|
Zisi
Zisi (), born Kong Ji, was a Chinese philosopher and the grandson of Confucius. Intellectual genealogy, teaching, criticism Zisi was the son of Kong Li (孔鯉) (:zh:孔鲤, Boyu (伯鱼)) and the only grandson of Confucius. He is traditionally accredited with transmitting Confucian teaching to Mencius and writing the ''Doctrine of the Mean'', ''Biaoji'' 表記, "Book of Rites#Contents, Ziyi" (The Black Robes") 緇衣, and "Fangji" (The Record of the Dikes) 坊記, presently chapters of the ''Liji''. (Since Zisi's dates of life do not overlap with those of Mengzi, it has been suggested that the intermediary role in the transmission was played by Shi Shuo 世碩.) Where his grandfather began to distinguish between true and supposed knowledge, Zisi proceeded upon meditations on the relativism, relativity in human knowledge of the universe. He attempted to analyse as many types of action as possible, and believed that wise people who are conscious of their moral and intellectual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctrine Of The Mean
The ''Doctrine of the Mean'' or ''Zhongyong'' is one of the Four Books of classical Chinese philosophy and a central doctrine of Confucianism. The text is attributed to Zisi (Kong Ji), the only grandson of Confucius (Kong Zi). It was originally a chapter in the ''Classic of Rites''. The phrase "doctrine of the mean" occurs in Book VI, verse 29 of the ''Analects'' of Confucius, which states: The ''Analects'' never expands on what this term means, but Zisi's text, ''The Doctrine of the Mean'', explores its meaning in detail, as well as how to apply it to one's life. The application of Confucian metaphysics to politics and virtue ethics. The text was adopted into the canon of the Neo-Confucian movement, as compiled by Zhu Xi. While Burton Watson translated ''Zhōngyōng'' as ''Doctrine of the Mean'', other English-language translators have rendered it differently. James Legge in 1861 called it ''Constant Mean'', Pierre Ryckmans (writer), Pierre Ryckmans (aka Simon Leys) use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zengzi
Zeng Shen (505–435 BC), better known as Zengzi (Master Zeng), courtesy name Ziyu (), was a Chinese philosopher and disciple of Confucius. He later taught Zisi (Kong Ji), the grandson of Confucius, who was in turn the teacher of Mencius, thus beginning a line of transmitters of orthodox Confucian traditions. He is revered as one of the Four Sages of Confucianism. Life Zeng Shen was 46 years younger than Confucius. He was a native of South Wu City in the State of Lu, and was the son of Zeng Dian, one of the earliest disciples of Confucius. When he was sixteen, he was sent by his father to study under Confucius. Confucians later considered him to be his second most senior student, after Yan Hui. Duanmu Ci said of him, "There is no subject which he has not studied. His appearance is respectful. His virtue is solid. His words command credence. Before great men he draws himself up in the pride of self-respect. His eyebrows are those of longevity." He was noted for his filial pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
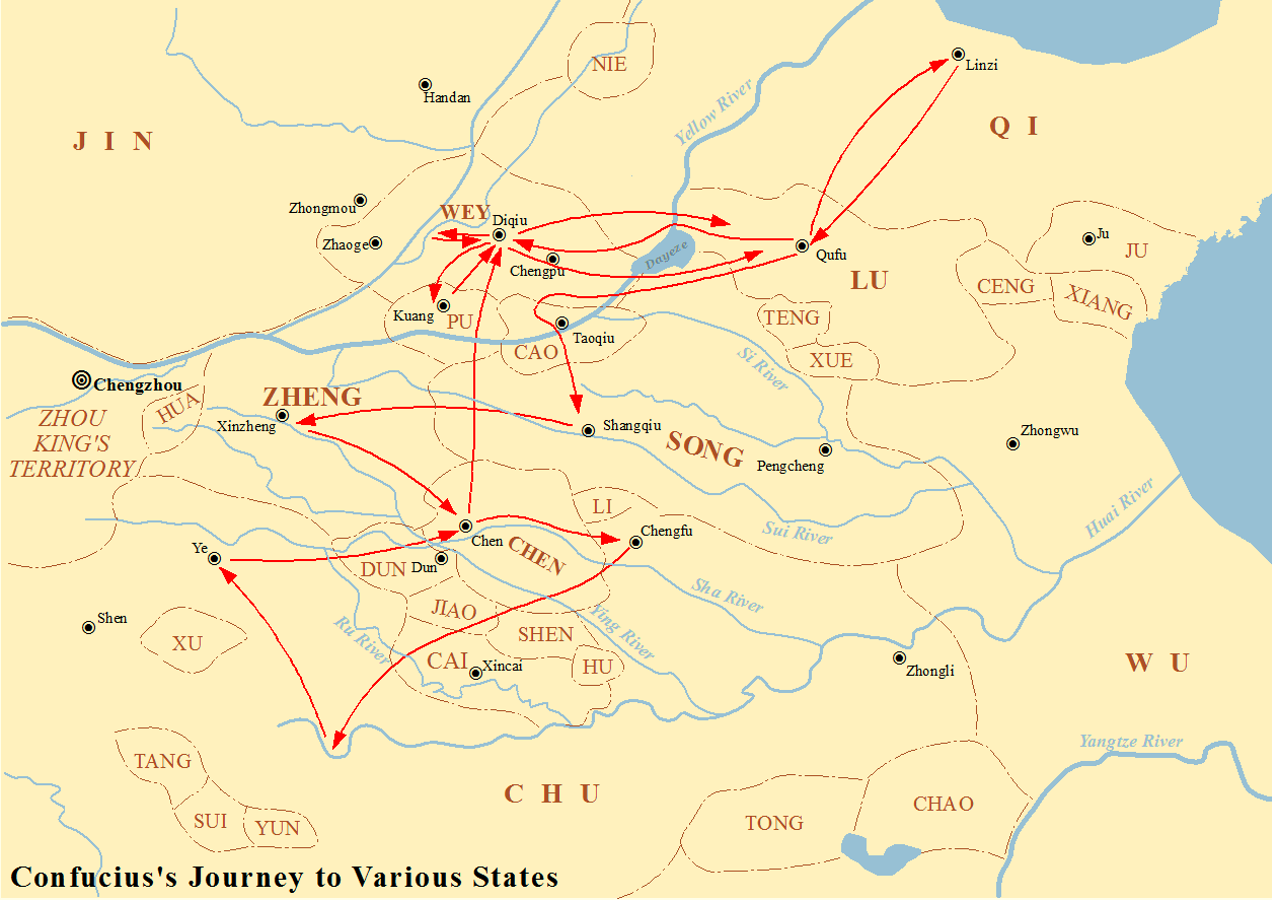
Confucius
Confucius (; pinyin: ; ; ), born Kong Qiu (), was a Chinese philosopher of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Much of the shared cultural heritage of the Sinosphere originates in the philosophy and teachings of Confucius. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, harmonious social relationships, righteousness, kindness, sincerity, and a ruler's responsibilities to lead by virtue. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of Ancient China, earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. He advocated for filial piety, endorsing strong family loyalty, Ancestor veneration in China, ancestor veneration, the respect of elders by their children and of husbands by their wives. Confucius recommended a robust family unit as the cornerstone for an ideal government. He championed the Silver Rule, or a negative form of the Golden Rule, advising, "Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kong Li
Kong Li (), courtesy name Boyu, is the only son of Confucius and Lady Qiguan (亓官氏), and the father of Kong Ji. Birth and naming When Confucius was twenty years old, his son Kong Li was born. The Duke Zhao of Lu sent a gift of carp to Confucius to celebrate the birth. Confucius, feeling honored by the ruler's gesture, named his son Kong Li, with "Li" meaning carp. Teachings from Confucius Line 16.13 of the Analects recorded the interaction between Kong Li and his father Confucius: Confucius' disciple Chen Gang (or Chen Ziqin) once asked Kong Li (Boyu), “Have you received any special teaching from your father?” The other replied: “No. Once, as he was standing alone, and I was discreetly crossing the courtyard, he asked me: ‘Have you studied the Poems? I replied: ‘No.’ He said: ‘If you do not study the Poems, you will not be able to hold your own in any discussion.’ I withdrew and studied the Poems. Another day, as he was again standing alone and I was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuxing (text)
''Wu xing'' () is a Warring States period text ascribed to Zisi, known mainly due to the Mawangdui Han tombs site (1973, sealed 168 BCE) and Guodian (1993, sealed about 300 BCE) discoveries. The Relationship between the two versions of the text remains debated. Unlike the Guodian version, written on bamboo strips, the Mawangdui "Wu xing" is written on silk and contains both the main text (''jing'') identical to that of the Guodian and the explanation (''shuo''). The text is related to the " Zhongyong" and " Daxue" (presently chapters in the ''Classic of Rites''). However, in Mawangdui Han tombs site it was discovered written in the same scroll with the ''Laozi Laozi (), also romanized as Lao Tzu #Name, among other ways, was a semi-legendary Chinese philosophy, Chinese philosopher and author of the ''Tao Te Ching'' (''Laozi''), one of the foundational texts of Taoism alongside the ''Zhuangzi (book) ...''. Li Xueqin. 帛书《五行》与《尚书·洪范》 Literature * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mencius
Mencius (孟子, ''Mèngzǐ'', ; ) was a Chinese Confucian philosopher, often described as the Second Sage () to reflect his traditional esteem relative to Confucius himself. He was part of Confucius's fourth generation of disciples, inheriting his ideology and developing it further. Living during the Warring States period, he is said to have spent much of his life travelling around the states offering counsel to different rulers. Conversations with these rulers form the basis of the ''Mencius (book), Mencius'', which would later be canonised as a Confucian classic. One primary principle of his work is that human nature is righteous and humane. The responses of citizens to the policies of rulers embodies this principle, and a state with righteous and humane policies will flourish by nature. The citizens, with freedom from good rule, will then allocate time to caring for their wives, brothers, elders, and children, and be educated with rites and naturally become better citizens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guodian Chu Slips
The Guodian Chu Slips () were unearthed in October 1993 in Tomb no. 1 of the Guodian tombs in Jingmen, Hubei Province and dated to the latter half of the Warring States period. Scott Cook completed a study and translation of all the manuscript of this corpus. Background Tomb no. 1 is located in Jishan District's Guodian tomb complex, near Jingmen City in the village of Guodian. It is located just nine kilometers north of Ying, which was the ancient Chu capital from about 676 BC until 278 BC, before the State of Chu was overrun by Qin. Studies of the tomb's contents revealed its occupant to be an elderly noble scholar, and teacher to a royal prince. The prince has been identified as Crown Prince Heng, who later became King Qingxiang of Chu. Since King Qingxiang was the Chu king when Qin sacked their old capital Ying in 278 BC, the Chu slips are dated to around 300 BC. Content There are in total about 804 bamboo slips in this cache, including 702 strips and 27 broken strips. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Books And Five Classics
The Four Books and Five Classics are authoritative and important books associated with Confucianism, written before 300 BC. They are traditionally believed to have been either written, edited or commented by Confucius or one of his disciples. Starting in the Han dynasty, they became the core of the Chinese classics on which students were tested in the Imperial examination system. Four Books The Four Books () are Chinese classic texts illustrating the core value and belief systems in Confucianism. They were selected by intellectual Zhu Xi in the Song dynasty to serve as general introduction to Confucian thought, and they were, in the Ming and Qing dynasties, made the core of the official curriculum for the civil service examinations. More information of them are as follows: List ; ''Great Learning'' : Originally one chapter in the '' Book of Rites''. It consists of a short main text attributed to Confucius and nine commentary chapters by Zengzi, one of the disciples of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Learning
The ''Great Learning'' or ''Daxue'' was one of the " Four Books" in Confucianism attributed to one of Confucius' disciples, Zengzi. The ''Great Learning'' had come from a chapter in the '' Book of Rites'' which formed one of the Five Classics. It consists of a short main text of the teachings of Confucius transcribed by Zengzi and then ten commentary chapters supposedly written by Zengzi. The ideals of the book were attributed to Confucius, but the text was written by Zengzi after his death. The "Four Books" were selected by the neo-Confucian Zhu Xi during the Song dynasty as a foundational introduction to Confucianism. Examinations for the state civil service in China came to follow his lead. Writing and influence Confucius, who incorporated ideas from earlier philosophers, compiled or edited the '' Classic of Rites'' and the '' Spring and Autumn Annals'', two of the Five Classics. Confucius' student Zengzi wrote the introduction and exposition of the ''Great Learnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemetery Of Confucius
The Cemetery of Confucius () is a cemetery of the Kong clan (the descendants of Confucius) in Confucius' hometown Qufu in eastern Shandong province. Confucius himself and some of his disciples are buried there, as well as many thousands of his descendants. Since 1994, the Cemetery of Confucius has been part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Temple and Cemetery of Confucius and the Kong Family Mansion in Qufu". The two other components of the site are the Temple of Confucius dedicated to the memory of the statesman and philosopher and the Kong Family Mansion, where his descendants lived. The three sites are collectively known in Qufu as ''San Kong'' (), i.e. "The Three Confucian ites. History By the 2nd century AD, at least 50 of Confucius's descendants had been buried alongside him. In 1331 construction work began on the wall and gate of the cemetery. In total, the cemetery has undergone 13 renovations and extensions. Eventually, by the late 18th century, the perimeter wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huainanzi
The ''Huainanzi'' is an ancient Chinese text made up of essays from scholarly debates held at the court of Liu An, Prince of Huainan, before 139 BCE. Compiled as a handbook for an enlightened sovereign and his court, the work attempts to define the conditions for a perfect socio-political order, derived mainly from a perfect ruler. With a notable Zhuangzi (book), Zhuangzi 'Taoist' influence, including Chinese folk religion, Chinese folk theories of yin and yang and Wuxing (Chinese philosophy), Wu Xing, the ''Huainanzi'' draws on Taoist, Legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalist, Confucian, and Mohist concepts, but subverts the latter three in favor of a wu wei, less active ruler, as prominent in the early Han dynasty before the Emperor Wu of Han, Emperor Wu. The early Han authors of the Huainanzi likely did not yet call themselves Taoist, and differ from Taoism as later understood. But K.C. Hsiao and the work's modern translators still considered it a 'principle' example of Han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |