|
Yawarlukru
Yawarlukru or Yawar Lukru (Kichwa ''yawar'' blood, ''lukru'' soup,Vocabulario comparativo quechua ecuatoriano - quechua ancashino -- castellano - English (pdf), collected by Robert Beér, Armando Muyolema and Hernán S. Aguilar, 2006 "blood soup", hispanicized spellings ''Yahuarlocro, Yahuar Locro'') is a traditional dish of Ecuadorian cuisine. Is a light stew prepared with meat and entrails of lamb including brain, intestines, liver, lung, tongue, rumen, etc. It's usually served with fried lamb blood, avocado and pickled red onion rings. It can be consumed as a snack or as a main dish depending on the size of the plate. It's consumed in the Ecuadorian Andes range and is considered a representative dish of Ecuadorian cuisine. Recipe Boil the meat parts with onions (red or Spanish onion), two garlic heads and some spring onions, until the meat is soft, separate and keep the stock in a bowl. Chop the intestines and other meats in cubes; fry garlic and onions with a dash of oregan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kichwa Language
Kichwa (, , also Spanish ) is a Quechuan language that includes all Quechua varieties of Ecuador and Colombia (''Inga''), as well as extensions into Peru. It has an estimated half million speakers. The most widely spoken dialects are Chimborazo, Imbabura and Cañar Highland Quechua, with most of the speakers. Kichwa belongs to the Northern Quechua group of Quechua II, according to linguist Alfredo Torero. Overview Kichwa syntax has undergone some grammatical simplification compared to Southern Quechua, perhaps because of partial creolization with the pre-Inca languages of Ecuador. A standardized language, with a unified orthography (, ), has been developed. It is similar to Chimborazo but lacks some of the phonological peculiarities of that dialect. The earliest grammatical description of Kichwa was written in the 17th century by Jesuit priest Hernando de Alcocer. First efforts for language standardization and bilingual education According to linguist Arturo Muyulema, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuadorian Cuisine
Ecuadorian cuisine is diverse, varying with altitude, and associated agricultural conditions. Ecuadorian cuisine is an amalgamation of Spanish, Andean, and Amazonian cuisines and to a lesser degree Italian, Lebanese, African, and Chinese. Beef, chicken, and seafood are popular in the coastal regions, especially ceviche, and are typically served with carbohydrate-rich foods, such as rice accompanied with lentils, pasta, or plantain. In the mountainous regions pork, chicken, beef and ''cuy'' (guinea pig) are popular and are often served with rice, maize, or potatoes. A popular street food in mountainous regions is ', consisting of potatoes served with roasted pig. Some examples of Ecuadorian cuisine in general include ' (green plantain slices fried in oil, mashed up, and then refried), ' (a pan-seared potato ball), and ' (a type of stew made from goat). A wide variety of fresh fruit is available, particularly at lower altitudes, including ', passionfruit, ', several types of ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is the enabling of speech in humans and vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral part at the front and a pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of muscles of the tongue. The four intrinsic muscles alter the shape of the tongue and are not attached to bone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment allows it to serve as the primary site for microbial fermentation of ingested feed. The smaller part of the reticulorumen is the reticulum, which is fully continuous with the rumen, but differs from it with regard to the texture of its lining. Brief anatomy The rumen is composed of several muscular sacs, the cranial sac, ventral sac, ventral blindsac, and reticulum. The lining of the rumen wall is covered in small fingerlike projections called papillae, which are flattened, approximately 5mm in length and 3mm wide in cattle. The reticulum is lined with ridges that form a hexagonal honeycomb pattern. The ridges are approximately 0.1–0.2mm wide and are raised 5mm above the reticulum wall. The hexagons in the reticulum are approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avocado
The avocado (''Persea americana'') is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family ( Lauraceae). It is native to the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Then as now it was prized for its large and unusually oily fruit. The tree likely originated in the highlands bridging south-central Mexico and Guatemala. Its fruit, sometimes also referred to as an alligator or avocado pear, is botanically a large berry containing a single large seed. Avocado trees are partially self-pollinating, and are often propagated through grafting to maintain consistent fruit output. Avocados are presently cultivated in the tropical and Mediterranean climates of many countries. Mexico is the world's leading producer of avocados as of 2020, supplying nearly 30% of the global harvest in that year. The fruit of domestic varieties have smooth, buttery, golden-green flesh when ripe. Depending on the cultivar, avocados have green, brown, pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
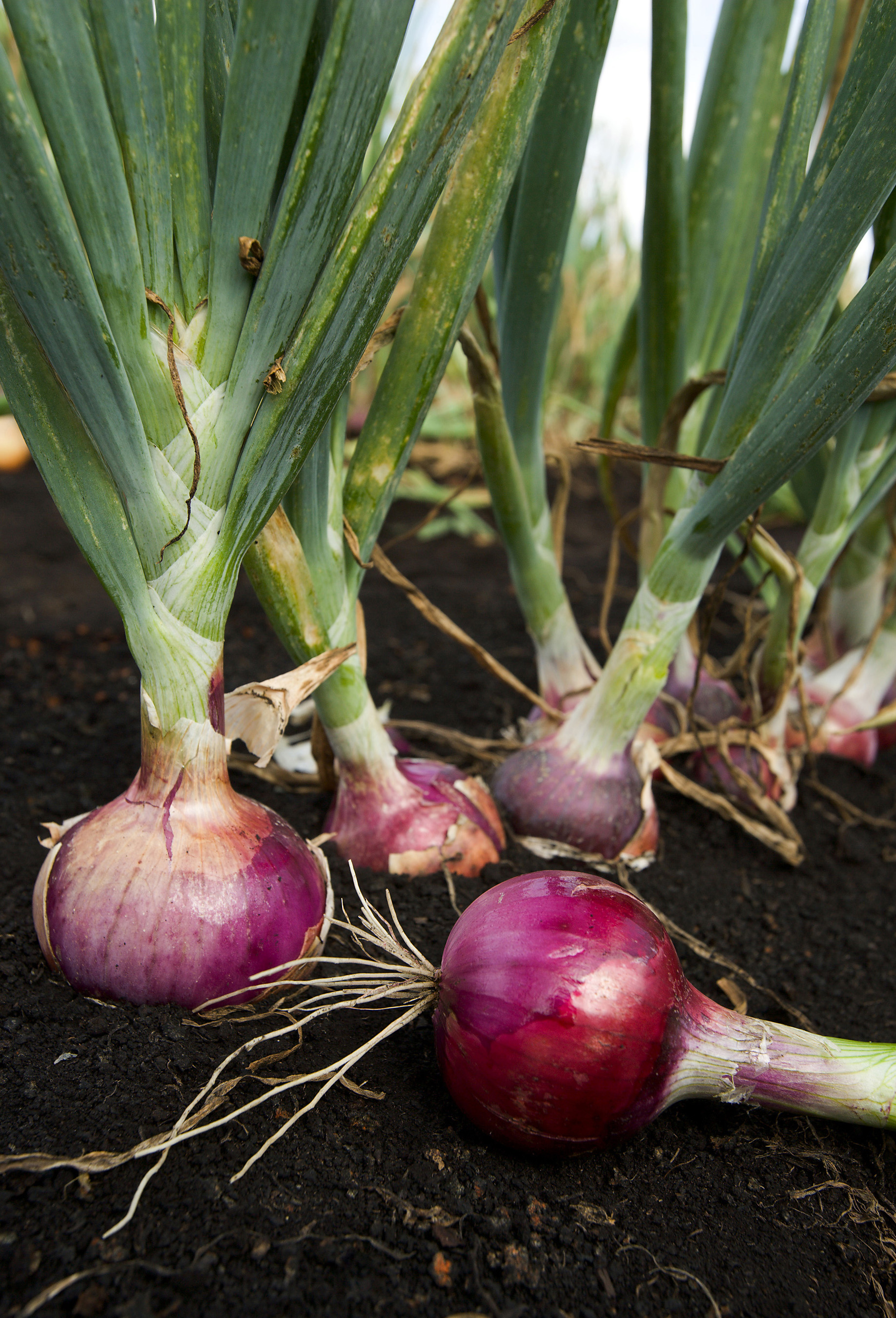
Red Onion
Red onions (also known as purple or blue onions in some mainland European countries, though not the UK) are cultivars of the onion ('' Allium cepa''), and have purplish-red skin and white flesh tinged with red. They are most commonly used in cooking, but the skin has also been used as a dye. Red onions tend to be medium to large in size and have a sweeter flavor than white or yellow onions due to low levels of pyruvic acid and sulfur compounds. They are often consumed raw (and can be added to salads for color and bite), grilled, or lightly cooked with other foods. Red onions are available throughout the year and are high in flavonoids and fiber (compared to white and yellow onions).Bill Jones Cut red onion can be soaked in cool water for a period of time, and the water can be drained off, resulting in less "bite" and pungency. Varieties Tropea The red onion from Tropea, Italy, (Italian: "Cipolla Rossa di Tropea") grows in a small area of Calabria in southern Italy, Cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion which was classified as a separate species until 2010. Its close relatives include garlic, scallion, leek, and chive. This genus also contains several other species variously referred to as onions and cultivated for food, such as the Japanese bunching onion (''Allium fistulosum''), the tree onion (''A.'' × ''proliferum''), and the Canada onion (''Allium canadense''). The name ''wild onion'' is applied to a number of ''Allium'' species, but ''A. cepa'' is exclusively known from cultivation. Its ancestral wild original form is not known, although escapes from cultivation have become established in some regions. The onion is most frequently a biennial or a perennial plant, but is usually treated as an annual and harvested in its f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achiote
''Bixa orellana'', also known as achiote, is a shrub native to Central America. ''Bixa orellana'' is grown in many countries worldwide. The tree is best known as the source of annatto, a natural orange-red condiment (also called or ) obtained from the waxy arils that cover its seeds. The ground seeds are widely used in traditional dishes in Central and South America, Mexico, and the Caribbean, such as ''cochinita pibil'', chicken in , , and . Annatto and its extracts are also used as an industrial food coloring to add yellow or orange color to many products such as butter, cheese, margarine, ice creams, meats, and condiments. Some of the indigenous peoples of North, Central, and South American originally used the seeds to make red body paint and lipstick, as well as a spice. For this reason, the ''Bixa orellana'' is sometimes called the lipstick tree. Etymology and common names The name, ''Bixa orellana'', was given by Linnaeus. The botanical genus name derives from the aborig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coriander
Coriander (;coriander in the Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary ''Coriandrum sativum'') is an annual in the family Apiaceae. It is also known as Chinese parsley, dhania, or cilantro (). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuadorian Culture
The majority of Ecuador's population is descended from a mixture of both European and Amerindian ancestry. The other 10% of Ecuador's population originate east of the Atlantic Ocean, predominantly from Spain, Italy, Lebanon, France and Germany. Around the Esmeraldas and Chota regions, the African influence would be strong among the small population of Afro-Ecuadorians that account for no more than 10%. Close to 80% of Ecuadorians are Roman Catholic, although the indigenous population blend Christian beliefs with ancient indigenous customs. Ethnic makeup of Ecuador: mestizo (mixed Amerindian and white) 70%, Amerindian 7%, Spanish and others 12%, black 11%.Ecuador can be split up into four parts, geographically; the ''Costa'' (coast), the ''Sierra'' (highlands), and ''El Oriente'' (the east; which includes the Amazonic region). The Galápagos Islands, or ''Archipiélago" de Colón'', also belong to Ecuador. There is tension and dislike between the residents of Quito and Guayaquil. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin American Cuisine
Latin American cuisine is the typical foods, beverages, and cooking styles common to many of the countries and cultures in Latin America. Latin America is a highly diverse area of land whose nations have varying cuisines. Some items typical of Latin American cuisine include maize-based dishes arepas, pupusas, tacos, tamales, tortillas and various salsas and other condiments ( guacamole, pico de gallo, mole, chimichurri, chili, aji, pebre). Sofrito, a culinary term that originally referred to a specific combination of sautéed or braised aromatics, exists in Latin American cuisine. It refers to a sauce of tomatoes, roasted bell peppers, garlic, onions and herbs. Rice and beans are also staples in Latin American cuisine. Latin American beverages are just as distinct as their foods. Some of the beverages can even date back to the times of the Native Americans. Some popular beverages include coffee, mate, hibiscus tea, horchata, chicha, atole, cacao and aguas fresc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)


