|
Z80-RIO
The Z80 Operating System with Relocatable Modules and I/O Management (Z80-RIO) is a general-purpose operating system developed by Zilog in the late 1970s for various computer systems including the ''Z80 Micro Computer System'' (MCZ-1) series and the ''Z80 Development System'' (ZDS). The MCZ systems were primarily used for software development and automation solutions. RIO was designed to facilitate the development and integration of user's programs into a production environment. Features The system provides a ''modest environment'' with a minimum of system support and an ''enhanced environment''. The ''modest environment'' provides a program debugger with file manipulation capability, a floppy disk driver (supporting up to eight disk drives), and a basic console driver with provision for paper tape operation. The ''enhanced environment'' provides access to the ''RIO Executive'' and to system support utilities such as the ''Zilog Floppy Disk File System'' (ZDOS), and the ''Zilog H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debug (command)
The line-oriented debugger DEBUG.EXE is an external command in operating systems such as DOS, OS/2 and Windows (only in 16-bit/32-bit versions). DEBUG can act as an assembler, disassembler, or hex dump program allowing users to interactively examine memory contents (in assembly language, hexadecimal or ASCII), make changes, and selectively execute COM, EXE and other file types. It also has several subcommands which are used to access specific disk sectors, I/O ports and memory addresses. Overview Traditionally, all computers and operating systems have included a maintenance function, used to determine whether a program is working correctly. DEBUG was originally written by Tim Paterson to serve this purpose in 86-DOS. When Paterson began working for Microsoft in the early 1980s he brought the program with him. DEBUG was part of and has been included in MS-DOS/ PC DOS and certain versions of Microsoft Windows. Originally named DEBUG.COM, the executable was renamed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echo (command)
echo is shell command that writes input text to standard output. It is available in many operating system and shells. It is often used in a shell script to log status, provide feedback to the user and for debugging. For an interactive session, output by default displays on the terminal screen, but output can be re-directed to a file or piped to another process. Many shells implement echo as a builtin command rather than an external application as are many other commands. Multiple, incompatible implementations of echo exist in different shells. Some expand escape sequences by default; some do not; some accept options; some do not. The POSIX specification leaves the behavior unspecified if the first argument is -n or any argument contains backslash characters while the Unix specification (XSI option in POSIX) mandates the expansion of some sequences and does not allow any option processing. In practice, many echo implementations are not compliant in the default environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copy (command)
copy is a shell command for copying files. Different implementations provide various capabilities, such as: * Combining (concatenating) multiple files into a single file * If multiple source files are specified before the path to an existing directory, then files are copied to the directory * Support for text vs. binary data; for text, the command stops when it reaches an end-of-file (EOF) character; for binary, files are copied in their entirety; ignoring EOF * In DOS, a file can be copied to or from a device. For example, copy ''path'' con outputs the file at ''path'' to the console, and copy con ''path'' copies text typed at the console to a file at ''path'' Implementations The command is available in RT-11, OS/8,"Concise Command Language" (CCL). RSX-11, ISIS-II, iRMX 86, TOPS-10, TOPS-20, OpenVMS, MetaComCo TRIPOS, HDOS, Z80-RIO, OS-9, DOS, FlexOS, 4690 OS, PC-MOS, HP MPE/iX, OS/2, Windows, ROM-DOS, ReactOS, SymbOS, DexOS, and 86-DOS. Under IBM PC DOS/MS- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ren (command)
ren (or rename) is a shell command for renaming a file and in some implementations (such as AmigaDOS) a directory. Some shells with also provide a move command that provides for moving between directories. On systems that do not support a move command (such as MS-DOS older than 6.00), the user could copy a file to a new destination and then delete the original file. In DOSBox, ren can move files. The command is in various shells such as COMMAND.COM, Command Prompt, 4DOS, 4NT and PowerShell. In MS-DOS, the command is available in versions 1 and later. In PowerShell, ren is a predefined alias for the Rename-Item Cmdlet which serves the same essential purpose. Similar commands are available in many operating systems. The command is available in the CP/M, MP/M, Cromemco DOS, TRIPOS, OS/2, ReactOS, SymbOS, and DexOS. Multics includes a rename command to rename a directory entry; which could be contracted to rn. A command which in some cases can be contracted to ren i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Format (command)
In computing, format is a command-line utility that carries out disk formatting. It is a component of various operating systems, including 86-DOS, MS-DOS, IBM PC DOS and OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS. Overview The command performs the following actions by default on a floppy disk, hard disk drive, solid state (USB), or other magnetic medium (it will not perform these actions on optical media): # clearing the FAT entries by changing them to # clearing the FAT root directory by changing any values found to (NB. While the publishers claim this would be MS-DOS 1.1 and 2.0, it actually is SCP MS-DOS 1.25 and a mixture of Altos MS-DOS 2.11 and TeleVideo PC DOS 2.11.) (NB. While the author claims this would be MS-DOS 1.1 and 2.0, it actually is SCP MS-DOS 1.25 and a mixture of Altos MS-DOS 2.11 and TeleVideo PC DOS 2.11.) (NB. While the author claims this would be MS-DOS 1.1 and 2.0, it actually is SCP MS-DOS 1.25 and a mixture of Altos MS-DOS 2.11 and TeleVideo PC D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Help (command)
In computing, help is a command in various command line shells such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, Bash, qshell, 4DOS/ 4NT, Windows PowerShell, Singularity shell, Python, MATLAB and GNU Octave. It provides online information about available commands and the shell environment. Implementations The command is available in operating systems such as Multics, Heath Company HDOS, CP/M Plus, DOS, IBM OS/2, eComStation, ArcaOS, IBM i, Microsoft Windows, ReactOS, THEOS/OASIS, Zilog Z80-RIO, Microware OS-9, Stratus OpenVOS, HP MPE/iX, Motorola VERSAdos, KolibriOS and also in the DEC RT-11, RSX-11, TOPS-10 and TOPS-20 operating systems. Furthermore it is available in the open source MS-DOS emulator DOSBox and in the EFI shell. On Unix, the command is part of the Source Code Control System and prints help information for the SCCS commands. Multics The Multics help command prints descriptions of system commands/active functions and subroutines. It also prints vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
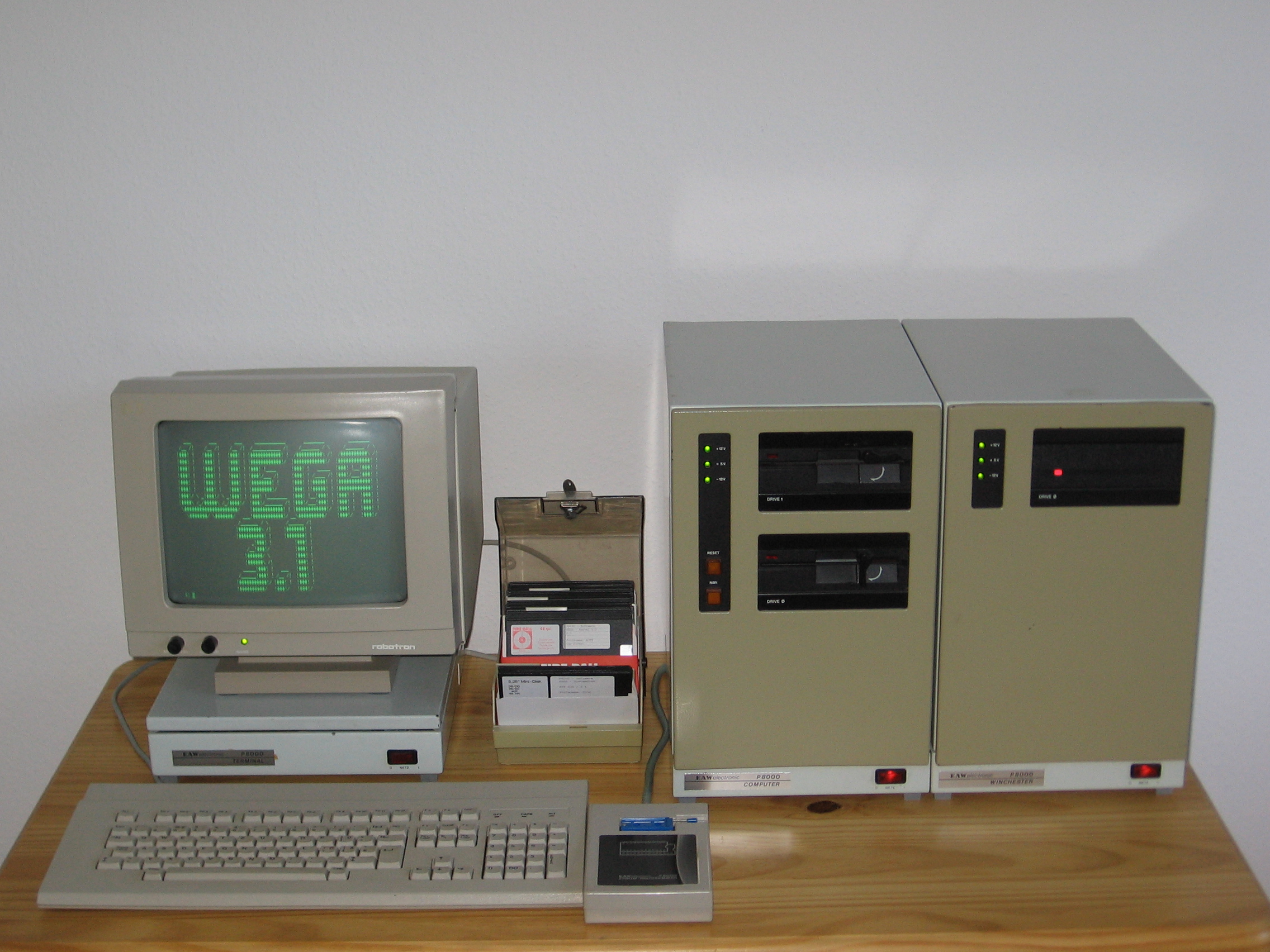
P8000
The P8000 is a microcomputer system developed in 1987 by the Elektro-Apparate-Werke, VEB Elektro-Apparate-Werke Berlin-Treptow „Friedrich Ebert“ (EAW) in the German Democratic Republic (DDR, East Germany). It consisted of an 8-bit and a 16-bit microprocessor and a Winchester disk controller. It was intended as a universal programming and development system for multi-user/multi-task applications. The initial list price of the P8000 was 172,125 East German marks (around 86,000–172,000 DM). There was also a budget version with only an 8-bit microprocessor. The 8-bit microcomputer The 8-bit version of P8000 was completely contained on a single 4-layer printed circuit board. The processor, with a clock frequency of 4 MHz, was based on the U880 microprocessor (near clone of Zilog Z80) and peripheral circuits along with the U8272 floppy-disk controller. Direct memory access was accomplished by U880, U858 DMA controller chip. The system featured a main memory of 64&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PC 1715
The PC 1715 was an office computer produced by VEB Robotron in East Germany starting in 1985. The system featured an 8-bit microprocessor, the U880, a clone of the Zilog Z80. It was built for office work and education, but was also put to some specialist uses, for example an optional interface was available for controlling a pacemaker. The 1715 had minimal graphics and sound capabilities. The price was 19,000 East German marks. In contrast to its predecessor, A5120, the PC1715 was not built around the K1520 bus standard. There was no back plane, but the main board had 2 58-pin connectors that were largely K1520 compliant, with some signals omitted and replaced with custom internal signals. The floppy controller of the PC1715 used one of those internal bus extensions and was built with discrete components and logic chips, whereas other robotron computers of the 1980s used a clone of an Intel 8272 Floppy disk controller. The floppy controller board clearly appears to be based on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A 5120
The A 5120 was an office computer produced by VEB Robotron in Karl-Marx-Stadt (now Chemnitz), East Germany starting in 1982. The system featured an 8-bit microprocessor, the U880. It was built for office work and had minimal graphics and sound capabilities. The price was between 27,000 and 40,000 East German marks (around 24,000-35,000 2016 US dollars) depending on equipment. In 1986, a new version was produced, the A 5120.16. The system was identical to the A 5120, with the addition of two additional boards, one with a U8000 16-bit microprocessor (a Zilog Z8000 clone), and one with 256KB DRAM. The original 8-bit system functioned as an I/O subsystem. In this configuration it could run the relatively powerful MUTOS8000 (Unix System III derivative). The price of this model was between about 32,000 and 48,000 East German marks. In total, about 17,000 A 5120 and A 5120.16 units were manufactured. In March 1983, a stamp was issued by the German Democratic Republic featuring the A 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog
Zilog, Inc. is an American manufacturer of microprocessors, microcontrollers, and application-specific embedded System on a chip, system-on-chip (SoC) products. The company was founded in 1974 by Federico Faggin and Ralph Ungermann, who were soon joined by Masatoshi Shima. All three had left Intel after working on the Intel 4004, 4004 and Intel 8080, 8080 microprocessors. The company's most famous product is the Zilog Z80, Z80 microprocessor, which played an important role in the evolution of early computing. Backward compatible, Software-compatible with the Intel 8080, it offered a compelling alternative due to its lower cost and increased performance, propelling it to widespread adoption in video game systems and home computers during the late 1970s and early 1980s. The name, pronounced with a long "i" (), is an acronym of ''Z integrated logic'', also thought of as "Z for the last word of Integrated Logic". History Zilog was started in California in 1974 by Federico Faggin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macro Assembler
In computing, assembly language (alternatively assembler language or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an '' assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book ''The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic Digital Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VEB Robotron
VEB Kombinat Robotron () (or simply Robotron) was the largest East German electronics manufacturer. It was headquartered in Dresden and employed 68,000 people in 1989. Its products included personal computers, SM EVM minicomputers, the ESER mainframe computers, various computer peripherals as well as microcomputers, radios, television sets and other items including cookie press ''Kleingebäckpresse Typ 102''. Divisions Robotron managed several different divisions: *VEB Robotron-Elektronik Dresden (headquarters) — typewriters, personal computers, minicomputers, mainframes *VEB Robotron-Meßelektronik Dresden — measurement and testing devices, home computers *VEB Robotron-Projekt Dresden — software department *VEB Robotron-Buchungsmaschinenwerk Karl-Marx-Stadt — personal computers, floppy disk drives *VEB Robotron-Elektronik Hoyerswerda — monitors, power supply units *VEB Robotron-Elektronik Radeberg — mainframes, radio receivers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |