|
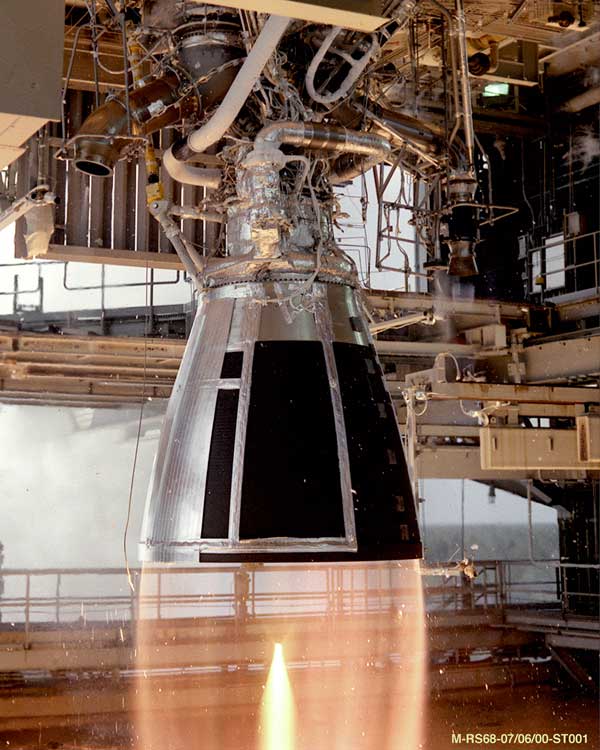
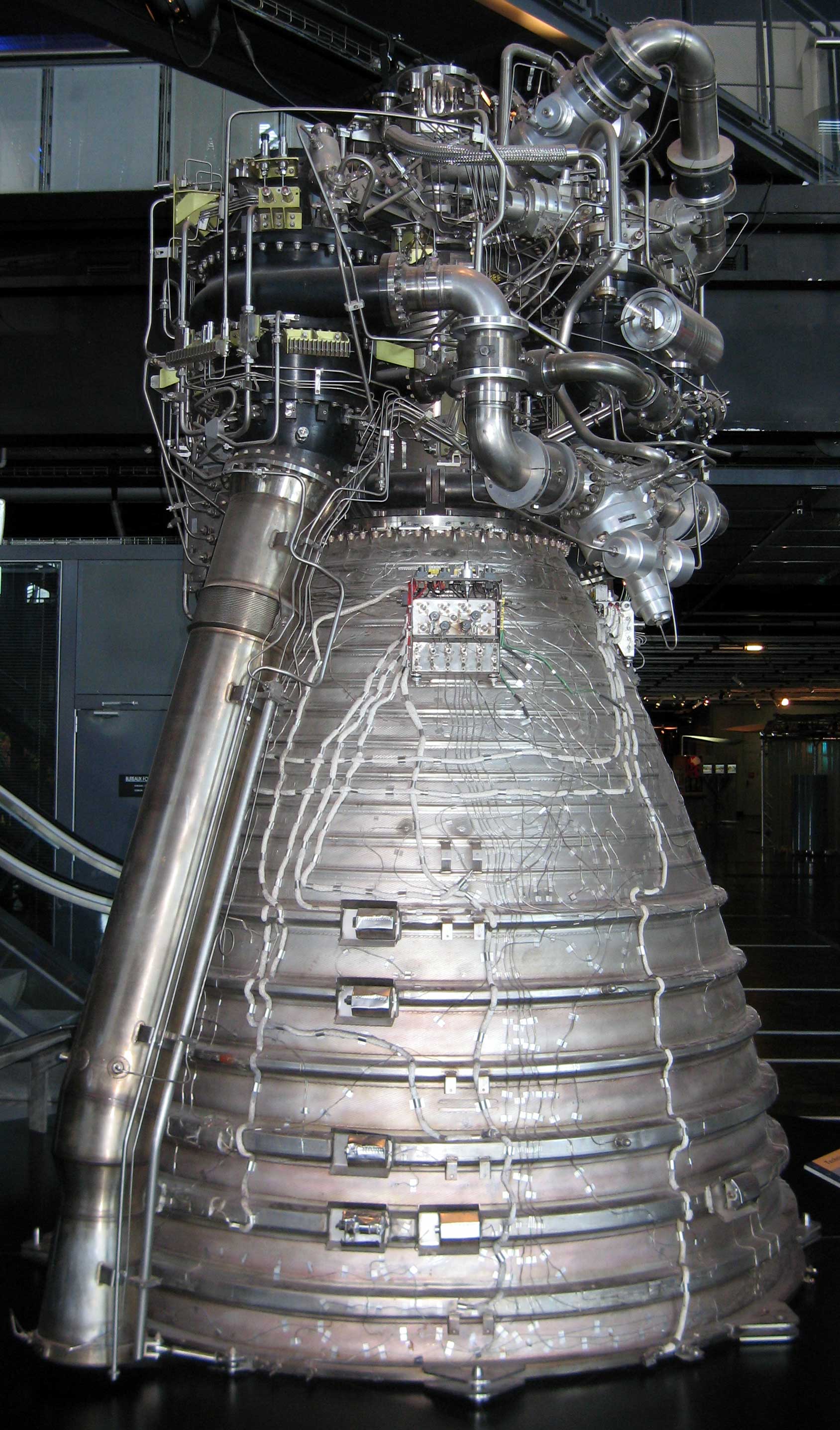
YF-215
The YF-215 is a liquid cryogenic rocket engine burning liquid methane and liquid oxygen in a full-flow staged combustion cycle The staged combustion cycle (sometimes known as topping cycle, preburner cycle, or closed cycle) is a Liquid-propellant rocket#Engine cycles, power cycle of a bipropellant rocket Rocket engine, engine. In the staged combustion cycle, propellant .... The engine is currently under development and is designed to power the super-heavy launch vehicle Long March 9. History The YF-215 engine has been designed to power the first stage of the Long March 9 rocket, with 26 of these engines in the first stage. A successful ignition test of the pre-combustion chamber and gas generator of the engine was conducted on 12 May 2023. References {{DEFAULTSORT:YF-215 Rocket engines using methane propellant Rocket engines of China Rocket engines using full flow staged combustion cycle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long March 9
Long March 9 (, LM-9 or Changzheng 9, CZ-9) is a Chinese Super heavy-lift launch vehicle, super-heavy carrier rocket that is currently under development. It is the ninth iteration of the Long March (rocket family), Long March rocket family, named for the Chinese Red Army's 1934–35 Long March campaign during the Chinese Civil War. Current plans call for the Long March 9 to have a maximum payload capacity of 150,000 kg to low Earth orbit (LEO) and 54,000 kg to trans-lunar injection. Its first flight is planned for 2033, in anticipation of an increase in cadence by China's crewed lunar missions during the 2030s. (As of 2023, the first crewed lunar landing attempt by China is expected to occur by the year 2030; this initial effort would use the under-development Long March 10 carrier rocket, the new Mengzhou (spacecraft), Mengzhou crewed spacecraft, and the Lanyue crewed lunar lander.) History 2016, early design The CZ-9 was initially designed as a three-staged rocket, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it is difficult because it is a gas at standard temperature and pressure. In the Earth's atmosphere methane is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. Methane is an organic compound, and among the simplest of organic compounds. Methane is also a hydrocarbon. Naturally occurring methane is found both below ground and under the seafloor and is formed by both geological and biological processes. The largest reservoir of methane is under the seafloor in the form of methane clathrates. When methane reaches the surface and the atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. The Earth's atmospheric methane concentration h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of Aerospace Liquid Propulsion Technology
The Academy of Aerospace Liquid Propulsion Technology or AALPT (in Chinese: 航天推进技术研究院; 航天六院) is a conglomerate of Chinese state-owned enterprises that develops liquid-propellant rocket engines and guidance systems for China's space launchers. It employs about 10,000 people in about ten entities located in the Shaanxi region. AALPT is a subsidiary of the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC). Activity AALPT's main activity is the development of liquid-propellant rocket engines for Chinese space launchers. The YF-77 and YF-100 engines, which will power the Long March 5 family of launchers, are produced in AALPT's facilities. The conglomerate brings together five research centers and four factories. History AALPT was created around 1970 under the base name 067 at Mount Quinling in Shaanxi as part of the industrialization of what was called the Third Front, that is, the inland regions of southwestern China. Later, the company con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Oxygen
Liquid oxygen, sometimes abbreviated as LOX or LOXygen, is a clear cyan liquid form of dioxygen . It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an application which is ongoing. Physical properties Liquid oxygen has a clear cyan color and is strongly paramagnetic: it can be suspended between the poles of a powerful horseshoe magnet. Liquid oxygen has a density of , slightly denser than liquid water, and is cryogenic with a freezing point of and a boiling point of at . Liquid oxygen has an expansion ratio of 1:861 and because of this, it is used in some commercial and military aircraft as a transportable source of breathing oxygen. Because of its cryogenic nature, liquid oxygen can cause the materials it touches to become extremely brittle. Liquid oxygen is also a very powerful oxidizing agent: organic materials will burn rapidly and energetically in liquid oxygen. Further, if soaked in liquid oxygen, some materials su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full-flow Staged Combustion
The staged combustion cycle (sometimes known as topping cycle, preburner cycle, or closed cycle) is a power cycle of a bipropellant rocket engine. In the staged combustion cycle, propellant flows through multiple combustion chambers, and is thus combusted in stages. The main advantage relative to other rocket engine power cycles is high fuel efficiency, measured through specific impulse, while its main disadvantage is engineering complexity. Typically, propellant flows through two kinds of combustion chambers; the first called and the second called . In the preburner, a small portion of propellant, usually fuel-rich, is partly combusted under non- stoichiometric conditions, increasing the volume of flow driving the turbopumps that feed the engine with propellant. The gas is then injected into the main combustion chamber and combusted completely with the other propellant to produce thrust. Tradeoffs The main advantage is fuel efficiency due to all of the propellant flowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid-fuel Rocket
A liquid-propellant rocket or liquid rocket uses a rocket engine burning liquid propellants. (Alternate approaches use gaseous or solid propellants.) Liquids are desirable propellants because they have reasonably high density and their combustion products have high specific impulse (''I''sp). This allows the volume of the propellant tanks to be relatively low. Types Liquid rockets can be monopropellant rockets using a single type of propellant, or bipropellant rockets using two types of propellant. Tripropellant rockets using three types of propellant are rare. Liquid oxidizer propellants are also used in hybrid rockets, with some of the advantages of a solid rocket. Bipropellant liquid rockets use a liquid fuel such as liquid hydrogen or RP-1, and a liquid oxidizer such as liquid oxygen. The engine may be a cryogenic rocket engine, where the fuel and oxidizer, such as hydrogen and oxygen, are gases which have been liquefied at very low temperatures. Most designs of liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic Rocket Engine
A cryogenic rocket engine is a rocket engine that uses a cryogenic fuel and oxidizer; that is, both its fuel and oxidizer are gases which have been liquefied and are stored at very low temperatures. These highly efficient engines were first flown on the US Atlas-Centaur and were one of the main factors of NASA's success in reaching the Moon by the Saturn V rocket. Rocket engines burning cryogenic propellants remain in use today on high performance upper stages and boosters. Upper stages are numerous. Boosters include ESA's Ariane 6, JAXA's H-II, ISRO's GSLV, LVM3, NASA's Space Launch System. The United States, Russia, India, Japan, France and China are the only countries that have operational cryogenic rocket engines. Cryogenic propellants Rocket engines need high mass flow rates of both oxidizer and fuel to generate useful thrust. Oxygen, the simplest and most common oxidizer, is in the gas phase at standard temperature and pressure, as is hydrogen, the simplest f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Engine
A rocket engine is a reaction engine, producing thrust in accordance with Newton's third law by ejecting reaction mass rearward, usually a high-speed Jet (fluid), jet of high-temperature gas produced by the combustion of rocket propellants stored inside the rocket. However, non-combusting forms such as cold gas thrusters and nuclear thermal rockets also exist. Rocket vehicles carry their own oxidiser, unlike most combustion engines, so rocket engines can be used in a vacuum, and they can achieve great speed, beyond escape velocity. Vehicles commonly propelled by rocket engines include missiles, Rocket-assisted projectile, artillery shells, ballistic missiles and rockets of any size, from tiny Rocket (firework), fireworks to Rocket (weapon), man-sized weapons to huge Space vehicle, spaceships. Compared to other types of jet engine, rocket engines are the lightest and have the highest thrust, but are the least propellant-efficient (they have the lowest specific impulse). The ideal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Oxygen
Liquid oxygen, sometimes abbreviated as LOX or LOXygen, is a clear cyan liquid form of dioxygen . It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an application which is ongoing. Physical properties Liquid oxygen has a clear cyan color and is strongly paramagnetic: it can be suspended between the poles of a powerful horseshoe magnet. Liquid oxygen has a density of , slightly denser than liquid water, and is cryogenic with a freezing point of and a boiling point of at . Liquid oxygen has an expansion ratio of 1:861 and because of this, it is used in some commercial and military aircraft as a transportable source of breathing oxygen. Because of its cryogenic nature, liquid oxygen can cause the materials it touches to become extremely brittle. Liquid oxygen is also a very powerful oxidizing agent: organic materials will burn rapidly and energetically in liquid oxygen. Further, if soaked in liquid oxygen, some materials su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staged Combustion Cycle
The staged combustion cycle (sometimes known as topping cycle, preburner cycle, or closed cycle) is a power cycle of a bipropellant rocket engine. In the staged combustion cycle, propellant flows through multiple combustion chambers, and is thus combusted in stages. The main advantage relative to other rocket engine power cycles is high fuel efficiency, measured through specific impulse, while its main disadvantage is engineering complexity. Typically, propellant flows through two kinds of combustion chambers; the first called and the second called . In the preburner, a small portion of propellant, usually fuel-rich, is partly combusted under non- stoichiometric conditions, increasing the volume of flow driving the turbopumps that feed the engine with propellant. The gas is then injected into the main combustion chamber and combusted completely with the other propellant to produce thrust. Tradeoffs The main advantage is fuel efficiency due to all of the propellant flowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |