|
Xserve G4
The Xserve is a discontinued series of rack-mounted servers that was manufactured by Apple Inc. between 2002 and 2011. It was Apple's first rack-mounted server, and could function as a file server, web server or run high-performance computing applications in clusters – a dedicated cluster Xserve, the Xserve Cluster Node, without a video card and optical drives was also available. The first Xserve had a processor, replaced by a in 2004, and by Intel Xeon processors in 2006; each was available in single-processor and dual-processor configurations. The Xserve was discontinued in 2011, and replaced with the Mac Pro Server and the Mac Mini Server. Before the Xserve, Apple's server line included the Apple Workgroup Server, Macintosh Server, and Apple Network Server. Xserve G4 Apple introduced the Xserve on May 14, 2002 (released in June). Initially, two configuration options were available: a single-processor Xserve at US$2999, and a dual-processor Xserve at US$3999. Xserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xserve Cluster NASA
The Xserve is a discontinued series of rack unit, rack-mounted server (computing), servers that was manufactured by Apple Inc. between 2002 and 2011. It was Apple's first rack-mounted server, and could function as a file server, web server or run high-performance computing applications in cluster (computing), clusters – a dedicated cluster Xserve, the Xserve Cluster Node, without a video card and optical drives was also available. The first Xserve had a processor, replaced by a in 2004, and by Intel Xeon processors in 2006; each was available in single-processor and dual-processor configurations. The Xserve was discontinued in 2011, and replaced with the Mac Pro#Mac Pro Server, Mac Pro Server and the Mac Mini#Server, Mac Mini Server. Before the Xserve, Apple's server line included the Apple Workgroup Server, Apple Workgroup Server, Macintosh Server, and Apple Network Server. Xserve G4 Apple introduced the Xserve on May 14, 2002 (released in June). Initially, two configur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xserve G4
The Xserve is a discontinued series of rack-mounted servers that was manufactured by Apple Inc. between 2002 and 2011. It was Apple's first rack-mounted server, and could function as a file server, web server or run high-performance computing applications in clusters – a dedicated cluster Xserve, the Xserve Cluster Node, without a video card and optical drives was also available. The first Xserve had a processor, replaced by a in 2004, and by Intel Xeon processors in 2006; each was available in single-processor and dual-processor configurations. The Xserve was discontinued in 2011, and replaced with the Mac Pro Server and the Mac Mini Server. Before the Xserve, Apple's server line included the Apple Workgroup Server, Macintosh Server, and Apple Network Server. Xserve G4 Apple introduced the Xserve on May 14, 2002 (released in June). Initially, two configuration options were available: a single-processor Xserve at US$2999, and a dual-processor Xserve at US$3999. Xserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with disk read-and-write head, magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual Block (data storage), blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small disk enclosure, rectangular box. Hard disk drives were introduced by IBM in 1956, and were the dominant secondary storage device for History of general-purpose CPUs, general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. Devices connected to the PCI bus appear to a bus master to be connected directly to its own bus and are assigned addresses in the processor's address space. It is a parallel bus, synchronous to a single bus clock. Attached devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard (called a ''planar device'' in the PCI specification) or an expansion card that fits into a slot. The PCI Local Bus was first implemented in IBM PC compatibles, where it displaced the combination of several slow Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slots and one fast VESA Local Bus (VLB) slot as the bus configuration. It has subsequently been adopted for other computer type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by graphics hardware, computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as Computer-generated imagery, computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of Computer graphics (computer science), computer science research. Some topics in computer graphics include user interface design, Sprite (computer graphics), sprite graphics, raster graphics, Rendering (computer graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
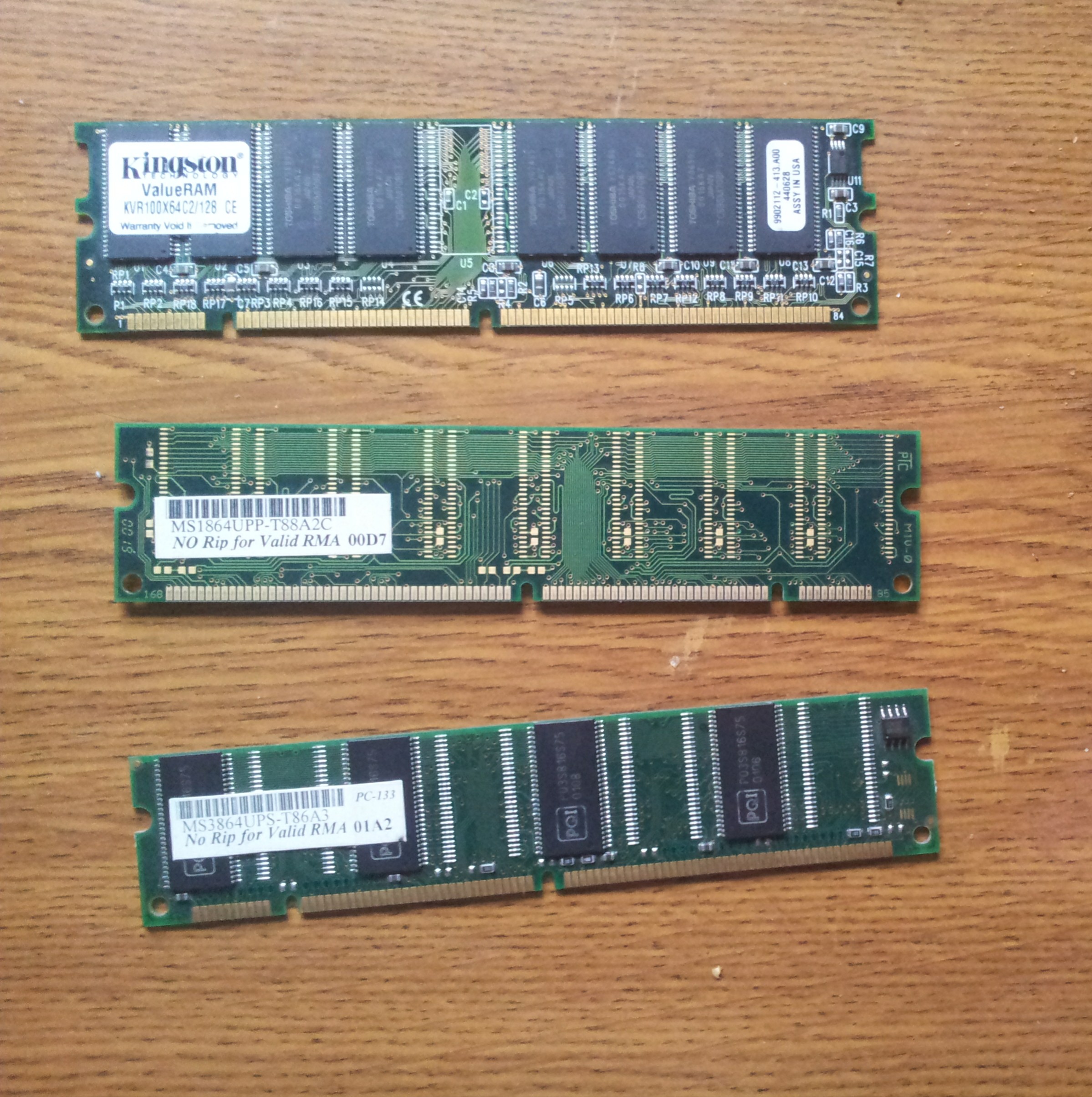
SDRAM
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to the early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions delayed only by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Access Memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks and magnetic tape), where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement. In today's technology, random-access memory takes the form of integrated circuit (IC) chips with MOS (metal–oxide–semiconductor) memory cells. RAM is normally associated with volatile types of memory where stored information is lost if power is removed. The two main types of volatile random-access semiconductor memory are static ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front Side Bus
The front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the central processing unit (CPU) and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge. Depending on the implementation, some computers may also have a back-side bus that connects the CPU to the cache. This bus and the cache connected to it are faster than accessing the system memory (or RAM) via the front-side bus. The speed of the front side bus is often used as an important measure of the performance of a computer. The original front-side bus architecture was replaced by HyperTransport, Intel QuickPath Interconnect, and Direct Media Interface, followed by Intel Ultra Path Interconnect and AMD's Infinity Fabric. History The term came into use by Intel Corporation about the time the Pentium Pro and Pentium II products were announced, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPU Cache
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from the main memory. A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. Most CPUs have a hierarchy of multiple cache levels (L1, L2, often L3, and rarely even L4), with different instruction-specific and data-specific caches at level 1. The cache memory is typically implemented with static random-access memory (SRAM), in modern CPUs by far the largest part of them by chip area, but SRAM is not always used for all levels (of I- or D-cache), or even any level, sometimes some latter or all levels are implemented with eDRAM. Other types of caches exist (that are not counted towards the "cache size" of the most important caches mentioned above), such as the translation lookaside buffer (TLB) which is part of the memory management unit (M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions of a computer program, such as arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations. This role contrasts with that of external components, such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized coprocessors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, CPU design, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic operation, arithmetic and Bitwise operation, logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the #Fetch, fetching (from memory), #Decode, decoding and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xserve RAID
Xserve RAID is a attachment mass-storage server that was offered by Apple Inc. Xserve RAID held up to 14 hot-swappable Ultra-ATA hard drives, and had a capacity of 10.5 TB when filled with 750 GB modules. Xserve RAID supported RAID levels of 0, 0+1, 1, 3 and 5 in hardware, hybrid RAID levels such as 10 and 50 could be created in software. It was rack-mountable and was 3 U high. Although the Xserve RAID contained 14 drives, they were split into two independent groups of 7 drives each managed by an identical RAID controller. Importantly, the controllers were independent, but not redundant; each managed seven of the storage array's fourteen drives, given a failure of one of the controllers those 7 drives were not accessible: the other could not take over its duties. Xserve RAID did, however, have redundant cooling units and power supplies. Xserve RAID's ports were two Fibre Channel ports for regular data transfer, a 10/100 Ethernet port for remote management, and a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drive Bay
A drive bay is a standard-sized area for adding hardware to a computer. Most drive bays are fixed to the inside of a case, but some can be removed. Over the years since the introduction of the IBM PC, it and its compatibles have had many form factors of drive bays. Four form factors are in common use today, the 5.25-inch, 3.5-inch, 2.5-inch or 1.8-inch drive bays. These names do not refer to the width of the bay itself, but rather to the width of the disks used by the drives mounted in these bays. Form factors 8.0-inch ''8.0-inch'' drive bays were found in early IBM computers, CP/M computers, and the TRS-80 Model II. They were high, wide, and approximately deep, and were used for hard disk drives and floppy disk drives. This form factor is obsolete. 5.25-inch ''5.25-inch'' drive bays are divided into two height specifications, ''full-height'' and ''half-height''. ''Full-height'' bays were found in old PCs in the early to mid-1980s. They were high, wide, and u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |