|
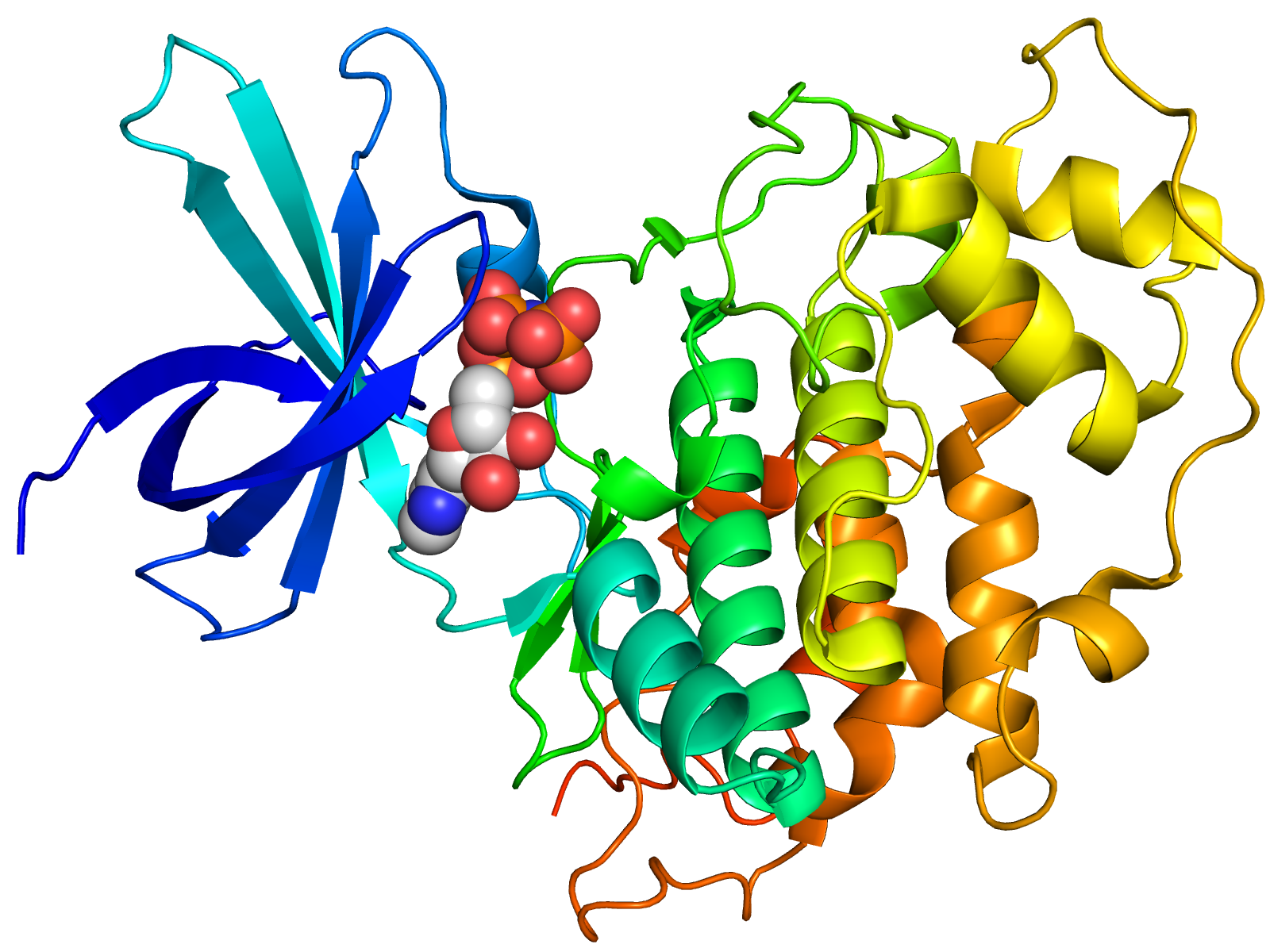
ZXDC
Zinc finger, X-linked, duplicated family member C (ZXDC) is a human CIITA-binding protein involved in the activation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) MHC Class I, class I and MHC Class II, II. For binding to occur, ZXDC must form an oligomeric complex with another copy of itself or with ZXDA, a related protein. ZXDC is activated by SUMO protein, sumoylation, a post-translational modification. ZXDC plays a role in controlling immunological responses, cancer formation and progression, and cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. History When Sakaue and colleagues searched for novel transcription factors involved in the development of Xenopus laevis, they discovered ZXDC (ZXD Family Zinc Finger C). This discovery was discovered in a research article that was published in 1998. They found a cDNA clone called "Xfin" that encodes a protein with two zinc finger C2H2 domains. Later research established the interspecies conservation of the Xfin protein, and the hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIITA
CIITA is a human gene which encodes a protein called the class II, major histocompatibility complex, transactivator. Mutations in this gene are responsible for the bare lymphocyte syndrome in which the immune system is severely compromised and cannot effectively fight infection. Chromosomal rearrangement of CIITA is involved in the pathogenesis of Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma. Function CIITA mRNA can only be detected in human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system class II-positive cell lines and tissues. This highly restricted tissue distribution suggests that expression of HLA class II genes is to a large extent under the control of CIITA. However, CIITA does not appear to directly bind to DNA. Instead CIITA functions through activation of the transcription factor RFX5. Hence CIITA is classified as a transcriptional coactivator. The CIITA protein contains an acidic transcriptional activation domain, 4 LRRs ( leucine-rich repeats) and a GTP binding d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing#Evolution of hairlessness, hairlessness, bipedality, bipedalism, and high Human intelligence, intelligence. Humans have large Human brain, brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are Sociality, highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a Level of analysis, multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and State (polity), political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of Value theory, values, norm (sociology), social norms, languages, and traditions (co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large Locus (genetics), locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for Cell (biology), cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. Its name comes from its discovery during the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules, which is to bind an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bring the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T cell, T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
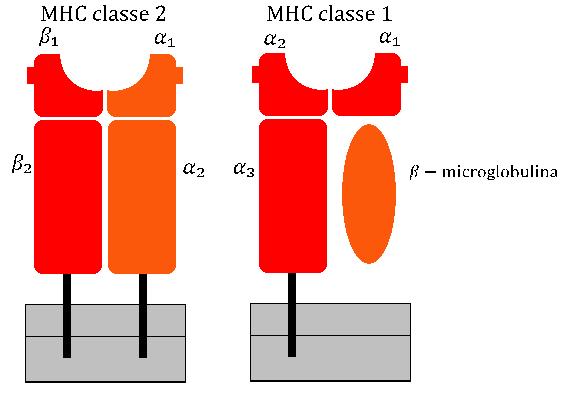
MHC Class I
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (the other being MHC class II) and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on platelets, but not on red blood cells. Their function is to display peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell to cytotoxic T cells; this will trigger an immediate response from the immune system against a particular non-self antigen displayed with the help of an MHC class I protein. Because MHC class I molecules present peptides derived from cytosolic proteins, the pathway of MHC class I presentation is often called ''cytosolic'' or ''endogenous pathway''. In humans, the HLAs corresponding to MHC class I are HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C. Function Class I MHC molecules bind peptides generated mainly from the degradation of cytosolic proteins by the proteasome. The MHC I: peptide complex is then inserted via the endoplasmic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MHC Class II
MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial cells, and B cells. These cells are important in initiating immune responses. Antigens presented by MHC class II molecules are exogenous, originating from extracellular proteins rather than cytosolic and endogenous sources like those presented by MHC class I. The loading of a MHC class II molecule occurs by phagocytosis. Extracellular proteins are endocytosed into a phagosome, which subsequently fuses with a lysosome to create a phagolysosome. Within the phagolysosome, lysosomal enzymes degrade the proteins into peptide fragments. These fragments are then loaded into the peptide-binding groove of the MHC class II molecule. Once loaded, the MHC class II-peptide complexes are transported to the plasma membrane via vesicular transport, where they prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SUMO Protein
In molecular biology, SUMO (Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier) proteins are a Protein family, family of small proteins that are covalent bond, covalently attached to and detached from other proteins in cell (biology), cells to modify their function. This process is called SUMOylation (pronounced soo-muh-lā-shun and sometimes written sumoylation). SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as cell nucleus, nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcription (genetics), transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. In human proteins, there are over 53,000 SUMO binding sites, making it a substantial component of fundamental biology. SUMO proteins are similar to ubiquitin and are considered members of the ubiquitin-like protein family. SUMOylation is directed by an Biochemical cascade, enzymatic cascade analogous to that involved in ubiquitination. In contrast to ubiquitin, SU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modification
In molecular biology, post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent process of changing proteins following protein biosynthesis. PTMs may involve enzymes or occur spontaneously. Proteins are created by ribosomes, which translation (biology), translate mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then change to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signal transduction, signalling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C-terminus, C- or N-terminus, N- termini. They can expand the chemical set of the 22 proteinogenic amino acid, amino acids by changing an existing functional group or adding a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is highly effective for controlling the enzyme activity and is the most common change after translation. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |