|
Xpress 200
The Radeon Xpress 200 is a computer chipset released by ATI. The chipset supports AMD 64-bit processors (Socket 939 and Socket 754) as well as supporting Intel Pentium 4, Pentium D and Celeron processors (LGA 775 and Socket 478). Additionally, it includes support for DDR400 RAM and DDR-2 667 RAM on the Intel Edition. ATI renamed its Radeon Xpress 200 Crossfire Edition chipset to CrossFire Xpress 1600. After the takeover from AMD, AMD renamed the Crossfire Xpress 1600 chipset for AMD socket AM2 platform to the AMD 480X CrossFire chipset. Types The Radeon Xpress 200 comes in five different versions: * Radeon Xpress 200 * Radeon Xpress 200P * Radeon Xpress 200M * Radeon Xpress 200 Crossfire Edition * Radeon Xpress 200 for Intel Common features *Support for up to 22 PCI Express lanes. *Support for up to 8 USB 2.0 ports. *Support for 4 SATA and 4 PATA drives, which can be linked together in any combination of SATA and PATA to form a RAID 0, 1, or 0+1. * AC'97 Audio for SB400. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Athlon 64
The Athlon 64 is a ninth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name ''Athlon'', and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP. The Athlon 64 was the second processor to implement the AMD64 architecture (after the Opteron) and the first 64-bit processor targeted at the average consumer. Variants of the Athlon 64 have been produced for Socket 754, Socket 939, Socket 940, and Socket AM2. It was AMD's primary consumer CPU, and primarily competed with Intel's Pentium 4, especially the ''Prescott'' and ''Cedar Mill'' core revisions. The Athlon 64 is AMD's first K8, eighth-generation processor core for desktop and mobile computers. Despite being natively 64-bit, the AMD64 architecture is backward-compatible with 32-bit x86 instructions. The Athlon 64 line was succeeded by the dual-core Athlon 64 X2 and Athlon X2 lines. Background The Athlon 64 was originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Socket 478
Socket 478, also known as mPGA478 or mPGA478B, is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series Central processing unit, CPUs. Socket 478 was launched in August 2001 in advance of the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and their Athlon XP processors. Socket 478 was intended to be the replacement for Socket 423, a Willamette-based processor socket which was on the market for only a short time. This was the last Intel desktop socket to use a pin grid array (Pin grid array, PGA) interface. All later Intel desktop sockets use a land grid array (Land grid array, LGA) interface. Socket 478 was phased out with the launch of LGA 775 in 2004. Technical specifications Socket 478 was used for all Pentium_4#Northwood, Northwood Pentium 4 and Celeron processors. It supported the first Pentium_4#Prescott, Prescott Pentium 4 processors and all Pentium_4#Willamette, Willamette Celerons, along with several of the Willamette-series Pentium 4s. Sock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. Devices connected to the PCI bus appear to a bus master to be connected directly to its own bus and are assigned addresses in the processor's address space. It is a parallel bus, synchronous to a single bus clock. Attached devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard (called a ''planar device'' in the PCI specification) or an expansion card that fits into a slot. The PCI Local Bus was first implemented in IBM PC compatibles, where it displaced the combination of several slow Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slots and one fast VESA Local Bus (VLB) slot as the bus configuration. It has subsequently been adopted for other computer types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Intel High Definition Audio
Intel High Definition Audio (IHDA) (also called HD Audio or development codename Azalia) is a specification for the audio sub-system of personal computers. It was released by Intel in 2004 as the successor to their AC'97 PC audio standard, but it is not backwards-compatible with it. Features The Intel High Definition Audio specification includes the following features: * Up to 15 input and 15 output streams * Up to 16 PCM audio channels per stream * Sample resolutions of 8–32 bits * Sample rates of 6–192 kHz * Support for audio codecs (e.g., ADC, DAC), modem codecs, and vendor-offered codecs * Discoverable codec architecture * Fine-grained codec power-control * Audio jack detection, sensing, and retasking * Vendor-offered (OEM or IHV) audio enhancement features Motherboards typically do not have any more than eight built-in output channels (7.1 surround sound) and four input channels (back and front panel microphone inputs, and a back-panel stereo line-in). Users ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AC'97
AC'97 (''Audio Codec '97;'' also MC'97 for ''Modem Codec '97'') is an audio codec standard developed by Intel Architecture Labs and various codec manufacturers in 1997. The standard was used in motherboards, modems, and sound cards. The specification covers two types of components, and the AC-Link digital interface between them: # an AC'97 ''digital controller'' (DC97), which is typically built into the southbridge of the chipset, and # an AC'97 audio and/or modem ''codec'', available from several vendors, which contains the analog components of the architecture. AC'97 defines a high-quality, 16- or 24- bit audio architecture with 5.1 surround sound support for the PC. AC'97 supports a 96 kHz sampling rate at 24-bit stereo resolution and a 48 kHz sampling rate at 24-bit stereo resolution for multichannel recording and playback. Integrated audio is implemented with the AC'97 Codec on the motherboard, a communications and networking riser card, or an audio/modem r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Redundant Array Of Independent Disks
RAID (; redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical data storage components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. This is in contrast to the previous concept of highly reliable mainframe disk drives known as ''single large expensive disk'' (''SLED''). Data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways, referred to as RAID levels, depending on the required level of redundancy and performance. The different schemes, or data distribution layouts, are named by the word "RAID" followed by a number, for example RAID 0 or RAID 1. Each scheme, or RAID level, provides a different balance among the key goals: reliability, availability, performance, and capacity. RAID levels greater than RAID 0 provide protection against unrecoverable sector read errors, as well as against failures of whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
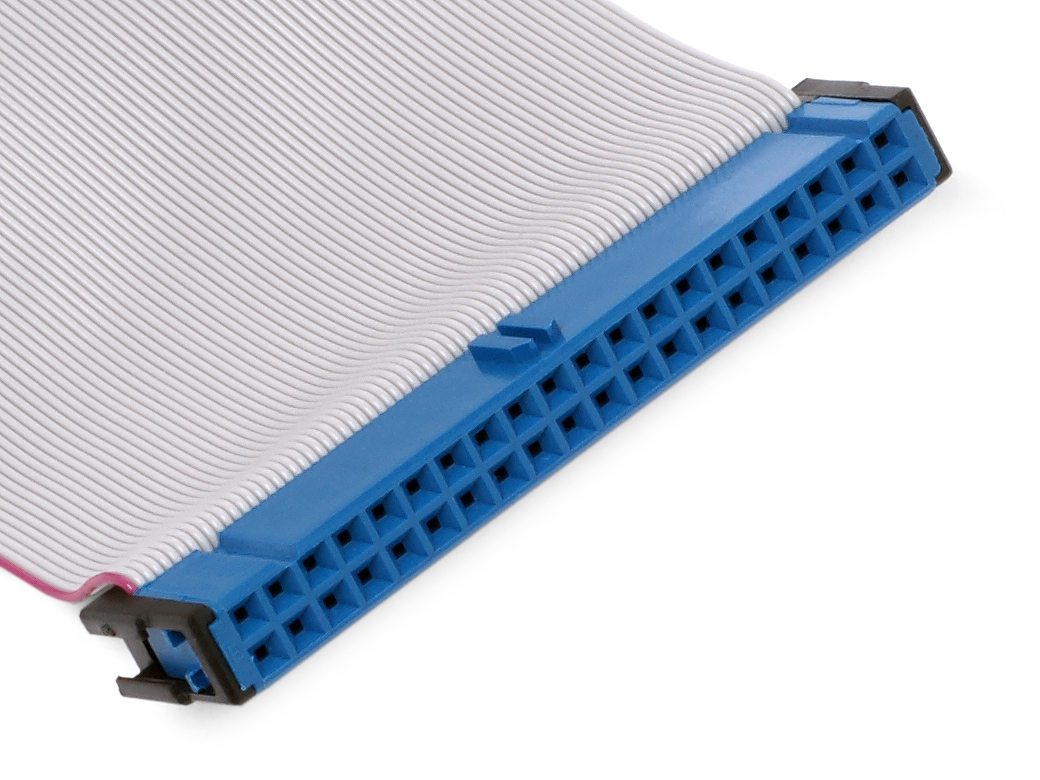
Advanced Technology Attachment
Parallel ATA (PATA), originally , also known as Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE), is a standard interface designed for IBM PC-compatible computers. It was first developed by Western Digital and Compaq in 1986 for compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives. The connection is used for storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, optical disc drives, and tape drives in computers. The standard is maintained by the X3/INCITS committee. It uses the underlying (ATA) and Packet Interface ( ATAPI) standards. The Parallel ATA standard is the result of a long history of incremental technical development, which began with the original AT Attachment interface, developed for use in early PC AT equipment. The ATA interface itself evolved in several stages from Western Digital's original Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface. As a result, many near-synonyms for ATA/ATAPI and its previous incarnations are still in common informal use, in particular Extended ID ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Serial ATA
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host adapter, host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) which are then released by the INCITS Technical Committee T13, AT Attachment (INCITS T13). History SATA was announced in 2000 in order to provide several advantages over the earlier PATA interface such as reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40 or 80), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. #1.0, Revision 1.0 of the specification was released in January 2003. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Universal Serial Bus
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical interfaces, and communication protocols to and from ''hosts'', such as personal computers, to and from peripheral ''devices'', e.g. displays, keyboards, and mass storage devices, and to and from intermediate ''hubs'', which multiply the number of a host's ports. Introduced in 1996, USB was originally designed to standardize the connection of peripherals to computers, replacing various interfaces such as serial ports, parallel ports, game ports, and Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) ports. Early versions of USB became commonplace on a wide range of devices, such as keyboards, mice, cameras, printers, scanners, flash drives, smartphones, game consoles, and power banks. USB has since evolved into a standard to replace virtually all common ports on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
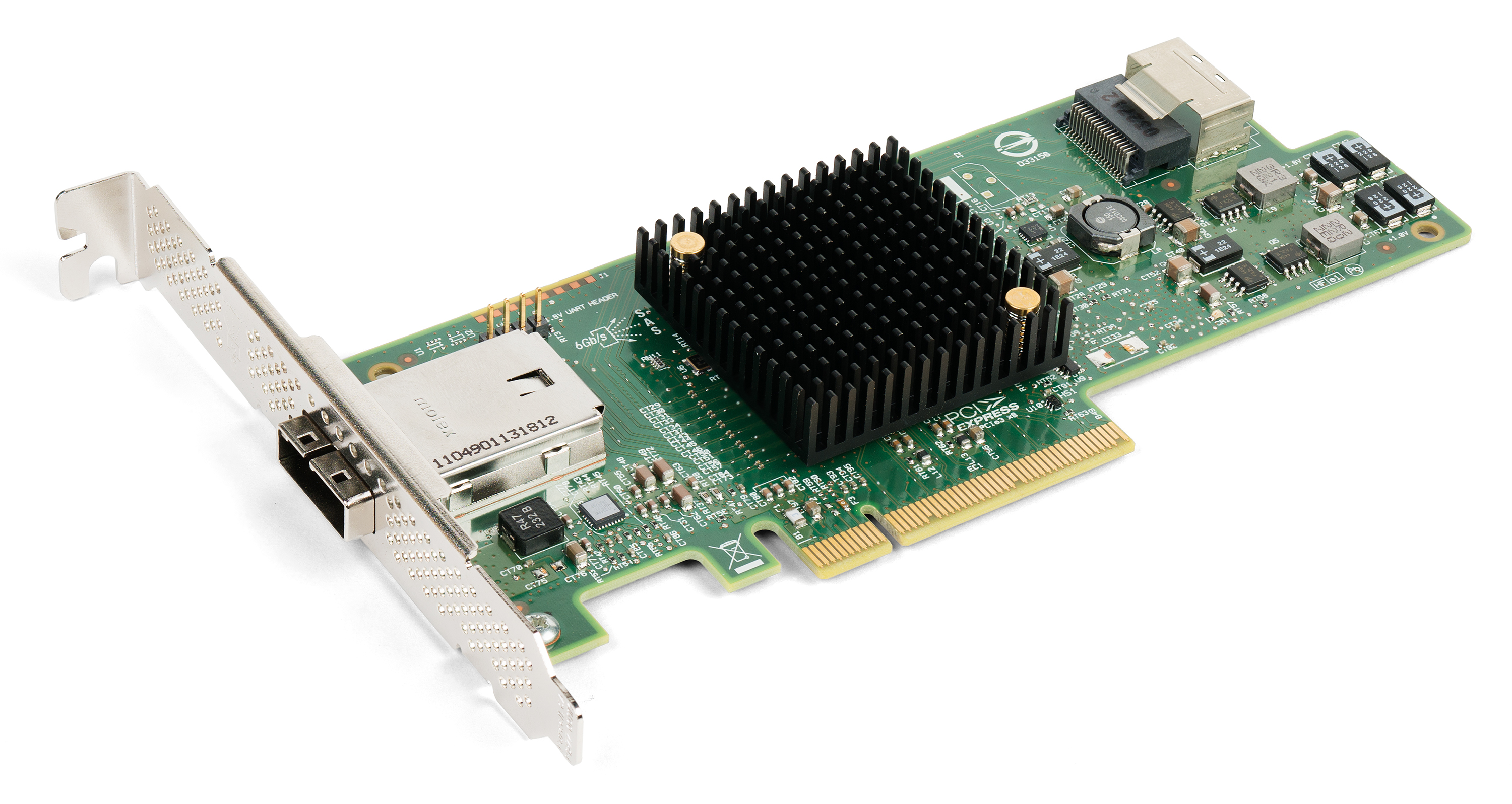
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI-X and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP. Developed and maintained by the PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group), PCIe is commonly used to connect graphics cards, sound cards, Wi-Fi and Ethernet adapters, and storage devices such as solid-state drives and hard disk drives. Compared to earlier standards, PCIe supports faster data transfer, uses fewer pins, takes up less space, and allows devices to be added or removed while the computer is running (hot swapping). It also includes better error detection and supports newer features like I/O virtualization for advanced computing needs. PCIe connections are made through "lanes," which are pairs of wires that send and receive data. Devices can use one or more lanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AMD 580 Chipset Series
AMD 580 chipset series is a computer chipset series designed by the AMD Graphics Product Group, for the AMD processors. It was designed for usage with ATI's CrossFire Multi GPU Technology, with both PCI Express slots running at x16 lanes each. History The 580X chipset was originally named the "ATI Radeon Xpress 3200 chipset". The Radeon Xpress chipset was designed by ATI to enter the realm of the desktop arena, especially the AMD Socket 939 platform where ATI's rival, nVidia, had a clear market advantage. The Xpress 200 was launched with the CrossFire edition of the chipset considered as the high end of the chipset. However, rolling delays with the Crossfire Master Cards forced ATI to launch the Socket 939 platform while the Intel platform was scrapped due to time constraints. Reviews painted the Xpress 200 Crossfire as a board that could match nVidia's nForce 4 SLI. With the release of the nForce 4 16x SLI, ATI changed strategy and announced the RD580 chipset. The RD580 was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
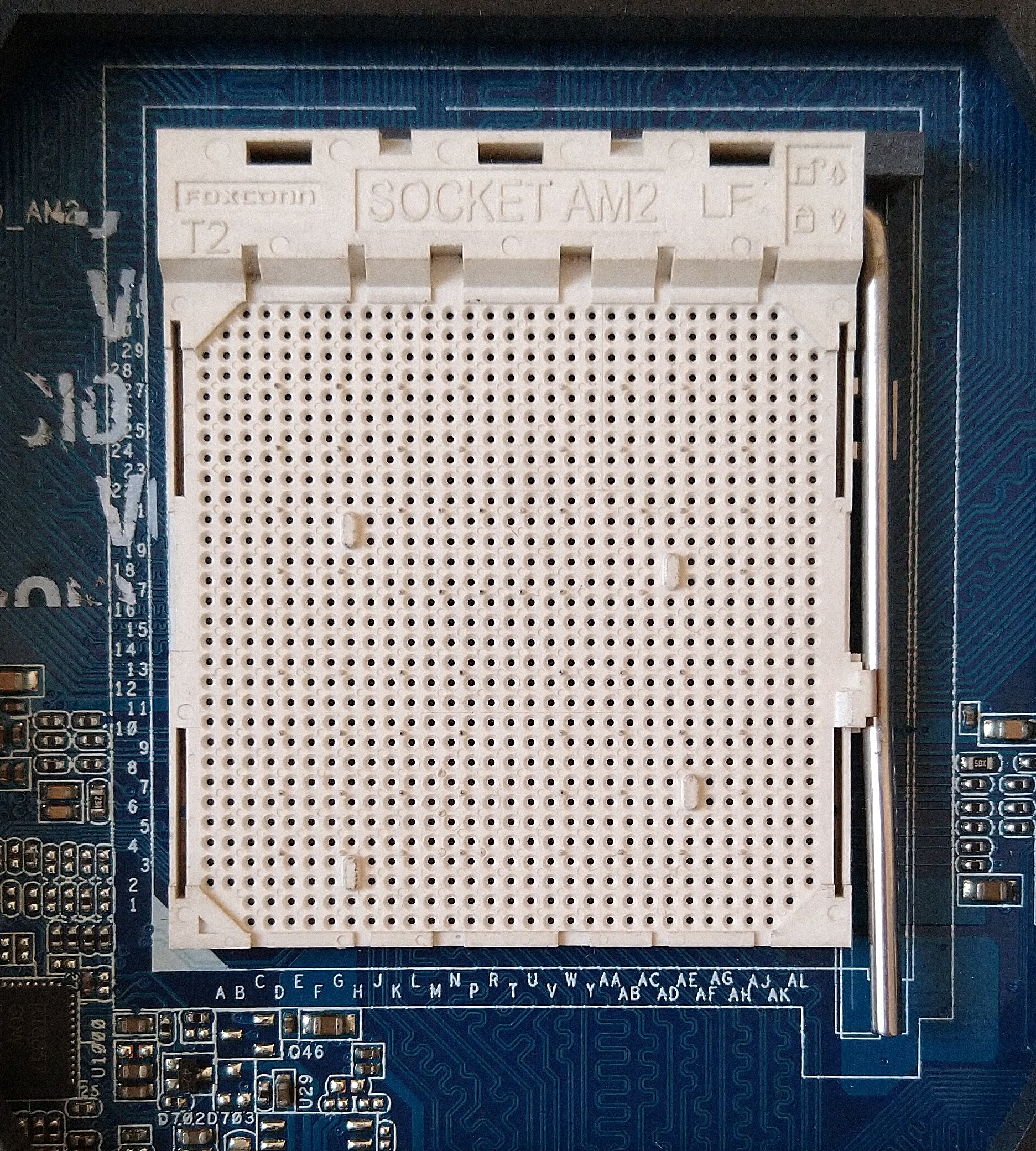
Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 (to prevent using the same name as Cyrix MII processors), is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments. It was released on May 23, 2006, as a replacement for Socket 939. Technical specifications AM2 processors are incompatible with 939 motherboards and vice versa, and although it has 940 pins, it is incompatible with Socket 940. Socket AM2 supports DDR2 SDRAM memory but not DDR memory, which the previous Socket 939 supported. ''AnandTech'' reported that Socket AM2 system performance was only about 7% faster than Socket 939 equivalents, with most applications about 2% faster, despite having over 30% greater memory bandwidth due to DDR2 support. The first processor cores to support socket AM2 were the single-core Orleans (Athlon 64) and Manila (Sempron), and the dual-core Windsor ( Athlon 64 X2 and Athlon 64 FX). Most processors on Socket AM2 include SSE3 instructions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |