|
Zeus Lycaeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the Greek pantheon. He is a sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus. Zeus is the child of Cronus and Rhea, the youngest of his siblings to be born, though sometimes reckoned the eldest as the others required disgorging from Cronus's stomach. In most traditions, he is married to Hera, by whom he is usually said to have fathered Ares, Eileithyia, Hebe, and Hephaestus.Hard 2004p. 79 At the oracle of Dodona, his consort was said to be Dione, by whom the ''Iliad'' states that he fathered Aphrodite. According to the ''Theogony'', Zeus's first wife was Metis, by whom he had Athena.Hesiod, ''Theogony'886900 Zeus was also infamous for his erotic escapades. These resulted in many divine and heroic offspring, including Apollo, Artemis, Hermes, Persephone, Dionysus, Perseus, Heracles, Helen of Troy, Minos, and the Muses. He was respected as a sky father who was chief of the gods and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; , or ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prominence. Since about 1930, the city's name has been İzmir. Two sites of the ancient city are today within İzmir's boundaries. The first, probably founded by indigenous peoples, rose to prominence during the Archaic period in Greece, Archaic Period as one of the principal ancient Greek settlements in western Anatolia. The second, whose foundation is associated with Alexander the Great, reached metropolitan proportions during the period of the Roman Empire. Most of the ancient city's present-day remains date to the Roman era, the majority from after a 2nd-century AD earthquake. In practical terms, a distinction is often made between these. ''Old Smyrna'' was the initial settlement founded around the 11th century BC, first as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attic Greek
Attic Greek is the Greek language, Greek dialect of the regions of ancient Greece, ancient region of Attica, including the ''polis'' of classical Athens, Athens. Often called Classical Greek, it was the prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige dialect of the Hellenistic period, Greek world for centuries and remains the standard form of the language that is taught to students of Ancient Greek. As the basis of the Hellenistic Koine Greek, Koine, it is the most similar of the ancient Greek dialects, ancient dialects to later Greek. Attic is traditionally classified as a member or sister dialect of the Ionic Greek, Ionic branch. Origin and range Greek language, Greek is the primary member of the Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. In ancient times, Greek had already come to exist in several dialects, one of which was Attic. The earliest Attested language, attestations of Greek, dating from the 16th to 11th centuries BC, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebe (mythology)
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Hebe (; ) is the goddess of youth or of the prime of life. She was the cup-bearer for the gods of Mount Olympus, serving their nectar and ambrosia. On Sicyon, she was worshipped as a goddess of forgiveness or mercy. She was often given the epithet ''Ganymeda'' (). Hebe is a daughter of Zeus and Hera, and the divine wife of Heracles (Roman mythology, Roman equivalent: Hercules). She had influence over eternal youth and the ability to restore youth to mortals, a power that appears exclusive to her, as in Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', some gods lament the aging of their favoured mortals. According to Philostratus the Elder, Hebe was the youngest of the gods and the one responsible for keeping them eternally young, and thus was the most revered by them. Her role of ensuring the eternal youth of the other gods is appropriate to her role of serving as cup-bearer, as the word ''ambrosia'' has been linked to a possible Proto-Indo-Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eileithyia
Eileithyia or Ilithyia (; ; (''Eleuthyia'') in Crete, also (''Eleuthia'') or (''Elysia'') in Laconia and Messene, and (''Eleuthō'') in literature)Nilsson Vol I, p. 313 was the Greek goddess of childbirth and midwifery, and the daughter of Zeus and Hera. In the cave of Amnisos (Crete) she was related with the annual birth of the divine child, and her cult is connected with ''Enesidaon'' (the earth shaker), who was the chthonic aspect of the god Poseidon. It is possible that her cult is related with the cult of Eleusis. In his ''Seventh Nemean Ode'', Pindar refers to her as the maid to or seated beside the Moirai (Fates) and responsible for the creation of offspring. Her son was Sosipolis, who was worshiped at Elis. Etymology The earliest form of the name is the Mycenaean Greek , ''e-re-u-ti-ja'', written in the Linear B syllabic script. Ilithyia is the latinisation of '. The etymology of the name is uncertain, but debated among scholars. R. S. P. Beekes suggests a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ares
Ares (; , ''Árēs'' ) is the List of Greek deities, Greek god of war god, war and courage. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. The Greeks were ambivalent towards him. He embodies the physical valor necessary for success in war but can also personify sheer brutality and bloodlust, in contrast to his sister Athena, whose martial functions include military strategy and generalship. An association with Ares endows places, objects, and other deities with a savage, dangerous, or militarized quality. Although Ares' name shows his origins as Mycenaean, his reputation for savagery was thought by some to reflect his likely origins as a Thracian deity. Some cities in Greece and several in Asia Minor held annual festivals to bind and detain him as their protector. In parts of Asia Minor, he was an oracular deity. Still further away from Greece, the Scythians were said to ritually kill one in a hundred prisoners of war as an offering to their equivalent of Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancient Greek religion's view of the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world; the lives and activities of List of Greek deities, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures; and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of mythmaking itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Religion
Religious practices in ancient Greece encompassed a collection of beliefs, rituals, and Greek mythology, mythology, in the form of both popular public religion and Cult (religious practice), cult practices. The application of the modern concept of "religion" to ancient cultures has been questioned as anachronistic. The Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks did not have a word for 'religion' in the modern sense. Likewise, no Greek writer is known to have classified either the gods or the cult practices into separate 'religions'. Instead, for example, Herodotus speaks of the Hellenes as having "common shrines of the gods and sacrifices, and the same kinds of customs". Most ancient Greeks recognized the Twelve Olympians, twelve major Olympian gods and goddesses—Zeus, Hera, Poseidon, Demeter, Athena, Ares, Aphrodite, Apollo, Artemis, Hephaestus, Hermes, and either Hestia or Dionysus—although philosophies such as Stoicism and some forms of Platonism used language that seems to assume a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunder God
Polytheistic peoples from many cultures have postulated a thunder deity, the creator or personification of the forces of thunder and lightning; a lightning god does not have a typical depiction and will vary based on the culture. In Indo-European cultures, the thunder god is frequently depicted as male and known as the chief or King of the Gods, e.g.: Indra in Hinduism, Zeus in Greek mythology, Zojz in Albanian mythology, and Perun in ancient Slavic religion. Mediterranean * Adad, Bel, Ishkur, Marduk ( Babylonian-Assyrian mythology) * Baʿal, Hadad ( Canaanite and Phoenician mythology) * I Verbti (Albanian mythology) * Novensiles (Etruscan mythology) * Perëndi (Albanian mythology) * Set (Egyptian mythology) * Shurdh (Albanian mythology) * Śuri (Etruscan mythology) * Tarḫunna ( Hittite mythology) * Tarḫunz ( Luwian mythology) * Teshub ( Hurrian mythology) * Vahagn (Armenian mythology) * Zibelthiurdos ( Thracian mythology) * Zis ( Messapian mythology) * Zojz (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sky Father
In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a "father", often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of "sky father" may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an " earth mother". "Sky Father" is a direct translation of the Vedic '' Dyaus Pita'', etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek '' Zeûs Pater'' and Roman ''Jupiter'', all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity's name, '' *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr''.''dyaus'' in Vedic still retained the meaning "sky", while the Greek Zeus had become a proper name exclusively. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father). In histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Greek Deities
In ancient Greece, deities were regarded as immortal, anthropomorphism, anthropomorphic, and powerful. They were conceived of as individual persons, rather than abstract concepts or notions, and were described as being similar to humans in appearance, albeit larger and more beautiful. The emotions and actions of deities were largely the same as those of humans; they frequently engaged in sexual activity, and were jealous and amoral. Deities were considered far more knowledgeable than humans, and it was believed that they conversed in a language of their own. Their immortality, the defining marker of their godhood, meant that they ceased aging after growing to a certain point. In place of blood, their veins flowed with ichor, a substance which was a product of their diet, and conferred upon them their immortality. Divine power allowed the gods to intervene in mortal affairs in various ways: they could cause natural events such as rain, wind, the growing of crops, or epidemics, and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
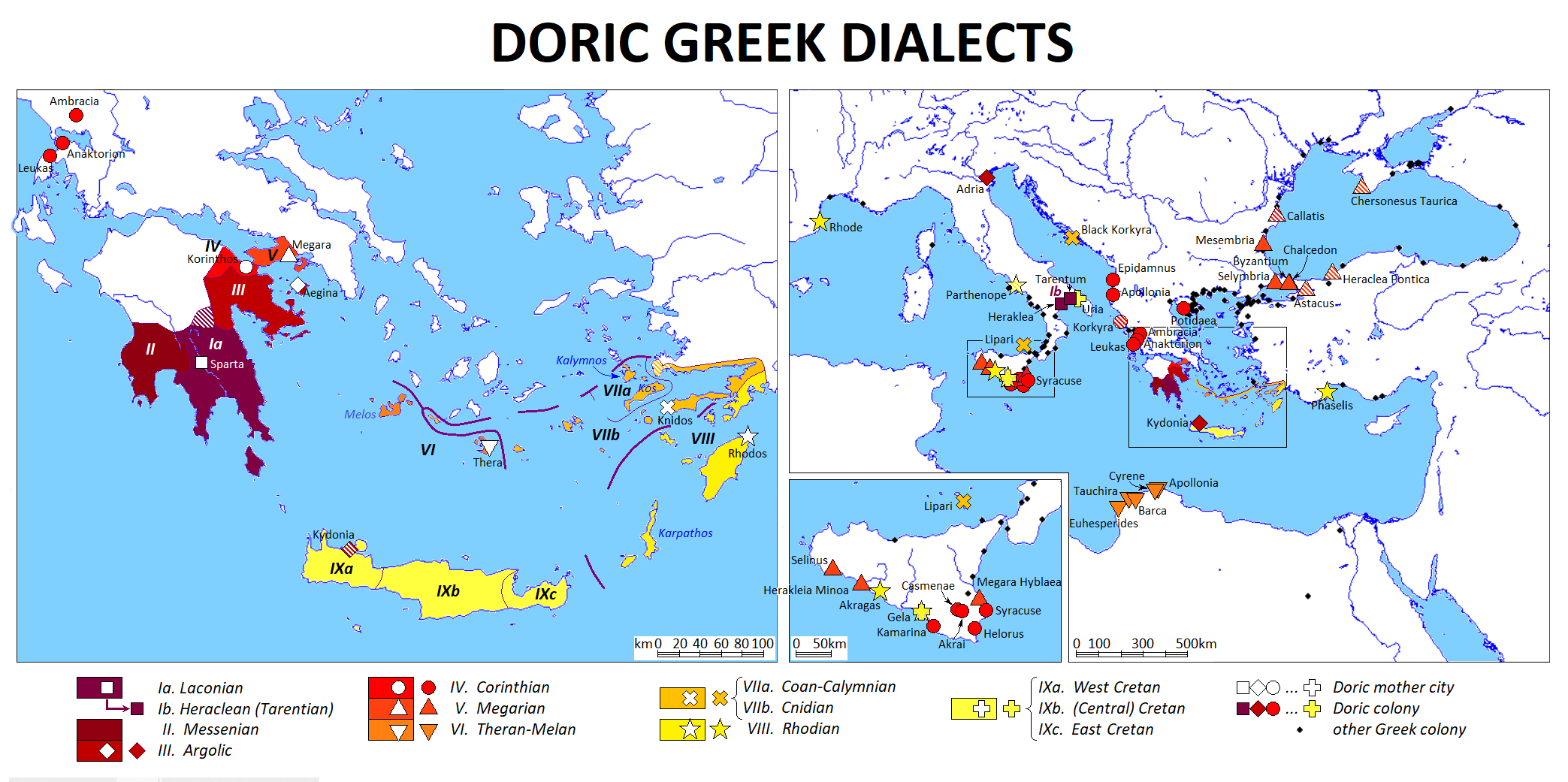
Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian (), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its Variety (linguistics), varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, including northern Greece (Acarnania, Aetolia, Epirus, Ozolian Locris, western and Opuntian Locris, eastern Locris, Phocis (ancient region), Phocis, Doris (Greece), Doris, and possibly Macedonia (ancient kingdom), ancient Macedonia), most of the Regions of ancient Greece#Peloponnese, Peloponnese (Achaea (ancient region), Achaea, Ancient Elis, Elis, Messenia (ancient region), Messenia, Laconia, Argolid, Aegina, Corinthia (ancient region), Corinthia, and Megara), the Southern Aegean (Kythira, Milos, Santorini, Thera, Crete, Karpathos, and Rhodes), as well as the colonies of some of those regions in Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene, Magna Graecia, the Greek colonisation#Black Sea and Propontis, Black Sea, Greek colonisation#Ionian Sea, Adriatic Sea, and Illyria, the Ionian Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |