|
Yamankan
Burmese names#Honorifics, Nga Yamankan ( my, ငရမန်ကန်း, ; 1039–1084) was List of rulers of Pegu, Governor of Pegu (Bago) from 1077 to 1084, who raised an unsuccessful rebellion against Sawlu, Saw Lu of Pagan Dynasty. He nearly succeeded. He captured and killed Lu. But he was driven out of Upper Burma by Lu's half-brother, Kyansittha and was killed while in retreat. Early life Yamankan, an ethnic Mon people, Mon, was raised in Bagan, Pagan at the court of King Anawrahta. His mother, who was of noble birth, was Anawrahta's son Lu's wet nurse.Htin Aung 1967: 38–39 his posthumous name Yamankan.(Htin Aung 1967: 38–39): The name Yamankan literally means "Karma" (Yaman or Raman means Mon, and Kan means Karma.) It was an insulting name given by the Burmese chronicles for his rebellion. His real personal name is lost to history.) He and Lu grew up together at the Pagan court, and became close friends. When Lu became in king in 1077, he appointed his childhood f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawlu
Saw Lu ( my, စောလူး ; also spelled Sawlu; also known as Min Lulin ( ), ; 19 April 1049 – 21 April 1084) was king of Pagan dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1077 to 1084. He inherited from his father Anawrahta the Pagan Empire, the first ever unified kingdom of Burma (Myanmar) but proved an inexperienced ruler. In 1082, he faced a rebellion in Lower Burma, and was captured c. April 1083. He was later killed in captivity about a year later. Early life Saw Lu was born to King Anawrahta and Queen Agga Mahethi of Pagan, Agga Mahethi, Queen of the Southern Palace. The Burmese chronicles do not agree on the dates regarding his life and reign. The table below lists the dates given by the four main chronicles,Maha Yazawin Vol. 1 2006: 348 and scholarship. Moreover, the chronicles do not agree whether or not Saw Lu was older than Kyansittha, Anawrahta's other son. According to early chronicles, Kyansittha was older (20 years per ''Zata'') and (two years per ''Maha Yazawin'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyansittha
Kyansittha ( my, ကျန်စစ်သား, ; also spelt as Kyanzittha or Hti-Hlaing Shin; 1030 – 1112/13) was king of Pagan dynasty of Burma (Myanmar) from 1084 to 1112/13, and is considered one of the greatest Burmese monarchs. He continued the social, economic and cultural reforms begun by his father, King Anawrahta. Pagan became an internationally recognized power during his 28-year reign. The Burmese language and culture continued to gain ground. In his early life, Kyansittha was a popular and successful general who led Anawrahta's major military campaigns that founded the Pagan Empire. He was exiled twice in the 1070s and 1080s for his affair with Queen Manisanda. Kyansittha ascended to the Pagan throne in 1084 after suppressing a major Mon rebellion that killed King Saw Lu.Coedès 1968: 155–157 His reign was largely peaceful. A great admirer of Mon culture, he pursued a conciliatory policy towards the Mon of the south, and continued the patronage of Mon languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rulers Of Pegu
This is a list of rulers of Pegu (Bago), one of the three main Mon-speaking provinces, located on the south-central coast of modern Myanmar. This is not a list of monarchs of the Hanthawaddy Kingdom, who ruled Lower Burma from Pegu during three separate periods (1369–1539, 1550–1552, 1740–1757). Backgrounder Various Mon language chronicles state different foundation dates of Pegu (Bago), ranging from 573 CE to 1152 CE.A version of the 18th century chronicle ''Slapat Rajawan'' as reported by Arthur Phayre (Phayre 1873: 32) states that the settlement was founded in 1116 Buddhist Era (572/573 CE). But another version of the ''Slapat'', used by P.W. Schmidt (Schmidt 1906: 20, 101), states that it was founded on 1st waxing of Mak (Tabodwe) 1116 BE ( 19 January 573 CE), which it says is equivalent to year 514 of "the third era", without specifying what the era specifically was. However, per (Phayre 1873: 39), one of the "native records" used by Maj. Lloyd says that Pegu was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mon Language
The Mon language (, mnw, ဘာသာမန်, links=no, (Mon-Thai ဘာသာမည်) ; my, မွန်ဘာသာ; th, ภาษามอญ; formerly known as Peguan and Talaing) is an Austroasiatic language spoken by the Mon people. Mon, like the related Khmer language, but unlike most languages in mainland Southeast Asia, is not tonal. The Mon language is a recognised indigenous language in Myanmar as well as a recognised indigenous language of Thailand. Mon was classified as a "vulnerable" language in UNESCO's 2010 ''Atlas of the World’s Languages in Danger''. The Mon language has faced assimilative pressures in both Myanmar and Thailand, where many individuals of Mon descent are now monolingual in Burmese or Thai respectively. In 2007, Mon speakers were estimated to number between 800,000 and 1 million. In Myanmar, the majority of Mon speakers live in Southern Myanmar, especially Mon State, followed by Tanintharyi Region and Kayin State. History Mon is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burmese People Of Mon Descent
Burmese may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to Myanmar, a country in Southeast Asia * Burmese people * Burmese language * Burmese alphabet * Burmese cuisine * Burmese culture Animals * Burmese cat * Burmese chicken * Burmese (horse), a horse given to Queen Elizabeth II * Burmese pony, a breed of horse * Burmese python See also * * :Burmese people * Bamar people The Bamar (, ; also known as the Burmans) are a Sino-Tibetan ethnic group native to Myanmar (formerly Burma) in Southeast Asia. With approximately 35 million people, the Bamar make up the largest ethnic group in Myanmar, constituting 68% of ..., the majority ethnic group in Myanmar * Burmese English, the dialect of English spoken in Myanmar/Burma * Bernese (other) {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1084 Deaths
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
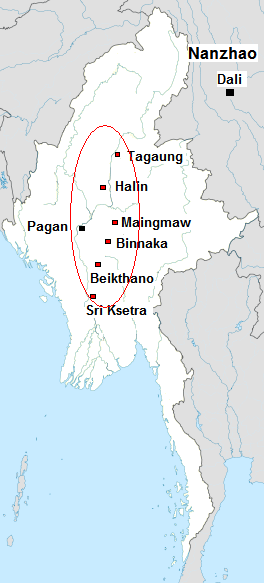
Pagan Dynasty
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying under one polity the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Razadarit Ayedawbon
''Razadarit Ayedawbon'' ( my, ရာဇာဓိရာဇ် အရေးတော်ပုံ) is a Burmese chronicle covering the history of Ramanya from 1287 to 1421. The chronicle consists of accounts of court intrigues, rebellions, diplomatic missions, wars etc. About half of the chronicle is devoted to the reign of King Razadarit (r. 1384–1421), detailing the great king's struggles in the Forty Years' War against King Minkhaung I and Crown Prince Minye Kyawswa of Ava.Thaw Kaung 2010: 29–30 It is the Burmese translation of the first half of the ''Hanthawaddy Chronicle'' from Mon by Binnya Dala, an ethnic Mon minister and general of Toungoo Dynasty. It is likely the earliest ''extant'' text regarding the history of the Mon people in Lower Burma,Aung-Thwin 2005: 133–135 probably the only surviving portion of the original Mon language The Mon language (, mnw, ဘာသာမန်, links=no, (Mon-Thai ဘာသာမည်) ; my, မွန်ဘာသာ; th, � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Purves Phayre
Sir Arthur Purves Phayre (7 May 1812 – 14 December 1885) was a career British Indian Army officer who was the first Commissioner of British Burma, 1862–1867, Governor of Mauritius, 1874–1878, and author. His brother, Sir Robert Phayre (1820–1897), also served in India. They were part of the Phayre family, of which Lt Col Robert Phayre, who served the British administration in Ireland in the 17th century, also had the death warrant of Charles I addressed to him and two other Colonels. Descendants: Colonel Robert Bernard Phayre MC 2/4th Prince of Wales Own Gurkha Rifles, son Colonel Robert Desmond Hensley Phayre Royal Artillery, son Lt Col Robert (Robin) Dermot Spinks Phayre LI, cousin Col Terence Peter Phayre Knott MC RM, of whom son Captain Robert Knott AAC changed name by deed poll to Phayre, to prevent family name dying out, lives in Kenya. Early life Phayre was born in Shrewsbury and educated at Shrewsbury School. He joined the Indian Army in 1828. In 1846 he was ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhamaman
Akhamaman ( my, အခမမန်း,The spelling "အခမမန်း" per (Pan Hla 2005: 27–30). The Mon language spelling in the ''Slapat Rajawan'' per (Schmidt 1906: 112) is "အာခမမန်". ; also known as Akhamwun (အခမွန်, ); d. 1287) was the self-proclaimed king of Pegu, in modern Myanmar, with the title of Thunekkhat Yaza (သုနက္ခတ် ရာဇာ) from 1285 to 1287. He was one of several regional strongmen who emerged during the final years of the Pagan Empire in the 1280s. As the ruler of Pegu, he successfully fended off two attacks by King Narathihapate's forces. After the victory, however, he became deeply unpopular for his increasingly autocratic rule, and was assassinated. Early life ChroniclesThe chronicles here are the ''Slapat Rajawan'' (Schmidt 1906) and (Phayre 1873), and the ''Pak Lat Chronicles'' (Pan Hla 2005: 29, footnote 1), which also states that the original ''Razadarit Ayedawbon'' chronicle does not cover Akham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slapat Rajawan
''Slapat Rajawan Datow Smin Ron'' ( mnw, သုပတ် ရာဇာဝင် ဒတောဝ် သ္ငီ ရောင်; ), more commonly known as ''Bago Yazawin'', is a Mon language chronicle that covers 17 dynasties from the legendary times to the Hanthawaddy period. Written by an ethnic Mon monk, the chronicle was a religion/legend-centric chronicle although it does cover secular history from Sri Ksetra and Pagan to Hanthawaddy periods. As the ''Hmannan Yazawin'' chronicle would follow later, ''Slatpat'' linked its kings to the Buddha and Buddhist mythology.Aung-Thwin 2005: 139–141 It was translated into German by P.W. Schmidt in 1906,Schmidt 1906: Chapter III and into English by R. Halliday in the ''Journal of the Burma Research Society'' in 1923.Aung-Thwin 2005: 419 Schmidt's 1906 publication contains a reprint of a Mon language manuscript of the chronicle. Versions Though the chronicle was written in 1766, it apparently has at least two versionsThe versions used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thayetmyo
Thayet (; pronounced ) is a capital city in Thayet District of Magway Region in central Myanmar. It is a port on the right (western) bank of the Irrawaddy River, across and just south of Allanmyo, between Pyay (Prome) and Magway. Thayet is the administrative seat of both Thayet District and Thayet Township. , the population was 20,251 in the city proper. Geography On the west are the Arakan Mountains The Arakan Mountains ( my, ရခိုင်ရိုးမ), also known as the Rakhine Yoma, are a mountain range in western Myanmar, between the coast of Rakhine State and the Central Myanmar Basin, in which flows the Irrawaddy River. It is th ..., and on the east the Pegu Range, and the face of the country is otherwise broken by low ranges of hills, many of which have no vegetation. The greater part of the district is wooded, and the ranges east and west are covered with forests. The chief river is the Irrawaddy, which traverses Thayet from north to south. Several salt a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)