|
Aircraft Tail
The empennage ( or ), also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', p. 194. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, ''From the Ground Up'', p. 10 (27th revised edition) The term derives from the French language verb which means " to feather an arrow". Most aircraft feature an empennage incorporating vertical and horizontal stabilising surfaces which stabilise the flight dynamics of yaw and pitch, as well as housing control surfaces. In spite of effective control surfaces, many early aircraft that lacked a stabilising empennage were virtually unflyable. Even so-called "tailless aircraft" usually have a tail fin (usually a vertical stabiliser). Heavier-than-air aircraft without any kind of empennage (such as the Northrop B-2) are rare, and generally use specially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailplane
A tailplane, also known as a horizontal stabilizer, is a small lift (force), lifting surface located on the tail (empennage) behind the main lifting surfaces of a fixed-wing aircraft as well as other non-fixed-wing aircraft such as helicopters and gyroplanes. Not all fixed-wing aircraft have tailplanes. Canard (aeronautics), Canards, tailless aircraft, tailless and flying wing aircraft have no separate tailplane, while in V-tail aircraft the vertical stabilizer, rudder, and the tail-plane and elevator are combined to form two diagonal surfaces in a V layout. The function of the tailplane is to provide stability and control. In particular, the tailplane helps adjust for changes in position of the center of pressure (fluid mechanics), centre of pressure or centre of gravity caused by changes in speed and attitude, fuel consumption, or dropping cargo or payload. Tailplane types The tailplane comprises the tail-mounted fixed horizontal stabilizer and movable Elevator (aeronautics), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trim Tab
Trim tabs are small surfaces connected to the trailing edge of a larger Flight control surfaces, control surface on a boat or aircraft, used to control the trim of the controls, i.e. to counteract hydro- or aerodynamic forces and stabilise the boat or aircraft in a particular desired Orientation (geometry), attitude without the need for the operator to constantly apply a control force. This is done by adjusting the angle of the tab relative to the larger surface. Changing the setting of a trim tab adjusts the neutral or resting position of a control surface (such as an Elevator (aircraft), elevator or rudder). As the desired position of a control surface changes (corresponding mainly to different speeds), an adjustable trim tab will allow the operator to reduce the manual force required to maintain that position—to zero, if desired. Thus the trim tab acts as a servo tab. Because the Center of pressure (fluid mechanics), center of pressure of the trim tab is farther away from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trim (aircraft)
A conventional fixed-wing aircraft flight control system (AFCS) consists of flight control surfaces, the respective cockpit controls, connecting linkages, and the necessary operating mechanisms to control an aircraft's direction in flight. Aircraft engine controls are also considered flight controls as they change speed. The fundamentals of aircraft controls are explained in flight dynamics. This article centers on the operating mechanisms of the flight controls. The basic system in use on aircraft first appeared in a readily recognizable form as early as April 1908, on Louis Blériot's Blériot VIII pioneer-era monoplane design. Cockpit controls Primary controls Generally, the primary cockpit flight controls are arranged as follows:Langewiesche, WolfgangStick and Rudder: An Explanation of the Art of Flying McGraw-Hill Professional, 1990, , . * A control yoke (also known as a control column), centre stick or side-stick (the latter two also colloquially known as a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
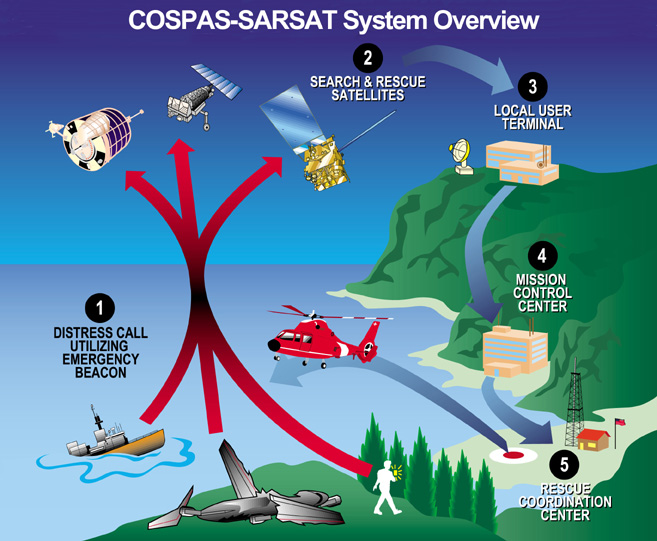
Emergency Locator Transmitter
An emergency position-indicating radiobeacon (EPIRB) is a type of emergency locator beacon for commercial and recreational boats; it is a portable, battery-powered radio transmitter used in emergencies to locate boaters in distress and in need of immediate rescue. In the event of an emergency, such as a ship sinking or medical emergency onboard, the transmitter is activated and begins transmitting a continuous 406 MHz distress radio signal, which is used by search-and-rescue teams to quickly locate the emergency and render aid. The distress signal is detected by satellites operated by an international consortium of rescue services, COSPAS-SARSAT, which can detect emergency beacons anywhere on Earth transmitting on the distress frequency of 406 MHz. The satellites calculate the position or utilize the GPS coordinates of the beacon and quickly pass the information to the appropriate local first responder organization, which performs the search and rescue. As the sear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Data Recorder
A flight recorder is an electronic recording device placed in an aircraft for the purpose of facilitating the investigation of aviation accidents and incidents. The device may often be referred to colloquially as a "black box", an outdated name which has become a misnomer—they are now required to be painted bright orange, to aid in their recovery after accidents. There are two types of flight recording devices: the flight data recorder (FDR) preserves the recent history of the flight through the recording of dozens of parameters collected several times per second; the cockpit voice recorder (CVR) preserves the recent history of the sounds in the cockpit, including the conversation of the pilots. The two devices may be combined into a single unit. Together, the FDR and CVR objectively document the aircraft's flight history, which may assist in any later investigation. The two flight recorders are required by international regulation, overseen by the International Civil Aviat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called rolling or banking. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal resolution. A much earlier aileron concept was patented in 1868 by British scientist Matthew Piers Watt Boul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudders
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (usually aircraft, air or watercraft, water). On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull (watercraft), hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yaw (rotation), yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or afterend. Often rudders are shaped to minimize Drag (physics), hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may link rudders to steering wheels. In typical aircraft, the rudder is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stabilator
A stabilator is a fully movable aircraft horizontal stabilizer (aircraft), stabilizer. It serves the usual functions of longitudinal stability, control and stick force requirements otherwise performed by the separate parts of a conventional horizontal stabilizer (which is fixed) and elevator (aeronautics), elevator (which is adjustable). Apart from reduced drag, particularly at high Mach numbers, it is a useful device for changing the aircraft balance within wide limits, and for reducing stick forces. Stabilator is a portmanteau of ''stabilizer'' and ''elevator''. It is also known as an all-moving tailplane (British English), all-movable tail(plane), all-moving stabilizer, all-flying tail (American English), all-flying horizontal tail, full-flying stabilizer, and slab tailplane. General aviation Because it involves a moving balanced surface, a stabilator can allow the pilot to generate a given pitching moment with a lower control force. Due to the high forces involved in tail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerofoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is a streamlined body that is capable of generating significantly more lift than drag. Wings, sails and propeller blades are examples of airfoils. Foils of similar function designed with water as the working fluid are called hydrofoils. When oriented at a suitable angle, a solid body moving through a fluid deflects the oncoming fluid (for fixed-wing aircraft, a downward force), resulting in a force on the airfoil in the direction opposite to the deflection. This force is known as aerodynamic force and can be resolved into two components: lift (perpendicular to the remote freestream velocity) and drag ( parallel to the freestream velocity). The lift on an airfoil is primarily the result of its angle of attack. Most foil shapes require a positive angle of attack to generate lift, but cambered airfoils can generate lift at zero angle of attack. Airfoils can be designed for use at different speeds by modifying their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevator (aircraft)
Elevators are flight control surfaces, usually at the rear of an aircraft, which control the aircraft's pitch, and therefore the angle of attack and the lift of the wing. The elevators are usually hinged to the tailplane or horizontal stabilizer. They may be the only pitch control surface present, and are sometimes located at the front of the aircraft (early airplanes and canards) or integrated into a rear "all-moving tailplane", also called a slab elevator or stabilator. Elevator control effectiveness The elevator is a usable up and down system that controls the plane, horizontal stabilizer usually creates a ''downward'' force which balances the nose down moment created by the wing lift force, which typically applies at a point (the wing center of lift) situated aft of the airplane's center of gravity. The effects of drag and changing the engine thrust may also result in pitch moments that need to be compensated with the horizontal stabilizer. Both the horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |