond: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon–carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is formed between one hybridized orbital from each of the carbon atoms. In ethane, the orbitals are sp3- hybridized orbitals, but single bonds formed between carbon atoms with other hybridizations do occur (e.g. sp2 to sp2). In fact, the carbon atoms in the single bond need not be of the same hybridization. Carbon atoms can also form double bonds in compounds called alkenes or triple bonds in compounds called alkynes. A double bond is formed with an sp2-hybridized orbital and a p-orbital that is not involved in the hybridization. A triple bond is formed with an sp-hybridized orbital and two p-orbitals from each atom. The use of the p-orbitals forms a pi bond. Chains and branching Carbon is one of the few elements that can form long chains of its own atoms, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elimination Reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one- or two-step mechanism. The one-step mechanism is known as the E2 reaction, and the two-step mechanism is known as the E1 reaction. The numbers refer not to the number of steps in the mechanism, but rather to the kinetics of the reaction: E2 is bimolecular (second-order) while E1 is unimolecular (first-order). In cases where the molecule is able to stabilize an anion but possesses a poor leaving group, a third type of reaction, E1cB-elimination reaction, E1CB, exists. Finally, the pyrolysis of xanthate and acetate esters proceed through an "internal" elimination mechanism, the Ei mechanism, Ei mechanism. E2 mechanism The E2 mechanism, where E2 stands for bimolecular elimination, involves a one-step mechanism in which ''carbon-hydrogen'' and ''carbon-halogen'' bonds break to form a double bond (''C=C molecular geometry, Pi bond''). The specifics of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aldol Reaction
The aldol reaction (aldol addition) is a Chemical reaction, reaction in organic chemistry that combines two Carbonyl group, carbonyl compounds (e.g. aldehydes or ketones) to form a new β-hydroxy carbonyl compound. Its simplest form might involve the nucleophilic addition of an Enolate, enolized ketone to another: These products are known as ''aldols'', from the ''ald''ehyde + alcoh''ol'', a structural motif seen in many of the products. The use of aldehyde in the name comes from its history: aldehydes are more reactive than ketones, so that the reaction was discovered first with them. The aldol reaction is paradigmatic in organic chemistry and one of the most common means of forming carbon–carbon bonds in organic chemistry. It lends its name to the family of aldol reactions and similar techniques analyze a whole family of carbonyl α-substitution reactions, as well as the Claisen condensation, diketone condensations. Scope Aldol structural units are found in many importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Addition Reaction
In organic chemistry, an addition reaction is an organic reaction in which two or more molecule A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...s combine to form a larger molecule called the '' adduct''.. An addition reaction is limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds. Examples include a molecule with a carbon–carbon double bond (an alkene) or a triple bond (an alkyne). Another example is a compound that has rings (which are also considered points of unsaturation). A molecule that has carbon— heteroatom double bonds, such as a carbonyl group () or imine group (), can undergo an addition reaction because its double-bond. An addition reaction is the reverse of an elimination reaction, in which one molecule divides into two or more molecules. For insta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aldolase
Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (), often just aldolase, is an enzyme catalyzing a reversible reaction that splits the aldol, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, into the triose phosphates dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). Aldolase can also produce DHAP from other (3S,4R)-ketose 1-phosphates such as fructose 1-phosphate and sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate. Gluconeogenesis and the Calvin cycle, which are anabolic pathways, use the reverse reaction. Glycolysis, a catabolic pathway, uses the forward reaction. Aldolase is divided into two classes by mechanism. The word aldolase also refers, more generally, to an enzyme that performs an aldol reaction (creating an aldol) or its reverse (cleaving an aldol), such as Sialic acid aldolase, which forms sialic acid. See the list of aldolases. Mechanism and structure Class I proteins form a protonated Schiff base intermediate linking a highly conserved active site lysine with the DHAP carbonyl carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Simple Aldol Reaction
Simple or SIMPLE may refer to: *Simplicity, the state or quality of being simple Arts and entertainment * ''Simple'' (album), by Andy Yorke, 2008, and its title track * "Simple" (Florida Georgia Line song), 2018 * "Simple", a song by Johnny Mathis from the 1984 album ''A Special Part of Me'' * "Simple", a song by Collective Soul from the 1995 album ''Collective Soul'' * "Simple", a song by Katy Perry from the 2005 soundtrack to ''The Sisterhood of the Traveling Pants'' * "Simple", a song by Khalil from the 2017 album ''Prove It All'' * "Simple", a song by Kreesha Turner from the 2008 album ''Passion'' * "Simple", a song by Ty Dolla Sign from the 2017 album ''Beach House 3'' deluxe version * ''Simple'' (video game series), budget-priced console games Businesses and organisations * Simple (bank), an American direct bank * SIMPLE Group, a consulting conglomeration based in Gibraltar * Simple Shoes, an American footwear brand * Simple Skincare, a British brand of soap an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pharmaceuticals
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are classified in many ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the medical prescription) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Medicines may be classified by mode of action, route of administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines. Drug discovery and drug development are complex and expensive endeavors undertaken by pharmaceutical companies, academic scientists, and governments. As a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chemical Structure
A chemical structure of a molecule is a spatial arrangement of its atoms and their chemical bonds. Its determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen) to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |