|
Xephyr
Xephyr is display server software implementing the X11 display server protocol based on KDrive which targets a window on a host X Server as its framebuffer. It is written by Matthew Allum. Xephyr is an X-on-X implementation and runs on X.Org Server and can work with Glamor. Future versions could make use of libinput. Replacing Xephyr with the xf86-video-dummy and xf86-video-nested drivers in the normal X.Org server is being considered as part of X11R7.8. Features Unlike the similar ''Xnest'', Xephyr supports modern X extensions (even if host server doesn't) such as composite, damage, randr, etc. It uses SHM images and shadow framebuffer updates to provide good performance. It also has a visual debugging mode for observing screen updates. Limitations Xorg's version of Xephyr uses only software rendering for OpenGL, but Feng Haitao has developed forked version of Xephyrwhich can do hardware-accelerated rendering if the underlying X server has the capability. See also * Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glamor (software)
X.Org Server is the free and open-source implementation of the X Window System display server stewarded by the X.Org Foundation. Implementations of the client-side X Window System protocol exist in the form of ''X11 libraries'', which serve as helpful APIs for communicating with the X server. Two such major X libraries exist for X11. The first of these libraries was Xlib, the original C language X11 API, but another C language X library, XCB, was created later in 2001. Other smaller X libraries exist, both as interfaces for Xlib and XCB in other languages, and as smaller standalone X libraries. The services with which the X.Org Foundation supports X Server include the packaging of the releases; certification (for a fee); evaluation of improvements to the code; developing the web site, and handling the distribution of monetary donations. The releases are coded, documented, and packaged by global developers. Software architecture The X.Org Server implements the server sid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
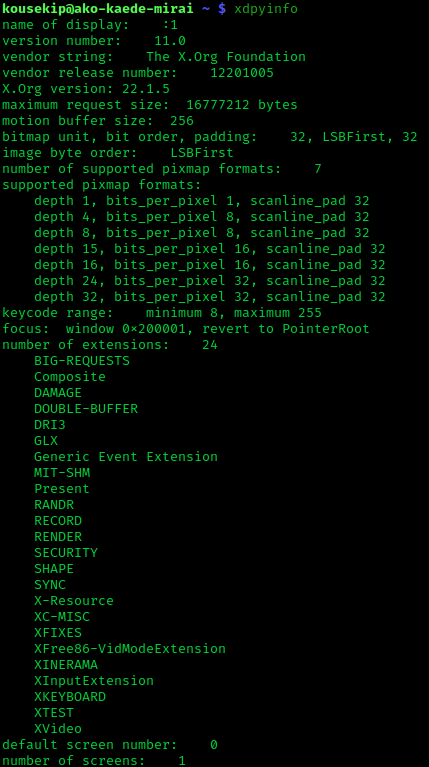
Xorg
X.Org Server is the free and open-source implementation of the X Window System display server stewarded by the X.Org Foundation. Implementations of the client-side X Window System protocol exist in the form of ''X11 libraries'', which serve as helpful APIs for communicating with the X server. Two such major X libraries exist for X11. The first of these libraries was Xlib, the original C language X11 API, but another C language X library, XCB, was created later in 2001. Other smaller X libraries exist, both as interfaces for Xlib and XCB in other languages, and as smaller standalone X libraries. The services with which the X.Org Foundation supports X Server include the packaging of the releases; certification (for a fee); evaluation of improvements to the code; developing the web site, and handling the distribution of monetary donations. The releases are coded, documented, and packaged by global developers. Software architecture The X.Org Server implements the server side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KDrive
X.Org Server is the free and open-source implementation of the X Window System display server stewarded by the X.Org Foundation. Implementations of the client-side X Window System protocol exist in the form of ''X11 libraries'', which serve as helpful APIs for communicating with the X server. Two such major X libraries exist for X11. The first of these libraries was Xlib, the original C language X11 API, but another C language X library, XCB, was created later in 2001. Other smaller X libraries exist, both as interfaces for Xlib and XCB in other languages, and as smaller standalone X libraries. The services with which the X.Org Foundation supports X Server include the packaging of the releases; certification (for a fee); evaluation of improvements to the code; developing the web site, and handling the distribution of monetary donations. The releases are coded, documented, and packaged by global developers. Software architecture The X.Org Server implements the server side of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedesktop
freedesktop.org (fd.o) is a project to work on interoperability and shared base technology for Free software, free-software desktop environments for the X Window System (X11) and Wayland (display server protocol), Wayland on Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. It was founded by Havoc Pennington, a GNOME developer working for Red Hat in March 2000. The project's servers are hosted by Portland State University, sponsored by Hewlett-Packard, Intel, and Google. Widely used open-source software, open-source X-based desktop projects, such as GNOME, KDE Plasma 5, KDE's Plasma Desktop, and Xfce, are collaborating with the freedesktop.org project. In 2006, the project released Portland Project, Portland 1.0 (xdg-utils), a set of common interfaces for desktop environments. However, freedesktop.org is a "collaboration zone" for standards and specifications where users can freely discuss ideas, and not a formal standards organization. freedesktop.org was formerly known as the X De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Mint
Linux Mint is a community-driven Linux distribution based on Ubuntu (which is in turn based on Debian), bundled with a variety of free and open-source applications. It can provide full out-of-the-box multimedia support for those who choose to include proprietary software such as multimedia codecs. The Linux Mint project was created by Clément Lefèbvre and is actively maintained by the Linux Mint Team and community. History Linux Mint began in 2006 with a beta release, 1.0, code-named 'Ada', based on Kubuntu. Linux Mint 2.0 'Barbara' was the first version to use Ubuntu as its codebase. It had few users until the release of Linux Mint 3.0, 'Cassandra'. Linux Mint 2.0 was based on Ubuntu 6.10, using Ubuntu's package repositories and using it as a codebase. It then followed its own codebase, building each release from the previous one, but continuing to use the package repositories of the latest Ubuntu release. This made the two systems' bases almost identical, guaranteeing fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Client
In computer networking, a thin client is a simple (low-performance) computer that has been optimized for establishing a remote connection with a server-based computing environment. They are sometimes known as ''network computers'', or in their simplest form as ''zero clients''. The server does most of the work, which can include launching software programs, performing calculations, and storing data. This contrasts with a rich client or a conventional personal computer; the former is also intended for working in a client–server model but has significant local processing power, while the latter aims to perform its function mostly locally. Thin clients occur as components of a broader computing infrastructure, where many clients share their computations with a server or server farm. The server-side infrastructure uses cloud computing software such as application virtualization, hosted shared desktop (HSD) or desktop virtualization (VDI). This combination forms what is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenGL
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D and 3D vector graphics. The API is typically used to interact with a graphics processing unit (GPU), to achieve hardware-accelerated rendering. Silicon Graphics, Inc. (SGI) began developing OpenGL in 1991 and released it on June 30, 1992; applications use it extensively in the fields of computer-aided design (CAD), virtual reality, scientific visualization, information visualization, flight simulation, and video games. Since 2006, OpenGL has been managed by the non-profit technology consortium Khronos Group. Design The OpenGL specification describes an abstract API for drawing 2D and 3D graphics. Although it is possible for the API to be implemented entirely in software, it is designed to be implemented mostly or entirely in hardware. The API is defined as a set of functions which may be called by the client program, alongside a set of named in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Rendering
Software rendering is the process of generating an image from a model by means of computer software. In the context of computer graphics rendering, software rendering refers to a rendering process that is not dependent upon graphics hardware ASICs, such as a graphics card. The rendering takes place entirely in the CPU. Rendering everything with the (general-purpose) CPU has the main advantage that it is not restricted to the (limited) capabilities of graphics hardware, but the disadvantage is that more semiconductors are needed to obtain the same speed. Rendering is used in architecture, simulators, video games, movies and television visual effects and design visualization. Rendering is the last step in an animation process, and gives the final appearance to the models and animation with visual effects such as shading, texture-mapping, shadows, reflections and motion blur. Rendering can be split into two main categories: real-time rendering (also known as online rendering), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT-SHM
The MIT Shared Memory Extension or MIT-SHM or XShm is an X Window System extension for exchange of image data between client and server using shared memory (usually ). The mechanism only works when both pieces are on the same computer. The basic capability provided is that of shared memory XImages. This is essentially a version of the ximage interface where the actual image data is stored in a SysV shared memory segment, and thus need not be transferred across the socket to the X server. For large images, use of this facility can result in some real performance increases. Additionally, some implementations provide shared memory pixmaps. These are two-dimensional arrays of pixels in a format specified by the X server, where the image data is stored in the shared memory segment. Through use of shared memory pixmaps, it is possible to change the contents of these pixmaps without using any Xlib routines at all. Shared memory pixmaps can only be supported when the X server can use regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Framebuffer
A framebuffer (frame buffer, or sometimes framestore) is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Modern video cards contain framebuffer circuitry in their cores. This circuitry converts an in-memory bitmap into a video signal that can be displayed on a computer monitor. In computing, a screen buffer is a part of computer memory used by a computer application for the representation of the content to be shown on the computer display. The screen buffer may also be called the video buffer, the regeneration buffer, or regen buffer for short. Screen buffers should be distinguished from video memory. To this end, the term off-screen buffer is also used. The information in the buffer typically consists of color values for every pixel to be shown on the display. Color values are commonly stored in 1-bit binary (monochrome), 4-bit palettized, 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libinput
Wayland is a communication protocol that specifies the communication between a display server and its clients, as well as a C library implementation of that protocol. A display server using the Wayland protocol is called a ''Wayland compositor'', because it additionally performs the task of a compositing window manager. Wayland is developed by a group of volunteers initially led by Kristian Høgsberg as a free and open-source community-driven project with the aim of replacing the X Window System with a modern, secure simpler windowing system in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. The project's source code is published under the terms of the MIT License, a permissive free software licence. As part of its efforts, the Wayland project also develops a reference implementation of a Wayland compositor called ''Weston''. Overview The Wayland Display Server project was started by Red Hat developer Kristian Høgsberg in 2008. Beginning around 2010, Linux desktop graphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Window (computing)
In computing, a window is a graphical control element. It consists of a visual area containing some of the graphical user interface of the program it belongs to and is framed by a window decoration. It usually has a rectangular shape that can overlap with the area of other windows. It displays the ''output'' of and may allow ''input'' to one or more processes. Windows are primarily associated with graphical displays, where they can be manipulated with a pointer by employing some kind of pointing device. Text-only displays can also support windowing, as a way to maintain multiple independent display areas, such as multiple buffers in Emacs. Text windows are usually controlled by keyboard, though some also respond to the mouse. A graphical user interface (GUI) using windows as one of its main " metaphors" is called a windowing system, whose main components are the display server and the window manager. History The idea was developed at the Stanford Research Institute (led by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |