|
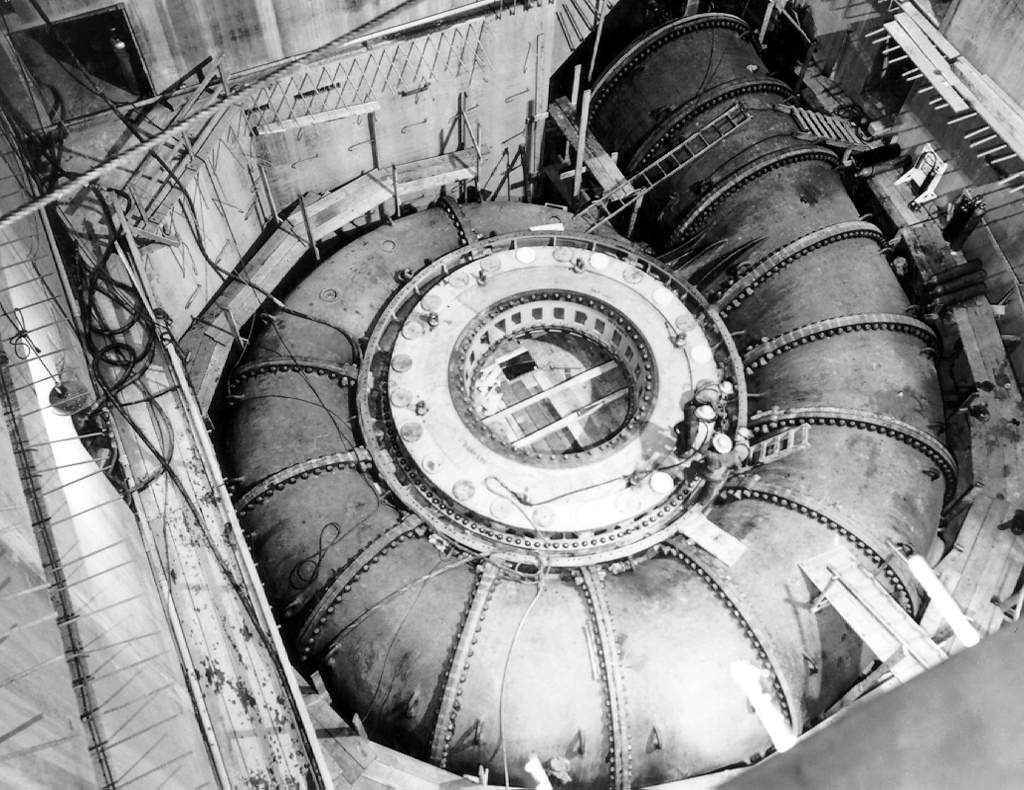
Zangmu Dam
The Zangmu Dam (藏木) is a gravity dam on the Yarlung Zangbo/Brahmaputra River northwest of Gyaca in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. This dam is built a few kilometers from the Bhutan-India border. The purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production using run-of-the-river technology. It is part of the Zangmu Hydropower Project and supports a 510 MW power station. Construction began in 2009 and the first generator was commissioned in November 2014. The last became operational on 13 October 2015. It is the first dam on the Brahmaputra/Yarlung Zangbo River and has caused controversy in India. Background In 1972, the Chinese Academy of Sciences created the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Comprehensive Scientific Expedition which in part studied conditions in the Tsangpo-Brahmaputra River basin. The study concluded that 114,000 MW of hydroelectric power generation capacity could be established in the basin, 79,000 MW from the main stem alone. A more in-depth hydrological study be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmaputra River
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. It is the 9th largest river in the world by discharge, and the 15th longest. With its origin in the Manasarovar Lake region, near Mount Kailash, on the northern side of the Himalayas in Burang County of Tibet where it is known as the Yarlung Tsangpo River, It flows along southern Tibet to break through the Himalayas in great gorges (including the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon) and into Arunachal Pradesh. It flows southwest through the Assam Valley as the Brahmaputra and south through Bangladesh as the Jamuna (not to be confused with the Yamuna of India). In the vast Ganges Delta, it merges with the Ganges, popularly known as the Padma in Bangladesh, and becomes the Meghna and ultimately empties into the Bay of Bengal. About long, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagu Dam
Dagu may refer to: * Nyala language (Sudan), also known as Dagu, an Eastern Sudanic language of Darfur * Daju people China *Dagu Subdistrict (大沽街道), a subdistrict in Binhai, Tianjin **Taku Forts, also known as Dagu Forts, historical coastal forts located in Binhai * Dagu, Sichuan (打古), a town in Naxi District, Luzhou, Sichuan *Dagu Township (大沽乡), a township in Ningdu County, Jiangxi *Dagu River, a river in Shandong Chinese culture * Dagu (instrument) Dagu may refer to: * Nyala language (Sudan), also known as Dagu, an Eastern Sudanic language of Darfur * Daju people China *Dagu Subdistrict (大沽街道), a subdistrict in Binhai, Tianjin **Taku Forts, also known as Dagu Forts, historical coast ... (大鼓), a bass drum, see List of Chinese musical instruments * Dagu (music), a form of ''Shuochang'', or storytelling accompanied by music See also * Daguan (other) * Degu (other) * Dogu (other) * Dugu (other) {{dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Run-of-the-river Power Stations
Run-of-river hydroelectricity (ROR) or run-of-the-river hydroelectricity is a type of hydroelectric generation plant whereby little or no water storage is provided. Run-of-the-river power plants may have no water storage at all or a limited amount of storage, in which case the storage reservoir is referred to as pondage. A plant without pondage is subject to seasonal river flows, thus the plant will operate as an intermittent energy source Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable ener .... Conventional hydro uses reservoirs, which regulate water for flood control, dispatchable generation, dispatchable electrical power, and the provision of fresh water for agriculture. Concept Run-of-the-river, or ROR, hydroelectricity is considered ideal for streams or rivers that can sustain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectric Power Stations In Tibet
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dams In China
Dams and reservoirs in China are numerous and have had a profound effect on the country's development and people. According to the World Commission on Dams in 2000, there were 22,104 dams over the height of operating in China. Of the world's total large dams, China accounts for the most – of them; of which are used for irrigation. Accordingly, the oldest in China still in use belongs to the Dujiangyan Irrigation System which dates back to 256 BC. In 2005, there were over 80,000 reservoirs in the country and over 4,800 dams completed or under construction that stands at or exceed in height. As of 2007, China is also the world's leader in the construction of large dams; followed by Turkey, and Japan in third. The tallest dam in China is the Jinping-I Dam at , an arch dam, which is also the tallest dam in the world. The largest reservoir is created by the Three Gorges Dam, which stores 39.3 billion m3 (31,900,000 acre feet) of water and has a surface area of . Three Gorges is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dams And Reservoirs In China
Dams and reservoirs in China are numerous and have had a profound effect on the country's development and people. According to the World Commission on Dams in 2000, there were 22,104 dams over the height of operating in China. Of the world's total large dams, China accounts for the most – of them; of which are used for irrigation. Accordingly, the oldest in China still in use belongs to the Dujiangyan Irrigation System which dates back to 256 BC. In 2005, there were over 80,000 reservoirs in the country and over 4,800 dams completed or under construction that stands at or exceed in height. As of 2007, China is also the world's leader in the construction of large dams; followed by Turkey, and Japan in third. The tallest dam in China is the Jinping-I Dam at , an arch dam, which is also the tallest dam in the world. The largest reservoir is created by the Three Gorges Dam, which stores 39.3 billion m3 (31,900,000 acre feet) of water and has a surface area of . Three Gorges is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Dams On The Brahmaputra River
This is a list of dams on the Brahmaputra River and hydro–infrastructure in the Brahmaputra River Basin which is a key constituent of the Ganges-Brahmaputra basin of Himalayan rivers. Brahmaputra originates near Mount Kailash, flows through Tibet where it is called Yarlung Tsangpo. It enters India in Arunachal Pradesh in Eastern Himalaya, and then enters Bangladesh where it is called Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna (not to be mistaken with Yamuna tributary of Ganges in India). It finally flows into the Bay of Bengal where it merges with the Ganges at Sunderban Delta. There are existing and planned dams on Brahmaputra in Tibet and India, but none in Bangladesh. List of dams and other hydro–infrastructure ''Upstream to downstream'' Map See also * China's South–North Water Transfer Project * Dams and reservoirs in China * Geology of the Himalaya * India's National Projects of the Ministry of Water Resources * Indian Rivers Inter-link * List of rivers i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Longest Undammed Rivers
This is a list of the longest dam, undammed rivers of the world, ordered by length. {, class="wikitable sortable" ! !River !data-sort-type = number, Length !data-sort-type = number, Drainage area !data-sort-type = number, Average Discharge (hydrology), discharge (m³/s) !Mouth !Notes !Reference !Rank , - , bgcolor="#FFEBAD", , Amazon River , bgcolor="#4169E1", , , , Atlantic Ocean , Second-longest and largest river in the world, undammed as well as unbridged, does not form a River delta, delta while joining the sea due to adequate thrust of river water to overcome the sea water wave and tidal thrusts. , , 1 , - , bgcolor="#FFCBCB", , Lena River , bgcolor="#7B68EE", , , , Arctic Ocean , Longest undammed river in Asia. , , 2 , - , bgcolor="#FFCBCB", , Amur River, Amur–Shilka River, Shilka–Onon River, Onon , bgcolor="#7B68EE", , , , Strait of Tartary , , , 3 , - , bgcolor="#CCFFFF" , , Mackenzie River, Mackenzie–Slave River, Slave–Athaba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Generator
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power ( mechanical energy) or fuel-based power (chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all of the power for electric power grids. In addition to electromechanical designs, photovoltaic and fuel cell powered generators utilize solar power and hydrogen-based fuels, respectively, to generate electrical output. The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor, and motors and generators have many similarities. Many motors can be mechanically driven to generate electricity; frequently they make acceptable manual generators. Terminology Electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency. The process of arriving at the modern Francis runner design took from 1848 to approximately 1920. It became known as the Francis turbine around 1920, being named after British-American engineer James B. Francis who in 1848 created a new turbine design. Francis turbines are primarily used for producing electricity. The power output of the electric generators generally ranges from just a few kilowatts up to 1000 MW, though mini-hydro installations may be lower. The best performance is seen when the head height is between . Penstock diameters are between . The speeds of different turbine units range from 70 to 1000 rpm. A wicket gate around the outside of the turbine's rotating runner controls the rate of water flow through the turbine fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pondage
Pondage usually refers to the comparably small water storage behind the weir of a run-of-the-river hydroelectric power plant. Such a power plant has considerably less storage than the reservoirs of large dams and conventional hydroelectric stations which can store water for long periods such as a dry season or year. With pondage, water is usually stored during periods of low electricity demand and hours when the power plant is inactive, enabling its use as a peaking power plant Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers", are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity. Because they supply power only occasionally, the powe ... in dry seasons and a base load power plant during wet seasons. Ample pondage allows a power plant to meet hourly load fluctuations for a period of a week or more. As a daily hydropeaking cycle of a hydro power plant with pondage results in fast rising river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the '' drainage divide'', made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, "watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of a drainage divide. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, the water converges to a single point inside the basin, known as a sink, which may be a permanent lake, a dry lake, or a point where surface water is lost underground. Drainage basins are simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |