|
Z-disk
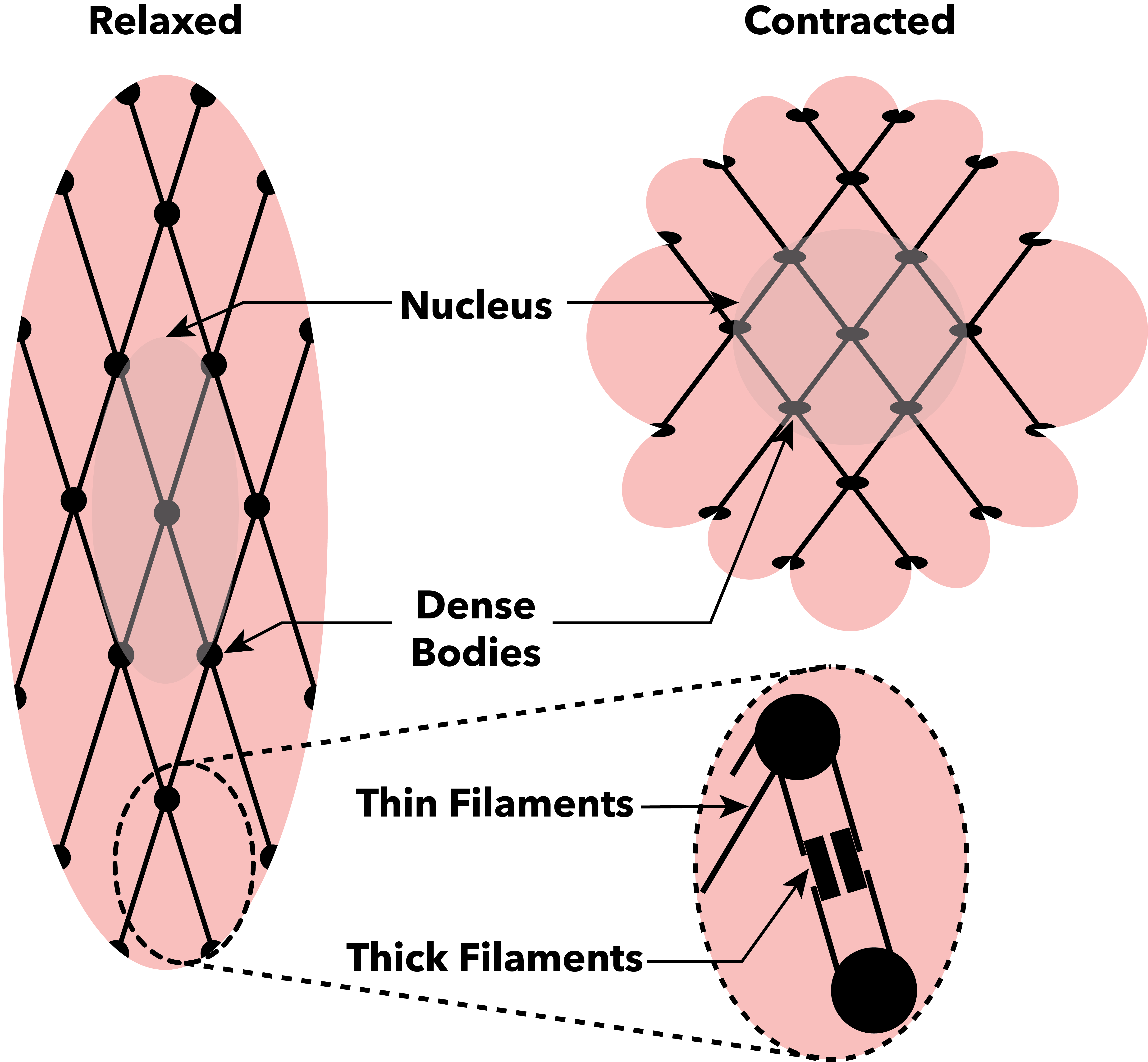
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal striated muscle, Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called muscle fibers or myofibers) which are formed during embryonic development, embryonic myogenesis. Muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils are composed of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which appear under the microscope as alternating dark and light bands. Sarcomeres are composed of long, fibrous proteins as filaments that slide past each other when a muscle contracts or relaxes. The costamere is a different component that connects the sarcomere to the sarcolemma. Two of the important proteins are myosin, which forms the thick filament, and actin, which forms the thin filament. Myosin has a long fibrous tail and a globular head that binds to actin. The myosin head also binds to Adenosine triphos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costamere
The costamere is a structural-functional component of striated muscle cells which connects the sarcomere of the muscle to the cell membrane (i.e. the sarcolemma).20: 2327-2331 Costameres are sub-sarcolemmal protein assemblies circumferentially aligned in register with the Z-disk of peripheral myofibrils. They physically couple force-generating sarcomeres with the sarcolemma in striated muscle cells and are thus considered one of several "Achilles' heels" of skeletal muscle, a critical component of striated muscle morphology which, when compromised, is thought to directly contribute to the development of several distinct myopathies. The dystrophin-associated protein complex, also referred to as the dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex (DGC or DAGC), contains various integral and peripheral membrane proteins such as dystroglycans and sarcoglycans, which are thought to be responsible for linking the internal cytoskeletal system of individual myofibers to structural protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebulin
Nebulin is an actin-binding protein which is localized to the thin filament of the sarcomeres in skeletal muscle. Nebulin in humans is coded for by the gene ''NEB''. It is a very large protein (600–900 kDa) and binds as many as 200 actin monomers. Because its length is proportional to thin filament length, it is believed that nebulin acts as a thin filament "ruler" and regulates thin filament length during sarcomere assembly. Other functions of nebulin, such as a role in cell signaling, remain uncertain. Nebulin has also been shown to regulate actin-myosin interactions by inhibiting ATPase activity in a calcium-calmodulin sensitive manner. Mutations in nebulin cause some cases of the autosomal recessive disorder nemaline myopathy. A smaller member of the nebulin protein family, termed nebulette, is expressed in cardiac muscle. Structure The structure of the SH3 domain of nebulin was determined by protein nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.; The SH3 domain from n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the mobility and contraction of cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell motility, cell division and cytokinesis, vesicle and organelle mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striated Muscle
Striated muscle tissue is a muscle tissue that features repeating functional units called sarcomeres. Under the microscope, sarcomeres are visible along muscle fibers, giving a striated appearance to the tissue. The two types of striated muscle are skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle. Structure Striated muscle tissue contains T-tubules which enables the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle includes skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. Skeletal muscle is wrapped in epimysium, allowing structural integrity of the muscle despite contractions. The perimysium organizes the muscle fibers, which are encased in collagen and endomysium, into fascicles. Each muscle fiber contains sarcolemma, sarcoplasm, and sarcoplasmic reticulum. The functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a sarcomere. Each muscle cell contains myofibrils composed of actin and myosin myofilaments repeated as a sarcomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek
Antonie Philips van Leeuwenhoek ( ; ; 24 October 1632 – 26 August 1723) was a Dutch microbiologist and microscopist in the Golden Age of Dutch art, science and technology. A largely self-taught man in science, he is commonly known as " the Father of Microbiology", and one of the first microscopists and microbiologists. Van Leeuwenhoek is best known for his pioneering work in microscopy and for his contributions toward the establishment of microbiology as a scientific discipline. Raised in Delft, Dutch Republic, Van Leeuwenhoek worked as a draper in his youth and founded his own shop in 1654. He became well-recognized in municipal politics and developed an interest in lensmaking. In the 1670s, he started to explore microbial life with his microscope. Using single-lensed microscopes of his own design and make, Van Leeuwenhoek was the first to observe and to experiment with microbes, which he originally referred to as , or . He was the first to relatively determine t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropomyosin
Tropomyosin is a two-stranded alpha-helical, coiled coil protein found in many animal and fungal cells. In animals, it is an important component of the muscular system which works in conjunction with troponin to regulate muscle contraction. It is present in smooth and striated muscle tissues, which can be found in various organs and body systems, including the heart, blood vessels, respiratory system, and digestive system. In fungi, tropomyosin is found in cell walls and helps maintain the structural integrity of cells. Tropomyosin is found in other eukaryotes too, but not in plants. Overall, tropomyosin is an important protein that plays a vital role in the proper functioning of many different organisms. Tropomyosin and the actin skeleton All organisms contain organelles that provide physical integrity to their cells. These types of organelles are collectively known as the cytoskeleton, and one of the most ancient systems is based on filamentous polymers of the protein actin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sliding Filament Model
Sliding may refer to: * Sliding (dance), also floating or gliding, a group of footwork-oriented dance techniques * Slide (baseball), an attempt by a baseball runner to avoid getting tagged out * Sliding (motion) See also * Slide (other) * Slider (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as when holding something heavy in the same position. The termination of muscle contraction is followed by muscle relaxation, which is a return of the muscle fibers to their low tension-generating state. For the contractions to happen, the muscle cells must rely on the change in action of two types of Myofilament, filaments: thin and thick filaments. The major constituent of thin filaments is a chain formed by helical coiling of two strands of actin, and thick filaments dominantly consist of chains of the Motor protein, motor-protein myosin. Together, these two filaments form myofibrils - the basic functional organelles in the skeletal muscle system. In vertebrates, Muscle cell#Muscle contraction in striated muscle, skele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myomesin
Myomesin is a protein Protein family, family found in the M-line of the sarcomere structure. Myomesin has various forms throughout the body in Striated muscle tissue, striated muscles with specialized functions. This includes both Slow twitch fiber, slow and Fast twitch muscle, fast muscle fibers. Myomesin are made of 13 domains including a unique N-terminus, N-terminal followed by two immunoglobulin-like (Ig) domains, five Fibronectin type III domain, fibronectin type III (Fn) domains, five more Ig domains. These domains all promote binding which indicates that myomesin is regulated through binding. Functions Sarcomere structure Myomesin plays an important role in the structure of sarcomeres. They are found in the M-line, M-band region of the sarcomere, between the thick filaments (myosin). Its main purpose in this setting is to provide structural integrity by linking the antiparallel myosin fibers and titin filaments which are connected to the Z-discs. These myosin filaments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titin
Titin (; also called connectin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TTN'' gene. The protein, which is over 1 μm in length, functions as a molecular spring that is responsible for the passive elasticity of muscle. It comprises 244 individually folded protein domains connected by unstructured peptide sequences. These domains unfold when the protein is stretched and refold when the tension is removed. Titin is important in the contraction of striated muscle tissues. It connects the Z disc to the M line in the sarcomere. The protein contributes to force transmission at the Z disc and resting tension in the I band region. It limits the range of motion of the sarcomere in tension, thus contributing to the passive stiffness of muscle. Variations in the sequence of titin between different types of striated muscle ( cardiac or skeletal) have been correlated with differences in the mechanical properties of these muscles. Titin is the third most abundant protein in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Sarcomere Structure
The heart is a muscular organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers: epicardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Model Of The Sarcomere In The A-band
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |